* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
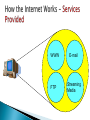
Communications, Networks, the Internet, and the World Wide Web Define communications (telecommunications) in the context of computer systems. Identify the basic components of a communications system. Describe how and why networked computers are used within schools and school districts. Explain what the internet is and how it works. List the major services on the Internet and explain how they work. Define the World Wide Web (WWW). Explain how a Web site delivers information. Demonstrate the ability to use WWW search tools. Demonstrate the ability to create a simple Web site (later in class) Describe the educational implications of the Internet and the World Wide Web Understand security and netiquette issues related to the Internet and the WWW. The exchange of information over significant distances by electronic means. Examples of applications ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ E-mail Telecommuting Videoconferencing Internet POTS Television Radio A communications network is a collection of computers and other equipment organized to share, data, hardware, and software. Networks also require communications software. notebook computers smart phones Web-enabled servers PDAs GPS receivers desktop computers mainframe computers set-top boxes Tablet PCs Local Area Networks (LAN) ◦ Covers limited geographical area ◦ Server manages resources Wide Area Networks (WAN) ◦ Covers large geographical area ◦ Can consist of several LANs Limited Local Area Network (LAN) connecting computers, printers and other devices within the confines of the classroom. Providing a network between the Classrooms Labs Library School Administrative areas. ◦ Outside world ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Providing a network between the ◦ Schools ◦ Administrative Buildings ◦ Outside world Provides access to networks without wire or cable. Most notebooks and other devices are coming with wireless capabilities. Most PC’s can be ordered with wireless network cards or they can be installed aftermarket. Great advantage in retrofitting a school. Sharing of computer hardware, software, and data resources Access to educational resources Communicate with other educators and students The Internet is a worldwide collection of networks that link together millions of businesses, governments, educational institutions, and individuals. Each of these networks provides resources and data that add to the abundance of goods, services, and information accessible via the Internet. The Pentagon’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) begins a project to network computers around the country, ARPNET. 1969 The first computers are connected to the ARPNET 1972 The first e-mail is sent 1981 the IBM PC is introduced 1984 Apple introduces the McIntosh computer 1989 Tim Bernes-Lee invents the World Wide Web 1969 1992 Windows 3.1 is introduced 1993 a graphic interface for the WWW is created called Mosaic. This will become Netscape Navigator. Slow speed technology ◦ Dial-up access High speed technology ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Digital subscriber line (DSL) Cable television Internet services (CATV), Satellite Wireless Broadband Connection is always on E-mail File Transfer Protocol World Wide Web Streaming media Chat rooms and message boards. These services are called protocols in the computer world. A protocol is a standard procedure for regulating data transmission between computers WWW FTP E-mail Streaming Media Data is divided into packets Packets are sent across the Internet using various types of equipment Packets are reassembled at receiving computer. Client Backbone Internet Cloud Server The Internet Protocol Address or IP Address ◦ Known as the dotted quad xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx ◦ Number that uniquely identifies each computer or device connected to Internet Domain Name is the text version of IP Address www.amazon.com = 207.171.166.252 The World Wide Web, or simply Web, consists of a worldwide collection of electronic documents, Web pages, organized into Web sites. The Universal Resource Locator (URL) Unique address for a web page located on a specific web server. protocol domain name path http://www.nationalgeographic.com/travel/index.html Web pages consist of three components; ◦ Text ◦ Multimedia Graphics Audio Video ◦ Hyperlinks Text or graphics that connect (link) to other web pages. Three types of links Hyperlinks can be text or graphics ◦ Items found elsewhere on the same page ◦ Different web pages in the same site. ◦ Other web sites. Web Browser Software ◦ Interprets HTML, displays Web pages and enables you to link to other Web pages and Web sites The two most popular browsers are; ◦ Internet Explorer ◦ FireFox A Web site that offers a variety of services from one, convenient location, usually for free Contains newsworthy material Stories and articles relating to current events, life, money, sports, and weather News Archives Contains factual information Created by organizations and government agencies Make sure that the web site is legitimate Contains content that describes a cause, opinion, or idea Contains content that promotes products Allows you to purchase products or services online Allows companies to purchase goods and service from other companies Offers avenues for formal and informal teaching and learning Colleges offer online classes and degrees Some companies offer online training for employees Offers an interactive environment featuring music, video, sports, games, and more Web page maintained by private individual Reasons: sharing life experience with the world or job hunting An informational Web site consisting of time stamped: ◦ Articles ◦ Posts In a diary or journal format. Netiquette is the code of acceptable behaviors users should follow while on the Internet. Golden Rule: Treat others as you would like them to treat you. Website for Netiquette information http://www.albion.com/netiquette/ Firewall Filtering software Acceptable Use Policy (AUP)