* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telecommunications and Networks
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
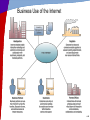
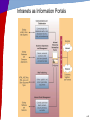
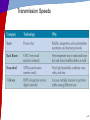
Chapter 6 Telecommunications and Networks McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2011 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives • Understand the concept of a network • Apply Metcalfe’s law in understanding the value of a network • Identify major developments and trends in the industries, technologies, and business applications of telecommunications and Internet technologies 6-2 Learning Objectives • Provide examples of the business value of Internet, intranet, and extranet applications • Identify the basic components, functions, and types of telecommunications networks used in business • Explain the functions of major components of telecommunications network hardware, software, media, and services 6-3 Learning Objectives • Explain the concept of client/server networking • Understand the two forms of peer-topeer networking • Explain the difference between digital and analog signals 6-4 Network Concepts • Interconnected chain, group, or system • Connections created by nodes • Exponential growth • Metcalf’s Law – Usefulness, or utility, of a network • Equals the square of the number of users • More users = more useful 6-5 RWC 1: Telepresence Is Finally Coming of Age • Immersive video experience • Saves travel time and expense • Video conferencing better for one-on-one • Allows people to think globally 6-6 Telecommunication Trends 6-7 Telecommunications-Based Services 6-8 Value of Telecommunications Networks 6-9 Business Use of the Internet 6-10 Business Value of the Internet Summary of bulleted list 6-11 Intranets as Information Portals 6-12 Extranet Connectivity 6-13 RWC 2: Medicine through Videoconferencing • Visual-communication workstation connected to major hospital stroke center • Improves – Diagnostic ability – Training of new doctors – Communication with patients • Handicapped • Second-languages – Discussion and collaboration 6-14 Telecommunications Network Model 6-15 Network Component Alternatives 6-16 Wide Area Network (WAN) 6-17 Local Area Network (LAN) • Connects computers in a limited physical area – Office, classroom, or building 6-18 Virtual Private Network 6-19 Client/Server Network 6-20 Network Computing 6-21 Peer-to-Peer Network Diagrams 6-22 Telecommunications Media • Twisted-Pair Wire – Similar to telephone wire • Coaxial Cable – Wire wrapped with insulation • Fiber-Optic Cable – One or more hair-thin filaments of glass 6-23 Wireless Technologies • Communications Satellites – Geosynchronous orbit – Serve as relay stations • Wireless LANS – Wireless radio-wave technology • Bluetooth – Short-range wireless technology • Other Wireless Systems – Cellular phones, Mobile radio, PDAs • Telecommunications vital and pervasive – Web-enabled e-business processes 6-24 Wireless Technologies • Other Wireless Systems – Cellular phones – Mobile radio – PDAs • Telecommunications pervasive role – Web-enabled e-business processes – Electronic commerce – Enterprise collaboration – Other applications • Business operations, management, strategic objectives 6-25 The Wireless Web • Web-enabled appliances proliferate – Smart telephones, pagers, PDAs – All are very thin clients in wireless networks 6-26 Telecommunications Processors • Modems – Most common type – Modulation and demodulation • Converts for transmission over telephone lines • Digital signal to analog • Analog to digital 6-27 Communications Processors 6-28 Comparing Technologies 6-29 Telecommunications Software • May reside in PCs, servers, mainframes, and communications processors – Vital part of all telecommunications networks – Used to manage network performance – WANs often use telecommunications monitors or teleprocessing monitors – Other networks use operating system software – Middleware helps diverse networks communicate with each other 6-30 Network Management Functions • Traffic Management • Security • Network Monitoring • Capacity Planning 6-31 Network Topologies 6-32 Network Architectures and Protocols • Protocol – Rules and procedures • Handshaking – Exchanging predetermined to agree on a protocol • Network Architecture – Master plan of standards – Goal is to promote an open, simple, flexible, and efficient telecommunications environment 6-34 OSI Model • Open Systems Interconnection Model – Seven-layer standard for network architectures – Controls how messages should be transmitted – Ensures consistency among products 6-35 OSI and TCP/IP Models 6-36 Transmission Speeds 6-37 RWC 3: Value of Secure Networks • • • • • • Improves operational efficiency Secures sensitive data Contains costs Enhances employee connectivity Enhances customer responsiveness Allows customers to securely track orders in real time • Empowers customer-service agents with detailed account information • Provides easy, inexpensive videoconferencing 6-38 RWC 4: Future of Public WiFi • • • • • Wi-Fi fast-growing popularity Wi-Fi coffee shops replaced cybercafes Moves towards free Advertising offsets costs or to make money Increasingly always free everywhere 6-39