* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
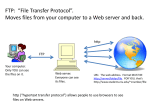
Getting Connected Overview Essential Questions What are the ways to transfer files between computers? How How do you use the tools? does the connectivity increase your productivity? Objectives Demonstrate basic operational procedures for Internet client software including e-mail, Network News, FTP, Telnet from multiple client stations. Use FTP to both send files to and retrieve files from a remote system. The Internet Today Worldwide network of networks Government agencies, educational institutions, hospitals, and commercial organizations Phenomenal growth - 1 million/month Largest connection of networks in the world How the Internet Works Local Connections: Modem ISDN DSL Cable Satellite Businesses/Universities T1, T3 Router at provider’s point-of-presence Small providers big providers The Internet uses TCP/IP TCP/IP is the basis for the Internet. IP resides in the Network Layer. TCP resides in the Transport Layer. Network Protocols IP TCP Application Protocols Telnet HTTP FTP SMTP SNMP DNS Internet Protocol (IP) IP provides delivery services taking care of addressing ensuring the routers know what to do with your data when it arrives. Every computer on the Internet has a unique address. Information sent across IP networks is broken up into bite-sized pieces, called packets. The information within a packet is usually between 1 and about 1500 characters long. Transmission Control Protocol Ensures reliability. TCP takes the information you want to transmit and breaks it into pieces. TCP numbers each piece so receipt can be verified and the data can be put back in the proper order. TCP/IP Applications/Services SLIP and PPP Terminal Emulation (Telnet) File Transfer Protocol (FTP) HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Domain Name Service (DNS) Various Connectivity Types Telnet: Terminal Emulation Logs into remote host systems FTP: File Transfer Protocol Client computer Remote Server Logs in to the special file system Various Connectivity Types HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Underlies the WWW HTML is standardized language Many different file types accessible. SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Provides a store-and-forward mail capability between host computer mail systems on the network MIME: Multimedia Internet Mail Exchange Standard for document attachments. DNS: Domain Name Service Maps network address numbers to an easy to remember name 136.24.64.138 Telnet, www.name.com FTP and SMTP access DNS to locate names you’ve specified and resolves them to a numeric address and inserts it into a message for transport. Concept Maps E-mail Evaluations References From Networking 101 Jim Cabral, Puget Technology Group, Inc. & Tammy Ruth, Children’s Hospital and Medical Center www.pugettech.com [email protected] [email protected]