* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap 8 The Internet - California State University, Sacramento
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
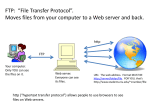
Chap 8 The Internet • How the Internet works, the short answer • What does the internet offer? – – – – – – – – Online services and ISP The World Wide Web and Hypertext Transfer Protocol E-mail FTP – File Transfer Protocol Newsgroup Chatting, Instant Message and Internet Relay Chat Telephony Virtual Networks and other Connections Accessing the Internet with Windows XP Accessing the Internet with Windows XP This lesson will cover: • The definition of the Internet • The “Web” • E-Mail • Newsgroups • Internet Tools • Web Browsers • Search Engines • FTP • Using Internet Explorer What is the Internet? The Internet is a worldwide computer network. It is a network of networks. There is no central control, all the computers and sub-networks are linked together on a voluntary basis. These computers use the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) as the method of connecting to each other and transferring information. TCP/IP is a “suite” of software programs that ensure traffic flows freely and efficiently on the ‘net. Before we really get started with the details you may want to go over a Glossary of Internet and Web Jargon courtesy of the UC Berkeley Library… More…What is the Internet? In 1969 four host computers were connected together to form ARPANET, this would later become the Internet as we know it. The first connections were between: •Stanford Research Institute •University of California Los Angeles •University of California Santa Barbara •University of Utah Although this project was highly motivated by the US Department of Defense, several separate networks were created by the Department of Energy, NASA and the National Science Foundation. These networks were unconnected…for a while… Click this link for a A Brief History of the Internet courtesy of the The Internet SOCiety (ISOC)… More…What is the Internet? …ARPANET grew into the Internet by connecting to other networks as technology advanced. The development of networking protocols like TCP/IP and Ethernet allowed greater connectability of diverse systems. Finally the growth of Local Area Networks (LAN) and the widespread use of PCs forced new growth, until in 1996 there were over 50,000 networks interconnected on the Internet. Originally the main concern of the Department of Defense was the “survivability” of the network, could it withstand a major attack and still operate effectively. More…What is the Internet? The "internetwork" in Theory redundant connections... More…What is the Internet? The "internetwork" in Theory redundant connections... mean no central control. More…What is the Internet? LAN sends a request out on the Internet to a "remote" network... LAN Router Remote LAN Router Telecom Connection Firewall LAN Server Router Telecom Connection How the Internet Works, the short answer • Because the internet is a network, each computer must have a unique address just like any node on a network. • Every Computer has an IP address, that is unique; for example the IP address of CSUS.edu is 130.86.90.1 • When the request is issued it first goes to a server that determines the address of the remote server and then it goes to a router that “routes” it to the destination. The routing can include visits to other routers that will reroute the request according to the current traffic and “state” of the Internet. • With Visual Route you can see the routers implicated and their place in the world What does the Internet Offer? Servers on the Internet can provide the following services to the users that logon to them: • FTP - The File Transfer Protocol is an efficient way to send or receive files from another computer. • E-mail - Provides electronic mail services which include mailing lists (listservs®) and discussion groups. • Newsgroups - These are organized “discussion” forums, sometimes called USENET, and are very narrowly classified by subject, such as rec.photo.equipment.35mm, or microsoft.public.windowsxp.general. • World Wide Web - Servers that use the HTTP to exchange files are part of the largest group users on the Internet. These computers “serve” HTML files, which are rendered as “web” pages on the users local computer. Online services and Internet Service Providers An internet Service Provider (ISP) is a business that provides its clients an access to the internet through a Point of Presence (POP). Dial-up connection The Internet ISP Point of Presence (POP) POP NAP Network Access Point (NAP) LAN using a leased line (T1) connection to the POP Main ISP • AOL : Leader of the market , 30 million subscribers Services: chat rooms, Shopping, AOL instant messenger, Internet Email, DSL Communication • CompuServe : Initially directed toward large companies Bought in 1997 by AOL. • Prodigy : Developed by IBM an Sear in 1984. Propriety of SBC Communication 3.5 million customers • MSN : Newcomer on the market Presence under the Name Microsoft Network The world wide web –Hyper Text Transfer Protocol The World Wide Web is a collection of computers connected via the Internet that support the use of documents written in HyperText Markup Language (HTML). The “web” uses the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) as the standard for the formatting and transmission of these documents. Not every server on the ‘net uses HTTP, and therefore is not part of the Web. The Web Since the World Wide Web supports documents that are formatted using HTML, you need to use a special application known as a “Web Browser” to open and view them. Most modern browsers also include the capability to “play” multimedia files such as video and audio. Retrieving files via FTP and accessing e-mail servers is another feature that has been added, but are really not web functions. The browser works by downloading (or retrieving from the remote server) a file and then rendering it according to the HTML specifications… E-mail • E-mail (or Electronic Mail) refers to the transmission of messages over computer network. • Although most browser includes e-mail capabilities, many people still rely on single purpose mail programs, like Pine, Eudora and Outlook. • Most Internet e-mail is sent from mail clients to mail servers using th Single Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). • Webmail account is e-mail that can be accessed without having an account with an ISP, like Hotmail or Yahoo!mail. FTP…Internet File Transfers The File Transfer Protocol is simply the protocol used on the Internet for sending files from one computer to another. It can be as “simple” as the command line program that comes with Windows 2000… The command ftp starts the program, and help displays help…transferring files like this takes a bit of skill because you need to access remote computers and navigate through their file systems, and it is all done by typing in commands like ls for a directory listing… Entering the command “bye” closes the session… …or you can… WS_FTP… WS_FTP is a Windows program that takes the work out of sending and receiving files on the Internet…this program can be used for free by students and is available from ZDNet…click the “About WS_FTP” window below to go to the download site…the next 2 slides show a few of the features of WS_FTP Limited Edition (the free version)… WS_FTP… Enter the address of the host you want to open a session with…the user name anonymous is a universal id that will gain access to many “public” computers. With an anonymous login you need only use a “dummy” password…many systems ask for your e-mail address, but you need not use your real one… WS_FTP… You are now browsing the /pub directory of the host computer cdrom.com Transferring files is now as easy as highlighting the filename(s) and clicking the appropriate arrow…the left arrow moves a file from the right pane (the remote computer) to the left pane (your computer)…and visa versa. Internet Newsgroups An Internet newsgroup is a specific type of online forum or discussion group. Newsgroups use a different application level protocol, the Network News Transfer Protocol, or NNTP to deliver its data to users. These groups are sometimes called USENET. They are like private e-mail lists that maintain the emails or “posted” messages in the order that they were sent and answered. This arrangement is called message threading. By using a newsgroup you can follow the messages of others, which is called lurking; or you can participate in the action by posting questions, comments or answers to other messages. Internet Newsgroups Newsgroups are an excellent way to connect with people that have the same interests, hobbies and problems. They are good for getting answers to technical questions on many subjects, as they generally deal with very narrow subjects. When using a newsgroup you should be careful about posting your e-mail address (or any contact information for that matter)…in fact, many people use a phony address like [email protected]. This is because spammers also lurk among the newsgroups looking for addresses that they can use or sell. Internet Newsgroups Newsgroups are accessed on the Internet by using a program called a newsreader. Most modern browsers include news reading capabilities in their software. The following slide shows Microsoft’s Internet Explorer 6 in its newsreading mode. There are, however, many more single purpose readers that incorporate added features, including enhanced security. Use this link to see a large list of newsreader programs on CNET. Using Internet Explorer 6 to “read” Newsgroups The listing of posted messages The current Newsgroup …and the number of messages posted to it. The text of the selected “post”… Chatting • Chat rooms as offered by service providers such as AOL are not features of the internet. • They exist only within the boundaries of the service provider, only subscriber of that provider can access them. • Chat room provide real time contact between users Instant Messaging and Internet Relay Chat (IRC) The original IRC network is EFNET (Eris Free). Instant messaging (IM) allows a real time discussion between two specific users. Two different users have to use the same software to converse. The most popular IM software are AOL Instant messenger and the MSN Messenger. Telephony • • Internet Telephony is a segment of internet technology that combines capabilities of a telephone system, such as voice communication and fax transmission, with Internet protocols. This idea promises low costs on long distances. Companies providing such services are Net2phone, ICQphone and NetMetting