* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IP spoofing
Server Message Block wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Remote Desktop Services wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Real-Time Messaging Protocol wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
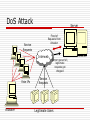
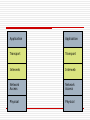
IP Spoofing Sometimes on the internet, a girl named Alice is really a man named Yves Sources General Information: Mitnick Attack Sequence: http://tarpit.rmc.ca/knight/EEE466Lectures/DA14/14%20%20Security%20I.ppt DoS and DDoS attacks: http://www.gulker.com/ra/hack/tsattack.html Session Hijack Sequence: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ip_spoofing http://www.securityfocus.com/infocus/1674 http://tarpit.rmc.ca/knight/EE579index.htm (See ppts on subject) http://tarpit.rmc.ca/knight/EEE466Lectures/DA14/14%20%20Security%20I.ppt Conversation with Todd ‘Hot Toddy’ Jackson Phrack Article: http://www.phrack.org/issues.html?issue=64&id=15#article Overview TCP/IP – in brief IP Spoofing Basic overview Examples Mitnick Attack Session Hijack DoS/DDoS Attack Defending Against the Threat Continuous Evolution Conclusion TCP/IP in 3 minute or less General use of term describes the Architecture upon which the Interweb is built. TCP/IP are specific protocols within that architecture. TCP/IP in 3 minutes or less Application Transport TCP Interweb IP Network Access Physical TCP/IP in 3 minute or less IP is the internet layer protocol. Does not guarantee delivery or ordering, only does its best to move packets from a source address to a destination address. IP addresses are used to express the source and destination. IP assumes that each address is unique within the network. TCP/IP in 3 minutes or less TCP is the transport layer protocol. It guarantees delivery and ordering, but relies upon IP to move packets to proper destination. Port numbers are used to express source and destination. Destination Port is assumed to be awaiting packets of data. TCP/IP in 3 minutes or less Client Using Mozilla HTTP - GET TCP – Port 80 Application Transport Some Web Server But what happens if someone is lying?? Application Transport IP – 10.24.1.1 Interweb MAC – Network Access Network Access 11010010011101 00110100110101 Physical Physical 00:11:22:33:44:55 Interweb IP Spoofing – Basic Overview Basically, IP spoofing is lying about an IP address. Normally, the source address is incorrect. Lying about the source address lets an attacker assume a new identity. IP Spoofing – Basic Overview Because the source address is not the same as the attacker’s address, any replies generated by the destination will not be sent to the attacker. Attacker must have an alternate way to spy on traffic/predict responses. To maintain a connection, Attacker must adhere to protocol requirements IP Spoofing – Basic Overview Difficulties for attacker: TCP sequence numbers One way communication Adherence to protocols for other layers IP Spoofing – The Reset Sucker - Alice 2.3.SYN RESET ACK–– Sure, Umm..what I have do no youidea want why to you talk are about? talking to me 1. SYN – Let’s have a conversation Victim - Bob 4. No connection – Guess I need to take Bob out of the picture… Attacker - Eve IP Spoofing – Mitnick Attack Merry X-mas! Mitnick hacks a Diskless Workstation on December 25th, 1994 The victim – Tsutomu Shinomura The attack – IP spoofing and abuse of trust relationships between a diskless terminal and login server. Mitnick Attack 6. Mitnick fakes 4. forgesthe a SYN ACKfrom using the server the proper to the TCP terminal sequence number Workstation 5. Terminals responds with an ACK, which is ignored by the 7. Mitnick has now flooded port (and not visible to established a one way Mitnick) Server communications channel 3. Mitnick discovers 2. Probes thethat the Workstation TCP sequence tonumber determine is the behaviour of by incremented its TCP 128000 sequence each number new connection generator 1. Mitnick Flood’s server’s login port so it can no longer respond Kevin Mitnick Mitnick Attack – Why it worked Mitnick abused the trust relationship between the server and workstation He flooded the server to prevent communication between it and the workstation Used math skillz to determine the TCP sequence number algorithm (ie add 128000) This allowed Mitnick to open a connection without seeing the workstations outgoing sequence numbers and without the server interrupting his attack IP Spoofing - Session Hijack IP spoofing used to eavesdrop/take control of a session. Attacker normally within a LAN/on the communication path between server and client. Not blind, since the attacker can see traffic from both server and client. Session Hijack Alice 3. At 1. 2. Eveany assumes can point, monitor Eve a man-in-thetraffic can assume between the middle Alice identity and position ofBob either without through Bob or altering some Alice the mechanism. packets through or thesequence Spoofed For example, numbers. IP address. Eve could use Arp This breaks Poisoning, the pseudo socialconnection engineering, as Eve will start router modifying hackingthe etc... sequence numbers I’m Bob! I’m Alice! Eve Bob IP Spoofing – DoS/DDoS Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) are attacks aimed at preventing clients from accessing a service. IP Spoofing can be used to create DoS attacks DoS Attack Service Requests Server Flood of Requests from Attacker Interweb Fake IPs Attacker Server queue full, legitimate requests get dropped Service Requests Legitimate Users DoS Attack The attacker spoofs a large number of requests from various IP addresses to fill a Services queue. With the services queue filled, legitimate user’s cannot use the service. DDoS Attack Queue Full Server (already DoS’d) SYN ACK 1. Attacker makes large number of SYN connection requests to target servers on behalf of a DoS’d server Interweb SYN ACK SYN SYN Attacker SYN ACK SYN ACK SYN SYN Target Servers 2. Servers send SYN ACK to spoofed server, which cannot respond as it is already DoS’d. Queue’s quickly fill, as each connection request will have to go through a process of sending several SYN ACKs before it times out DDoS Attack Many other types of DDoS are possible. DoS becomes more dangerous if spread to multiple computers. IP Spoofing – Defending IP spoofing can be defended against in a number of ways: As mentioned, other protocols in the Architectural model may reveal spoofing. TCP sequence numbers are often used in this manner New generators for sequence numbers are a lot more complicated than ‘add 128000’ Makes it difficult to guess proper sequence numbers if the attacker is blind “Smart” routers can detect IP addresses that are outside its domain. “Smart” servers can block IP ranges that appear to be conducting a DoS. IP Spoofing continues to evolve IP spoofing is still possible today, but has to evolve in the face of growing security. New issue of Phrack includes a method of using IP spoofing to perform remote scans and determine TCP sequence numbers This allows a session Hijack attack even if the Attacker is blind Conclusion IP Spoofing is an old school Hacker trick that continues to evolve. Can be used for a wide variety of purposes. Will continue to represent a threat as long as each layer continues to trust each other and people are willing to subvert that trust. Questions? Application Application Transport Transport Interweb Interweb Network Access Network Access Physical Physical Sucker - Alice Victim Bob Attacker - Eve Sucker - Alice Interweb Victim Bob Attacker - Eve Stolen from: http://tarpit.rmc.ca/knight/EE579/mitnik.ppt IP header 0 16 Version IHL Time to Live Total Length Type of Service Identification 31 Flags Protocol Source Address Destination Address Options and Padding Fragment Offset Header Checksum Stolen from: http://tarpit.rmc.ca/knight/EE579/mitnik.ppt TCP header 0 16 Source Port 31 Destination Port Sequence Number Acknowledgement Number Data Offset Reserved Checksum Flags Window Urgent Pointer Options and Padding TCP Sequence Numbers Client Start SEQ - 1892 2. 3. 1. Server Client Client ACKs, transmits transmits sends 50 20no bytes bytes data Server Start SEQ - 15562 SEQ – 1892 ACK – 15562 Size - 50 SEQ – 15562 ACK – 1942 Size - 25 SEQ – 1942 ACK – 15587 Size - 0 End SEQ - 1942 End SEQ - 15587