* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Networks and the Internet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
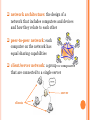
NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET DESKTOP COMPUTING (pp 1-2) Desktop computers are often generically referred to as PCs or MACs. Regardless of the brand name, desktop computers have the same components. Hardware: The physical components of the computer, such as the monitor and base unit. Input Devices: external devices used to enter data and instructions into the computer, such as a keyboard mouse, scanner microphone, digital camera, and flash drives. Peripheral Devices: external devices attached to the computer, such as printers and scanners Output Devices: devices used to convey useful information processed by the computer, such as monitors, printers, speakers and memory drives CPU: Central Processing Unit – the “brain” of the computer operating system software: programs that run automatically that allow the user to communicate with the computer and the computer to process data application software: programs written to perform specific tasks (word processing, photo editing) REVIEW QUESTIONS What are input devices used for? to enter data to the computer for processing What are output devices used for? to display processed data in a useful format Describe one difference between operating system software and application software. operating system software runs the computer, application software allows the user to tell the computer to perform specific tasks MOBILE COMPUTING (pp 2-3) Bluetooth: wireless technology that allows mobile computing devices to communicate with one another notebook computer: portable, lightweight computer with capabilities of a typical desktop system tablet PC: a computer that uses handwriting recognition software to interpret data the user “writes” on the screen with a stylus handheld computer (PDA): palmsized computers that are used primarily for personal management tasks such as scheduling, lists, games Smart phone: cell phones that have Internet and central processing capability wearable computer: computing devices integrated into clothing and wearable accessories cross-platform connectivity: the ability of different operating systems to communicate with one another REVIEW QUESTIONS Describe four types of mobile computing devices. notebook computer tablet PC handheld computer smart phone wearable computer Describe one type of wearable computer. MP3 player integrated into watches cameras integrated into eyewear Quiz tomorrow! NETWORKS (pp 3-5) A network is a combination of hardware and software that allows computers to exchange data and share software and devices. Businesses, schools and other organizations use networks because: o users can share and exchange data o costs are reduced by sharing devices o passwords can restrict access to certain files o software updates and file backups can be performed at one location o private email can be provided for network users. LAN: Local Area Network – connects devices within a small area such as a building or a campus WAN: Wide Area Network – connects devices over a large geographical distance HAN: Home Area Network – connects devices within a home network architecture: the design of a network that includes computers and devices and how they relate to each other peer-to-peer network: each computer on the network has equal sharing capabilities client/server network: a group of computers that are connected to a single server server clients wireless network : uses high frequency radio waves or infrared signals to transmit data WiFi: Wireless Fidelity – a protocol for wireless networks Netiquette: the polite rules for using a network do not access the account of another user without permission do not share your password use appropriate subject matter and language be considerate of other people’s beliefs and opinions REVIEW QUESTIONS What does “network architecture” refer to? the devices that are included in the structure of a network What are three rules of “netiquette”? do not access the account of another user without permission do not share your password use appropriate subject matter and language be considerate of other people’s beliefs and opinions Quiz tomorrow! FILES & FOLDERS (p 6) A collection of data stored on a memory drive is called a file. A file can be an application program or the product of an application (a word processor program or a document created with a word processor program) Each file must have a unique file name. Applications add an extension to the file name when it is saved. .doc = word processing file .htm = basic HTML document .css = cascading style sheet Folders are used to organized related files. Each folder must have a unique file name. A folder can contain other folders and all types of files. INTRANETS, EXTRANETS, AND THE INTERNET (p 7) An intranet is a private network used by a single organization firewall: network security system that prevents unauthorized access to the network An extranet allows the public to access a network, such as the district server The Internet is the largest and most widely accessed network – a world-wide network of computers that is not controlled by any one organization. IP Address: a unique identifier for a computer or device on a network REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the difference between an intranet and an extranet? An intranet is used by a single organization. An extranet can be accessed by the public. Who controls the Internet? No one person or organization. TELCOMMUNICATIONS SERVICES (pp 7-8) Telecommunications is transmitting and receiving of data through a line or cable conventional modem: uses standard phone lines to convert analog signals to digital; the slowest form of telecommunications DSL: Digital Subscriber Line – uses standard phone lines with high rates of data transmission cable modem: transmits data through coaxial cable TV networks dedicated line: allows a permanent connection to the internet that is always active ISDN: Integrated Services Digital Network – digital network access provided by a phone company REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the slowest telecommunications option? conventional modem Quiz tomorrow! INTERNET SERVICES (pp 8-10) Internet services include: World Wide Web - used to search and access information that is available on the Internet e-mail - messages transmitted over a communications network instant messaging - immediate text-based communication bulletin board services - allows users to participate in discussion groups The World Wide Web is the most widely used Internet service. A web browser application provides a graphical interface to present information in the form of web sites. TYPES OF WEB SITES Personal Web Sites created by individuals display information about hobbies, pets family members, etc. TYPES OF WEB SITES (CONT.) Commercial Web Sites created by companies and organizations corporate presence web sites = display information about products and services e-commerce web sites = sell products and services online TYPES OF WEB SITES (CONT.) Informational Web Sites display factual information about a topic created by educational institutions, governments, and organizations Types of Web Sites (cont.) Media Web Sites created by companies Inform readers about current events and issues; usually online newspapers and periodicals Types of Web Sites (cont.) Portal Web Sites created by businesses a starting point for people to enter the Web contain hyperlinks to a wide range of topics and access to a search engine. URL (UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR) Every web page has a URL A URL is an address that is interpreted by a web browser to identify the location of a page on the web. domain name http://www.earthday.net The web protocol used for transmission of pages from a server to a web browser. top-level domain – identifies the type of web site TOP LEVEL DOMAINS Top-level domains identify the type of web site. .gov = government agency .edu = educational institution .org = non profit organization .com = commercial business REVIEW QUESTIONS What is the most widely used Internet service? The World Wide Web What is a URL? the unique address of a web page on the Internet Identify each part of this URL: domain name http://www.google.com The web protocol used for transmission of pages from a server to a web browser. top-level domain – identifies the type of web site REVIEW QUESTIONS What is one benefit of e-mail over standard mail? Email is faster than regular mail What is one advantage of sending an instant message instead of an e-mail? Can be faster than email Quiz tomorrow! ASSIGNMENTS 1) Complete Exercise #3 on page 37 in your binder. Write your answers on a separate sheet of paper. Be sure to include your name and class period on your paper. 2) Grab a partner and complete the “Internet Search Skills Activity” handout. You can do it alone if you want. INTERNET EXPLORER (pp11-15) title bar: displays the web page title address bar: displays the URL of the web page status bar: displays information about the web page menu bar: displays menus from which you can select commands favorites bar: allows you to add sites for quick access scroll bar: drag to bring unseen parts of the page into view ASSIGNMENT Complete the Internet Explorer Practice on page 12-15 in your binder SEARCHING THE WEB (pp 16-17) search engine: a program that searches databases of web pages for key words sponsored site results: sites that contain information being searched for, but their owners have paid for them to be listed at first search criteria: words or phrases that are used to search for web pages o + (plus sign) or AND – limits a search to only web pages that contain all of the words in the search criteria insects+arachnids+achatina insectsANDarachnidsANDachatina o OR – used to find web pages that contain any words in the search criteria insectsORarachnidsORachatina o - (minus sign) or NOT – used to exclude web pages from a search insects-mosquitoes insectsNOTmosquitoes ASSIGNMENTS 1) Complete the “Searching the Web” Practice on page 17 of your binder. 2) Grab a partner and complete the “Search Criteria” Activity handout. EVALUATING AND CITING WEB -PAGES (pp 17-19) When evaluating a web site, ask these questions: Is the site up-to-date? When was the page last updated? Is the site biased? Does the information have a slanted view of the topic? Is the site valid? What is the primary source of the site’s information? Is the primary source trustworthy? Who is the site’s author? Does that person/organization have the credentials to be a reliable source on the topic? When citing a web site, use this general format: Author’s last name, first name, middle initial. Site Title. Access date. Organization name. <URL>. Specific instructions are included on the “Citing Electronic Resources in MLA Format” handout. REVIEW QUESTIONS What are four questions to answer when evaluating a web site? Is the site up-to-date? Is the site biased? Is the site valid? Who is the site’s author? REVIEW QUESTIONS On August 9, 2011 you accessed a posting on the Clewiston Kite Surfing discussion list at http://www.lpdatafiles.com/kitesurf/color.txt. The posting was made by Tara Perez on the topic of kite colors. Write a citation for a research paper that quotes Tara’s posting. Perez, Tara. Clewiston Kite Surfing. 9 August 2011. < http://www.lpdatafiles.com/kitesurf/ color.txt> ASSIGNMENTS 1) Complete the “Citing a Website” Practice on pages 18-19 2) Complete Exercise 4 through 6 on page 38 E-MAIL ETIQUETTE (p 21) spam: junk email Email Etiquette rules: o use your manners and polite words o write in short, complete sentences o be professional – use correct spelling and grammar o re-read the message before sending o send message through your account only o use appropriate subject matter and language o be considerate of other people’s beliefs and opinions INTERNET PRIVACY ISSUES (pp 22-23) Electronic Communications Privacy Act: makes it a crime to access and/or publish electronic data without permission Electronic Freedom of Information Act: required government agencies to make information available for pubic inspection online Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act: requires web sites that collect information from children under 13 to obtain parental consent Safety and Freedom Through Encryption Act: allows American to use any type of encryption to protect their personal information PATRIOT Act of 2001: allows law enforcement to monitor individual’s internet and email activity spyware: software that uses the Internet to gather information about users without their knowledge online profiling: a marketing technique that collects data about users visiting web sites cookie: a text file created by a server when a user enters information into a web site; it is stored on the user’s computer and accessed every time the site is visited web beacon/web bug/pixel tag: tiny, hidden graphics on web pages or in emails that collect data about users; monitored by ad agencies privacy policy: a legally binding document that explains how user’s personal information will be used REVIEW QUESTIONS Why is ending an email message like sending a post card? anyone along the path from sender to recipient can read it’s contents What are three examples of email etiquette? use your manners and polite words write in short, complete sentences be professional – use correct spelling and grammar re-read the message before sending send message through your account only use appropriate subject matter and language be considerate of other people’s beliefs and opinions REVIEW QUESTIONS Who usually monitors the information collected by web beacons? advertising agencies who design targeted ads on the Internet Quiz tomorrow! INTERNET ACCEPTEABLE USE POLICY (p 23) Enforceable rules for using computers and/or the Internet through an organization’s computers: o use appropriate language o do not reveal personal addresses or phone numbers o do not access, upload, download, or distribute inappropriate materials o do not access another user’s account o do not install or uninstall software o do not use organization computers for personal reasons REVIEW QUESTIONS Why would a school require an Acceptable Use Policy for students? You must have an AUP on file with the office to take this class! ETHICAL IMPLICATIONS OF COMPUTER USE (pp 23-24) identity theft – personal information is stolen and used to make fraudulent purchases or obtain loans Laws the protect privacy: Fair Credit Reporting Act – gives you the right to see information collected about you for use by credit, insurance, and employment agencies Privacy Act – restricts the way personal information can be used by federal agencies Financial Privacy Act – requires that government have a subpoena or search warrant to access your financial records ASSIGNMENTS 1) Complete Exercise 8 on page 39 PROTECTING SOFTWARE AND DATA (pp 24-25) copyright – the illegal use or reproduction of digital information, images, videos, photos, etc. No Electronic Theft Act – protect against copyright infringement piracy – the distribution of illegal copies of copyrighted files virus – a program the reproduces itself without the user’s knowledge; can destroy data on computers trojan horse – a damaging program that appears to be trustworthy; running the program damages a computer worm – a damaging program the reproduces itself on a network and uses up resources antivirus program – software that detects and removes damaging programs hacker/cracker – an individual who gains access to large computer networks to cause vandalism phishing – sending an email claiming to be a legitimate business to trick a user into providing personal information REVIEW QUESTIONS What are two precautions to take to protect yourself from damaging programs? Use and update antivirus software Don’t open email attachments until they have been scanned for damaging programs Quiz tomorrow! ASSIGNMENTS 1) Complete Exercises 4, 5, and 6 on page 38 and Exercise 12 on page 40