* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Internet
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
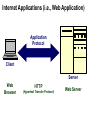
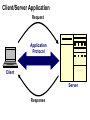
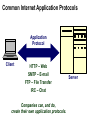
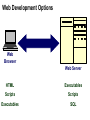
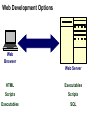
Introduction to Internet Chapter 1 Objectives • • • • • • • Origins of the Internet Packets and Routers TCP/IP DNS HTTP URL Client-Server Origins of Internet • Internet is a network of computer networks • Hub concept – 1966 ARPANET • Distributed network – no hub, flow around disabled units Routers • Routers replaces the central hub, the connectors • Routers run special-purpose software for connecting networks • Routers are the traffic cops of the Internet, they direct and route the network traffic Packets • The network traffic is the packets • When sending a file, it is broken up into packets • Packet size ranges from 100 bytes to 1500 bytes • Packet has a header (filename, origin & destination, order number of packet 5 of 22) Packet-switching • Packets are sent over the network • Nearest router receives, checks destination, sends to another router closer to destination • Once all packets arrive, file is reconstructed by putting the packets back together again TCP/IP • IP Internet Protocal – router software • TCP Transmission Control Protocol – software manages creating packets on both sending and receiving routers IP address • Destination addressing scheme • Four numbers 192.56.215.131 • Each number between 0 to 255 Domain Name System (DNS) • • • • DNS laid on top of IP addressing system Created to be more human friendly 192.56.215.131 = www.highpoint.edu Hostname.organizationname.countryname /type of organization • .us United States / .com company • ICANN manages domain names Hypertext • Answer to problem of various file formats • Imagine newspaper article with a foot note -> go to library and look up or-> click to electronically retrieve HTML • HTML Hypertext markup language – document format • HTTP Hypertext transfer protocal – transmission protocal • Browser – software to read the HTML Internet Applications (i.e., Web Application) Application Protocol Client Server Web Browser HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) Web Server URL’s • Uniform resource locator – used to tell where to find a document and how to retrieve it • The IP/DNS locates the computer • And specific document on computer to retrieve http://universityextension.ucdavis.edu /distancelearning/index.htm • http:// - protocal • universityextension.ucdavis.edu - combo host/domain name • distancelearning/index.htm - the index.htm document stored in the distancelearning folder Client-Server Computing • PC is the client • Server is the computer that the Web page document resides • Server comes from it’s task to serve documents to other computers on network • Source document contains HTML instructions to tell browser how to display Client/Server Application Request Application Protocol Client Server Response Client-Server Computing • Visit to a web page – you don’t actually go there. The page is sent to your computer. • After the page arrives the connection is broken. Unlike the phone network that keeps the connection until the call is ended. Common Internet Application Protocols Application Protocol Client HTTP – Web SMTP – E-mail FTP – File Transfer IRC – Chat Companies can, and do, create their own application protocols. Server Web Browsers and Servers Web Browsers Internet Explorer Netscape Mozilla Opera Web Servers Apache Microsoft IIS Netscape Internet Server Web Development Options Web Browser Web Server HTML Executables Scripts Scripts Executables SQL Web Development Options Web Browser Web Server HTML Executables Scripts Scripts Executables SQL End of Chapter 1 • • • • • • • Origins of the Internet Packets and Routers TCP/IP DNS HTTP URL Client-Server