* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VoCCN: Voice-over Content
Technological convergence wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
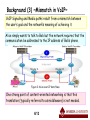
Review of the literature : VoCCN: Voice-over Content-Centric Networks Takashima Daiki Waseda University, Japan 2012.5.17 1/13 Outline 1. Introduction 2. VoIP background 3. VoCCN architecture -VoCCN/VoIP Interoperability 4. Simulation 5. Conclusion 2/13 Introduction Fact: There is widespread agreement that content should have a more central role in future network architectures than the Internet’s current host-to-host conversation model. Doubt: How well the idea fits more conversational traffic such as email, e-commerce transactions or VoIP? phone call Figure 1: Use case of Voice-over-IP Goal: To investigate Voice Over CCN – a real-time, conversational, telephony application over Content-Centric Networking (CCN). 3/13 Background (1) ~VoIP~ Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is dominant open protocol for Internet telephony. When making a phone call, VoIP phones set up a signaling path by using the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). Figure 2: Voice-over-IP data flows. As VoIP endpoints are often mobile, signaling path exchanges are mediated by VoIP that receive and forward messages on behalf of their client endpoints. 4/13 Background (2) ~SIP~ INVITE sip:[email protected] SIP/2.0 Via: SIP/2.0/CCN parc.com:5060 From: Alice Briggs <sip:[email protected]> To: Bob Jacobs <sip:[email protected]> Call-ID: 1911287229 CSeq: 20 INVITE ccnx.org parc.com Alice proxy Bob Content-Type: application/sdp proxy Max-Forwards: 70 ① INVITE ② INVITE User-Agent: Linphone/3.0.0 (eXosip2/3.1.0) ③ 100 Trying Subject: Phone call ④ INVITE Expires: 120 ⑤ 100 Trying ⑥ 180 Ringing Content-Length: 1477 ⑦ 180 Ringing [... ⑧ 180 Ringing ⑨ 200 OK o=alice 123456 654321 IN IP4 13.2.117.34 ⑩ 200 OK c=IN IP4 13.2.117.34 ⑪ 200 OK a=key-mgmt: mikey AQQFgE3dV+ACAA... m=audio 7078 RTP/AVP 111 110 0 3 8 101 ⑫ ACK (session-establishment is accepted) ...] Figure 4: Example of SIP INVITE message. Session is established (conversation is done) ⑬ BYE(session disconnect request) ⑭ 200 OK (session disconnect) Figure 3: Sequence diagram of SIP INVITE message. 5/13 Background (3) ~Mismatch in VoIP~ VoIP Signaling and Media paths result from a mismatch between the user’s goal and the network’s meaning of achieving it. Alice simply wants to talk to Bob but the network requires that the communication be addressed to the IP address of Bob’s phone. Figure 2: Voice-over-IP data flows. One strong point of content-oriented networking is that this translation (typically referred to as middleware) is not needed. 6/13 VoCCN architecture (1) A caller maps a SIP INVITE into an Interest packet asking for new content from callee, which generates a piece of Data with the requested name containing the SIP response, thus completing SIP signaling in a single round trip. Figure 5: Voice-over-CCN data flows. Challenges: ・Support service rendezvous: request a connection and get a confirmation response. ・On-demand publishing is needed: request data that was not published yet. ・Transition phase: from rendezvous to a bi-directional conversation. 7/13 VoCCN architecture (2) Figure 6: Protocol exchange. Inline message security: ・Caller: encrypt and authenticate SIP invite using random-Inline message encriptation generated symmetric key (sk) ・Caller: encrypt sk using callee’s public key (pk B) ・Callee: decrypt interest using his/her private key ・Callee: uses sk to verify and decrypt SIP invite message 8/13 Componets of Interest VoCCN/VoIP Interoperability VoIP VoCCN VoIP-VoCCN gateway Signaling Path Signaling and Media Path Media Path Fig 7.VoCCN/VoIP Interoperability The VoCCN/VoIP proxy serves as the SIP proxy for external inbound VoIP calls, and translates from VoIP packets (SIP and SRTP) to VoCCN packets and vice versa. The proxy examines a VoIP packet and generates a corresponding CCN packet whose name is determined based on information in the original inbound packet header. The proxy then performs the CCN-specific parts of the call on behalf of the VoIP client – generating and sending an Interest in the next packet of the exchange. 9/13 Simulation (1) ・Proof-of-concept of real-time CCN ・Extension of Linux VoIP phone (libeXoSIP, liboRTP) ・Open CCN toolkit (CCNx): routers run on endpoints. ・Support multi-point routing (mobility) ・ Easy to build advanced services (e.g. conference calls) To evaluate CCN’s ability to support timely delivery or realtime data the authors looked at the packet arrival times for their VoCCN implementation. 10/13 Simulation (2) CDF: Proportion of Packets LinPhone Packet Interarrival Time Performance for a 10 minutes conversation: ・More packets below the expected inter-packet interval ・Small number of long-interval packets ・No packets loss for both cases Stock LinPhone CCN LinPhone - Encrypted Packet interarrival Time (ms) Limitations/Open Issues ・Constructable names: flexibility may require partial names that are not unique Figure 4: Cumulative distribution of inter-packet ・ Pipeline of Interest packets: not intervals, or jitter, for a 10-minute voice call. proved to perform The VoCCN call has slightly fewer packet. With almost equal delivery performance, VoCCN and VoIP have same call quality. 11/13 Conclusion ・CCN can not only move content scalably and efficiently, they can also implement IP-like conversational services like voice calls, email or transactions. ・Voice-over-CCN is functionally and performance equivalent to Voice-over-IP. ・It is more simpler in architecture, implementation and configuration. ・VoCCN is completely interoperable with VoIP via simple, stateless gateways. 12/13 Reference [1] V.Jacobson, D. K. Smetters, N. H. Briggs, M. F. Plass, P. Stewart, J. D. Thornton, and R. L. Braynard, “VoCCN: Voice-over Content-Centric Networks,” Rome, Italy. , 2009. [2] Project CCNx . http://www.ccnx.org, Sep.2009. 13/13