* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPP
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Spanning Tree Protocol wikipedia , lookup
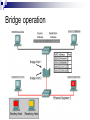
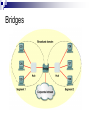
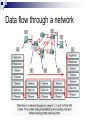
Introduction to IT and Communications Technology Ethernet Switching CE00378-1 Justin Champion C208 – 3292 Content Looking at Switching Bridges Collision Domains Switch operation A switch works with the inspection of the MAC address If the switch has a particular device attached the data will be forwarded to that machine Bridge operation Bridges Full duplex Transmit and receive concurrently due to separate cables for each Network latency This is the measure of the transfer time of a Ethernet frame The latency of the network is an important issue Particularly with Multimedia low Latency is needed Cut-through These switches Will start to forward the frame as soon as the destination MAC address has been read Reduces latency in the network Reduces reliability of the switch Store-and-forward The frames will be stored in the switch They are then forwarded to the destination When stored the frames can be checked for errors This increases latency on the network Does increase reliability Prevents corrupted packets being forwarded Spanning-tree-operation This is a protocol used between routers It is responsible for generating routes between points Ensuring that looping does not take place Storing alternative routes, in the event of failure STP states Each port which uses Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Will always be in one of the following 5 states Blocking Listening The port is preparing to transfer Ethernet frames Building a bridging table Forwarding Building an active knowledge of the topology connected Learning The port will only receive bridge protocol data unit (BDPU) frames These are used to exchange information with already operating ports on the network When a switch is first turned on it will be in this state Sending or receiving Ethernet frames Disabled This port will not be involved with the use of STP Collision domains A collision domain Is the part of the cable where multiple devices may potentially communicate at once A good network will have small collision domains and therefore less likely to have collisions corrupting data Collision domain segmentation Network devices which operate at different layers effect the collision domain Layer 1 devices – repeaters, Hubs Layer 2 devices – Switches, Bridges Will extend the domain Will break up the domain Layer 3 devices – routers Will break up the domain Increasing a collision domain If a computer anywhere in this network communicates every device will receive the frame! Repeaters extend the size of the collision domain Four repeaters (part of 5-4-3-2-1 rule) 5 segments of network media 4 repeaters or hubs 3 host segments of the network 2 link sections with no hosts 1 large collision domain Round-trip delay calculation Extension of a collision domain Layer 1 devices just repeat the signal with NO interpretation This extends the collision domain, by forwarding all traffic Limiting the collision domain The following items will limit the collision domain These devices processes the data before forwarding Bridge Router Switch A bridge can segment a collision domain A bridge can segment a collision domain Bridge A bridge can segment a collision domain Broadcasts in a bridged environment Level 2 devices These will segment the collision domain However they will have no effect on the broadcast domain A broadcast packet will be sent on all ports to all devices Effect of broadcast radiation on hosts in an IP network Average number of broadcasts and multicasts for IP Broadcast domain segmentation Data flow through a network Segments Summary Looked at Ethernet devices Operations of switches Types of switches Store and forward Cut through Network latency Collision domains Broadcast domains