* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Christopher Wilder - P2P Over MANET
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
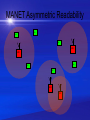
P2P Over MANET An Introduction to Mobile Resource Sharing Introduction to MANETs • Mobile Ad Hoc Network (MANET) • Under research for the past 10 years • Only a small amount of MANETs are currently used in the real world • Autonomous system of mobile routers and nodes • All elements reside on wireless domains • Nodes can join and leave the network at any time • Dynamic topology • Wireless connectivity implements node mobility • Primarily operates in the network layer (layer 3), but can be implemented in other layers as well MANET Interface • Connecting point where nodes can attach[1] • Allows MANETs to connect to each other • Every MANET interface must have a unique identifier • Neighborhood • Time-varying asymmetric Reachability[1] MANET Neighbors N3 N4 N2 MR1 MR2 MR3 N1 N5 MR4 N6 MANET Asymmetric Readability N3 N4 N2 MR3 MR1 N6 N1 N5 MR2 MR4 MANET Router (MR) • Has one or more MANET interfaces • May have zero or more non-MANET interfaces [1] • Hides MANET characteristics from all nodes that do not support MANET • Only one MR is required to setup a MANET, however, the more the better MANETs and Other Wireless Network Technologies • IEEE 802.11 (WI-FI) can not be used to implement a MANET, they do not share characteristics • WI-FI is just a wireless version of a wired network[3] • The two main differences in WI-FI and MANETs: – WI-FI operates in the data-link layer (layer 2) and MANETs must exist in the network layer – Access points are required for a WI-FI network to effectively work, which is a rule that is not bound to MANETs • Bluetooth has been successfully used to implemented a MANET MANETs and Existing Wired Networks • Can be implemented as an overlay on top of any wired topology or network • Routers which support intercommunication can have two or more interfaces including MANET interface • Specific MANET routing protocols are used to route traffic across its network • MANET packets are encapsulated in IP packets and vice versa • In an MANET overlay, a node on the MANET network can communication with a node located on an IP network. This transformation is bi-directional Asymmetric Reachability MR1 MR2 MR3 Peer to Peer (P2P) • An Overview of P2P will start here and continue for the next 3 to 5 slides P2P Over MANET • A mobile ad hoc network with a peer to peer overly • The MANET will operate in the first four layers of the OSI model, while P2P will run in the fourth through seventh layer • Both inhibit similar characteristics • Next generation of client based networks P2P Over MANET • Can be implemented in more than one way considering that: – There is more than one MANET protocol – P2P can be built as a structured, unstructured, data-centric, overlay, or hybrid architecture. – Each P2P architecture has a multitude of protocols and characteristics which inhibit different features and constraints • A structured P2P architecture works best with MANETs • Structured P2P uses Distributed Hash Tables (DHT), which there are many to choose from with different characteristics i.e. Chord, Pastry, etc. P2P Over MANET Protocol Stack OSI P2P Application Application Presentation Presentation Session Layer MANET Session Layer Transport Transport Transport Network Network Data-link Data-link Physical Physical Homogeneous Characteristics of P2P and MANET • Supports node churning[2]; consistency of nodes entering and leaving the network • Traffic patterns closely resemble those caused by multi-hop broadcasting or multicasting [3] • Dynamic topology • The ability for nodes to rearrange themselves when connecting to the network • Fault tolerant; resistant and transparent to errors • Unique Identifiers are required to identify nodes Why P2P Over MANET • Put some good stuff to say here about the benefits of P2P Over MANET P2P Over MANET Architectures • The P2P Over MANET description of architectures starts here and will continue for the next 3 to 5 slides. Example of P2P Over MANET Architecture • This slides starts the description of example and will continue for the next 4 to 6 slides Typical Problems with P2P Over MANET • Put some things that need to be fixed with P2P Over MANET here Possible Applications for P2P Over MANET • The applications for P2P Over MANET starts here and continues for maybe one more slide References • References will go here