* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
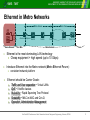
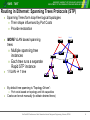
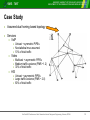
BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS On the Optimal Configuration of Metro Ethernet for Triple Play András Kern, Tibor Cinkler, István Moldován BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Triple-Play in Metro Ethernet Network » Three different services on a single infrastructure » High Speed Internet (HSI) » Voice over IP (VoIP) » Video service (IPTV, iVoD) Video VoD Head End Edge node Switch Data Switch Switch TV + Set Top Box Home Gateway Access Node VoIP Switch Edge node GW Customers’ Home Net. Local Access / First mile Metropolitan Network Service Providers’ Networks 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 2 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Ethernet in Metro Networks Metro Access TALK / DATA TALK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 * 8 # RS CS TR RD TD CD Cable Modem Home Network Metro Core Access Multiplexer Switch First Mile Switch Switch Switch Edge node Metro Network » Ethernet is the most dominating LAN technology » Cheap equipment + high speed (up to 10 Gbps) » Introduce Ethernet into the Metro network (Metro Ethernet Forum): Core » consistent network platform » Ethernet should be Carrier Grade: » » » » » Traffic and User separation ~ Virtual LANs QoS ~ 8 traffic classes Reliability ~ Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Scalability ~ MAC-in-MAC and Q-in-Q Operation, Administration Management 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 3 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Routing in Ethernet: Spanning Trees Protocols (STP) » Spanning Trees form loop-free logical topologies » Their shape influenced by Port Costs » Provide restoration Root I. » MORE VLAN based spanning Root II. trees » Multiple spanning tree instances » Each tree runs a separate Rapid STP instance Bridge D Bridge A Bridge C Bridge B Bridge » 1 VLAN 1 tree Bridge Bridge Bridge Bridge » By default tree spanning is “Topology-Driven”: » Port costs based on topology and link capacities » Costs can be set manually (to obtain desired trees) 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 4 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Resource Management Architecture » Network Management Entity TE-pipe » Runs between access and edge nodes » pre-provisioned resources » Per Service TE pipe Telephone » AN & EN » Enforcing traffic via » Policing » Shaping Computer Access Node Switch Switch TV and Set Top Box Edge node Switch Modem Switch » Network Management Entity » Manages the resources » Performs CAC based on service datas and QoS. » Configures network elements (e.g., SNMP) Access Node Switch e pip E T Edge node Switch Modem 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 5 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT QoS Model » Priority based scheduling: » Lower priority traffic is not served until there is higher priority traffic in the queue. » To ensure low delay for each QoS class: amount of higher priority traffic should be limited for each link » Static global limits are defined for each class Class ID Provided service BW ratio 1 VoIP 0.1 2 IPTV 0.2 3 - - 4 HSI remaining » The method of how to determine these limits is out of scope. 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 6 BME - TMIT BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS IPTV: Multicast in Metro Ethernet » Efficient distribution of Video needs multicast » Dynamic Multicast » Ethernet switches “snoops” IGMP messages » Decides on which ports sends the packet out. » Manual Filtering » VLAN are for restricting Broadcast Domains » Shaping the VLAN to Multicast-trees » Assumed method » Forming P2MP Pipes ~ VLANs » Carrying more MC tree » IGMP snooping can be also used 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 7 BME - TMIT BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS HSI: Statistical Multiplexing » Traffic of individual users highly varies » Considering it at PIPE dimensioning » Aggregation of these flows still fluctuates n » Guèrin's model assumed BWaggr mi » Variances of Flows have i 1 to be estimated » Flows ~ Independents & Normal Distribution n 2 i i 1 » TE pipes are described: (Mean Rate; Peak Rate) 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 8 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS On the Optimal Configuration of Metro Ethernet for Triple Play Proposed Method and Simulation Results BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Problem Formulation » Input parameters: » Topology » QoS model » Static Traffic Matrices for each service » Tree Instances » The proposed method » Defines uni/multicast pipes for demands, » Spans the tree instances and » Assign the pipes for the tree instances » Integer Linear Model was presented for the basic problem, but it does not deals with » statistical multiplexing » multicasting 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 10 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Proposed Heuristic Method » Decomposes the problem to » Sequential allocation of pipes AND appending them to a tree instances. » Demand ordering problem » In each iteration random selection between: » Allocation of NEW pipe » Remove an existing tree 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 11 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Case Study » Assumed dual homing based topology » Services » VoIP » Unicast + symmetric PIPEs » No statistical mux assumed. » 10% of total traffic » Video » Multicast + asymmetric PIPEs » Medium traffic variance (PMR ~1.2) » 30% of total traffic » HSI » Unicast + asymmetric PIPEs » Large traffic variance (PMR ~ 2.0) » 60% of total traffic 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 12 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Traffic Model » Demand sizes based on Gaussian distribution » PEAK rate: Total traffic level x Service Ratio » MEAN rate: PEAK rate / PMR » VoIP and HSI : separate PIPEs for each AN—EN pair » IPTV: 1 multicast PIPE for each EN. » Performance descriptor: ACHIEVABLE THROUGHPUT » Determined via binary search of Total traffic level 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 13 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT The effects of Statistic Multiplexing Same throughput – less resources 20% more throughput achieved 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 14 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Notes on scalability » „OFF-LINE” configuration method » No strict time constraints » Scalability still important » On larger networks » Perform Dynamic TE » The proposed method iterative + polynomial steps » Finds solutions within a minute in the Test Case » Needs 100 rounds to find the solutions » For 1000 and 10000 rounds only a slight increase of performance… » Recent simulation on larger networks also show its scalability 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 15 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS BME - TMIT Conclusion » To provide Triple-Play QoS aware architecture is needed » To decrease costs Ethernet is a good choice » We propose » An efficient algorithm for off-line configuration » Deals with priority based QoS » Multicast » Exploit the effects of Statistical Multiplexing » Its performance is presented on a test case 2nd EuroNGI Conference on Next Generation Internet Design and Engineering, Valencia, SPAIN 16 BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS Thank you for your attention BUDAPEST UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND ECONOMICS DEPARTMENT OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND MEDIA INFORMATICS