* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Point Presentation
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
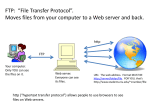
Networks and Internet Objectives Understand basic concepts in Networking Network Types Understand basic concepts in Internet Internet Services Become familiar with Web terminologies 1 Computer Networks Physical part of the definition: –Two or more computers linked together. Functional Part of the definition: –Communication –Sharing resources –Exchange of data 2 Computer Networks Types of Networks Local Area Network (LAN) – nodes are in close proximity Wide Area Network (WAN) – nodes of the network are geographically distant Internet – Network of networks and individual computers 3 Going Online The Internet Internet: worldwide collection of networks ARPANET: network for scientists that evolved into the Internet Internet backbone: major communications lines of the Internet 4 Going Online The Internet No one group controls the Internet Three Major Organizations: The Internet Society: Open development for the benefit of the public Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN): Assign names and addresses World Wide Web Consortium (W3C): Creates technical specifications 5 Going Online Connecting to the Internet Bandwidth – amount of information that can be sent over the channel 56,000 bits per second (bps) 9M (millions of bits, or megabits per second) 6 Going Online Connecting to the Internet Internet service provider (ISP): Colleges, Schools, Corporations, Communication companies ex. SBC Information service gateway: ex. AOL, MSN, CompuServe communications software (Interface with their information system) user ID and password Direct LAN connection T-1 line (1.544 Mbps) T-3 line (44.736 Mbps) 7 Going Online Connecting to the Internet Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Protocol: set of rules for how computers communicate Packet: the part of a message that contains the data and the address the message is being sent to 8 Going Online Retrieving and Viewing Information on the Internet Client program – Internet browser: runs on user’s computer Server program – runs on server computer 9 Going Online Retrieving and Viewing Information on the Internet Domain name: name or abbreviation of the name of the organization Uniform resource locator (URL): address of a web page 10 Going Online Retrieving and Viewing Information on the Internet URL access protocol domain name top-level domains: denote affiliation .com .edu folder filename 11 Going Online Internet Browsers Browsers retrieve and view Internet-based information interact with servers download and upload information 12 Going Online Internet Browsers Web site pages home page – first page you see at a site hyperlinks – allow user to click on an icon and be taken to other resources on the Internet 13 Going Online Navigating the Internet Microsoft Internet Explorer Netscape 14 Going Online Browser Plug-ins Plug-in – gives the browser added capabilities Shockwave Player Flash Player RealJukebox Liquid Player 15 Going Online Internet Resources and Applications Finding information on the Web browsing: just looking around searching: trying to find specific information 16 Going Online Internet Applications File Transfer Protocol (FTP) servers easily download/upload files Anonymous FTP sites E-mail Chatting Online conferences 17 Assignment# 3 18