* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6. Next Generation Networks A. Transition to NGN B. Key
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
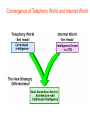
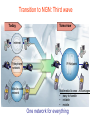
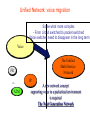
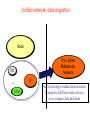
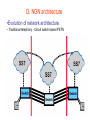
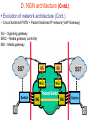
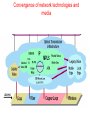
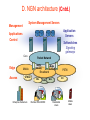
6. Next Generation Networks A. Transition to NGN B. Key drivers of NGN development C. Transport mechanism of the unified network D. NGN architecture E. Main NGN building blocks F. NGN protocols G. NGN as converged networks: concluding remarks A. Transition to NGN: First wave • Growth of Internet and other IP-based networks with their requirements for bandwidth and capacity has driven rapid innovation in telecommunication access and transport networks Examples: – leveraging copper wire “last-mile” networks through digital subscriber line (“DSL”) technologies – re-architecturing of cable networks to support IP services – advances in optical networking technologies (e.g. PON) Convergence of Telephony World and Internet World Transition to NGN: Second wave • Ongoing trend towards integration & interoperability of IPbased and PSTN network services and applications • Emergence of differentiated Quality of Service IP-based services • Managed end-to-end performance needed for new applications requiring real-time traffic (e.g., video, voice) • New network management, QoS, traffic engineering, pricing & accounting models Transition to NGN: Third wave • Evolution of current PSTN, mobile, wireless and IP-based networks to unified Next Generation Networks providing both Internet and carrier-grade telecommunications networks and services offerings with QoS • Transition to Third wave: Ubiquitous & Pervasive Networks – anybody, anytime, anywhere • Global Information Infrastructure (GII) – ITU, 1995 • EII ETSI Project (1995) • ITU NGN 2004 Project • Y.1xx ITU-T – SG 13 “NGN – Architecture, Evolution and Convergence” Transition to NGN: Third wave Today Tomorrow Internet Telephone network Mobile radio network IP-Network Multimedia Access - Advantages • easy to handle • reliable • mobile One network for everything ITU-T definition of NGN (Feb 2004) “A Next Generation Network (NGN) is a packet-based network able to provide services including Telecommunications Services and able to make use of multiple broadband, QoS-enabled transport technologies and in which service-related functions are independent from underlying transport-related technologies. It offers unrestricted access by users to different service providers. It supports generalized mobility which will allow consistent and ubiquitous provision of services to users.” B. Key drivers of NGN development Situation Today Target Solution Voice The Unified Multi Service Network FR ... ATM IP Unified Network: voice migration Some what more complex - From circuit switched to packet switched - Voice switches need to disappear in the long term Voice The Unified Multi Service Network FR ... ATM IP A new network concept supporting voice in a packetized environment is required The Next Generation Network Unified network: data migration Voice The Unified Multiservice Network FR ... ATM IP Pure technology/standardization matter: Transport of different data services over a unique data backbone B. Key drivers of NGN development (Cntd.) • Short Term objective: Create new revenue possibilities – Removal of boundaries between voice and data opens the way to new kind of services – Can be realized relatively quickly with limited investments • Long Term objective: Realize cost savings – Simpler network – More efficient network – Cheaper network components – Full benefit only realized when all separate networks have fully migrated towards to the target solution Example NGN Service Drivers Driven by Cost Reduction Possibilities Driven by Revenue Increase Possibilities C. Transport mechanisms of the unified network • The unified network will use packet-based technology as the common transport mechanism – Data is the fastest growing segment due to • Success of Internet • Growing use of E-mail • Growing data traffic between business users – Data should be handled in the most efficient way – Packet technology is the best way to transport data – Packet technology is only technology that allows simultaneous delivery of different information streams towards one and the same end-point on one single connection D. NGN architecture •Evolution of network architecture – Traditional telephony - Circuit switch based PSTN D. NGN architecture (Cntd.) • Evolution of network architecture (Cont.) – Circuit Switched PSTN + Packet Switched IP network (VoIP Gateway) SG – Signaling gateway MGC – Media gateway controller MG – Media gateway D. NGN architecture (Cntd.) •Evolution of network architecture (Cont.) – Comletely IP-oriented network D. NGN Architecture (Cntd.) Convergence of network technologies and media Nx64 kbps D. NGN architecture (Cntd.) System Management Servers Management Application Servers Applications Control Softswitches Signaling gateways Core Edge Access Mobile UTRAN Enterprise Customers Packet Network Media Gateway Media Gateway Broadband DSL Cable Remote Office/SOHO PSTN CO WLL Residential Users Mobile Users