* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Local Area Networks
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Low Pin Count wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Spanning Tree Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
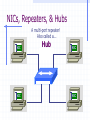
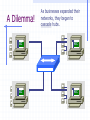
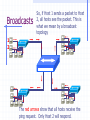
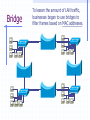
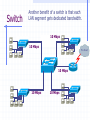
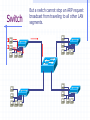
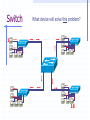
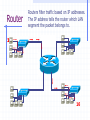
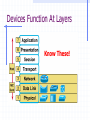
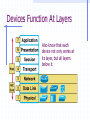
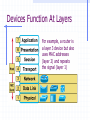
Wrapping The Package Devices & Data Encapsulation Evolution of LAN Devices NICs, Repeaters, & Hubs Bridges Switches Routers NIC Specifics NICs provide hosts with access to media by using a MAC address. MAC stands for Media Access Control NICs operate at Layer 2 !! NICs, Repeaters, & Hubs The First LAN NIC NIC To connect two computers, you must... Install a NIC card in each. Attach computers NIC using a crossover cable You made a crossover cable in Ch. 5 NICs, Repeaters, & Hubs Repeaters can be used to increase the distance NIC NIC So what can we use if this distance Repeaters amplify and What’s the maximum 100ismeters or approx. 300 feet greater than 100 meters? retime signals distance for Cat 5 cable? NICs, Repeaters, & Hubs NIC NIC Using repeaters was fine as long as a business only needed two computers networked. NIC What if a business wanted a third computer attached? Or a fourth? What device would they need? NIC NICs, Repeaters, & Hubs A multi-port repeater! Also called a... NIC NIC Hub NIC NIC A Dilemma! As businesses expanded their networks, they began to cascade hubs. NIC NIC NIC NIC What’s The Problem? 1) Hubs share bandwidth between all attached devices. 2) Hubs are stupid, Layer 1 devices. They cannot filter traffic. 3) Most LANs use a “broadcast topology,” so every device sees every packet sent down the media. Let’s take a look at how broadcasting works Broadcasts In this picture, all hubs forward all traffic to all devices. Broadcasts So, if Host 1 sends a packet to Host 2, all hosts see the packet. This is what we mean by a broadcast topology 1 2 The red arrows show that all hosts receive the ping request. Only Host 2 will respond. What’s The Solution? We need a smarter hub! What’s a “smarter hub” called? A Bridge! Bridges filter network traffic based on MAC addresses. Let’s take a look at how this works. Bridge To lessen the amount of LAN traffic, businesses began to use bridges to filter frames based on MAC addresses. Bridge 1 2 Now, if Host 1 sends a packet to 2, only the hosts on that LAN segment see the packet. Bridges--Summary More intelligent than hubs—that is, they can analyze incoming frames and forward (or drop) them based on addressing information. They create more collision domains, allowing more than one device to transmit simultaneously without causing a collision. They maintain address tables. Switch A switch (also know as a multi-port bridge), can effectively replace these four bridges. Switch Another benefit of a switch is that each LAN segment gets dedicated bandwidth. 10 Mbps 10 Mbps The Cloud 10 Mbps 10 Mbps 10 Mbps Switch 1 2 a switch is astop multi-port ButSince a switch cannot an ARPbridge, request we knowfrom it will stop local Traffic from broadcast traveling to all other LAN traveling to other network segments. segments. Switch For example, Host 1 ARP Host 16. Since the MAC address is unknown to the the What device will solve this switch, problem? switch will flood the ping request out all ports. 1 16 Router Routers filter traffic based on IP addresses. The IP address tells the router which LAN segment the packet belongs to. 1 16 Devices Function At Layers Know These! Devices Function At Layers Also know that each device not only works at its layer, but all layers below it. Devices Function At Layers For example, a router is a layer 3 device but also uses MAC addresses (layer 2) and repeats the signal (layer 1) Devices Function At Layers One last bit of information from Chapter 3 At what layers do ALL 7two LAYERS!! these operate? The Cloud Chapter 3 Labs 3.4.2