* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 451_Chap
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
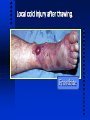
CHAPTER 22 Environmental Emergencies Thermoregulatory Emergencies Thermoregulatory emergency: An increase or decrease in the temperature of the body or body part that results in an injury. Temperature Regulation in the Body The body performs a delicate balancing act between the heat generated in the body and the heat lost from it. Types of Heat Loss Convection Respiration Conduction Radiation Evaporation Heat loss occurs during respiration - when the body warms and humidifies the air. Maintenance of Body Temp Falling body temperature Peripheral blood vessels constrict Muscles produce heat through shivering Rising body temperature Blood vessels dilate Sweat glands produce moisture The body also produces heat by shivering. Ambient temperature affects how the body maintains its temperature. This results from the combined effects of wind and humidity. Exposure to the Cold Extreme weather conditions can produce a variety of cold emergencies. Hypothermia: A condition in which the core body o o temperature falls below 35 C (95 F) and the body’s normal functions are impaired. Caused by prolonged exposure to cold. The most common cause of generalized hypothermia is exposure to a cold environment. Factors that Contribute to Hypothermia Cold environments Immersion or submersion in water Age (the very young and the elderly) Alcohol Shock (hypoperfusion) Some medications and poisons Factors that Contribute to Hypothermia continued Medical conditions Diabetes and hypoglycemia Metabolic and infectious processes Trauma Hypovolemia or shock Head injuries Spinal cord injuries Burns Alcohol use is a complicating factor in many hypothermic patients. Mental & Motor Function Changes caused by Hypothermia Dizziness and poor coordination Altered mental status Memory disturbances Poor judgement Mood changes Communication and speech difficulties Mental & Motor Function Changes caused by Hypothermia continued Stiffness/rigid posture Reduced or absent sense of touch Changes in vital signs Joint or muscle pain Vital Signs in Hypothermia SIGN EARLY LATE Pulse Rapid Slow & barely palpable Blood Pressure Normal Low or absent Breathing Rapid Shallow, slow or absent Skin Red Pale, cyanotic Stiff & hard Pupils Reactive Sluggish Focused Assessment What was the source of the cold? If water, what was the temperature? What were the general environmental conditions like? Did the patient experience a loss of consciousness? Are the effects general or local? Hypothermia Treatment Remove the patient from the cold environment and protect from heat loss Remove any cold or wet clothing, and cover the patient with blankets Handle the patient with care, and avoid rough handling Warm the patient compartment of the ambulance as much as possible Hypothermia Treatment continued Apply high-flow oxygen; warmed and humidified if possible Use no stimulants such as caffeine or alcohol Do not massage the extremities Check for a pulse for 30 - 45 seconds before starting CPR Do not attempt to actively warm hypothermic patients who have a decreased level of consciousness... ...simply prevent further heat loss. Care for Hypothermia with No Signs of Life Ensure a patent airway Ventilate the patient with 100% oxygen Begin CPR if no pulse for 30 - 45 seconds Use the AED according to local established protocols, or call medical direction Local cold injuries result from decreased blood flow to, or freezing of, a body part. These injuries are often called frostbite or frostnip. Local cold injury after thawing. Frostbite Early or Superficial Cold Injury Pale skin with delayed capillary refill Loss of feeling/sensation in injured area Skin still soft Tingling sensation when rewarmed Late or Deep Cold Injury White or waxy skin appearance Firm or frozen skin presentation Swelling and blister formation Loss of sensation in injured area If thawed, skin may be purple and pale Care for Local Cold Injuries Remove patient from cold environment Protect the cold extremity from injury Administer oxygen Remove wet or restrictive clothing and all jewelry Splint if extremity involved, and cover with dry, sterile dressing Place dressings between those fingers affected by local cold injury. Never re-expose the area to cold, break blisters, rub or massage the area, apply heat, or allow the patient to use the affected area. In a cold emergency, if transport time will be long: Immerse the affected part in warm water (102o - 104o F) Continuosly stir and add warm water to maintain temperature Continue immersion until the area is soft and color and sensation return Pat gently and dress with dry, sterile dressings Protect the injured area from refreezing Refer to local protocols for other treatment Exposure to Heat Hyperthermia: A condition in which the core body temperature exceeds normal limits and starts to malfunction. Caused by exposure to heat. Predisposing Factors for Heat Emergencies Hot, humid weather Vigorous physical activity Age (the very young and the elderly) Medical conditions Diabetes Heart disease Fever Predisposing Factors for Heat Emergencies continued Dehydration Obesity Fatigue Drugs and medications Previous history of hyperthermia Working in a hot environment can result in a heat emergency. Signs and Symptoms of Hyperthermia Muscle cramps Weakness or exhaustion Dizziness or fainting Rapid, bounding pulse Altered mental status Moist, pale, cool, hot or normal skin Nause, vomiting and abdominal cramps Care for Hyperthermia with Moist, Pale, Cool or Normal Skin (Heat Exhaustion) Remove patient from hot environment Administer oxygen Loosen or remove clothing Cool the patient by fanning Place responsive patient supine with legs elevated; if vomiting, place on side If no nausea, provide cool water to drink Remove patients from the hot environment and allow them to cool off. Care for Hyperthermia with Hot, Dry Skin (Heat Stroke) Remove patient from hot environment Remove clothing and administer oxygen Apply cold to neck, groin and armpits Moisten patient’s skin with wet towels Fan the patient aggressively Transport patient immediately Severe hyperthermia can lead to cardiac arrest. Drowning and Near Drowning Water-related Emergencies: Drowning is death following submersion in water. Near-Drowning is survival (either short or long term) following submersion in water. Water rescue requires specialized training - NEVER ENDANGER yourself or others by attempting something you are not trained to do. Water Rescue with Spinal Immobilization Care of the Near Drowning Patient Immobilize spine if trauma is suspected Ensure adequate airway, provide oxygen and ventilate if necessary Provide CPR if pulseless (use AED if allowed by local protocols) Suction as needed If no trauma, place patient on left side Transport immediately DO NOT attempt to relieve gastric distention unless it interferes with ventilation. There is significant risk of aspiration. Bites and Stings Creatures that Bite and Sting Signs & Symptoms of Bites and Stings Rash, redness Headache, dizziness Local pain, swelling Nausea, vomiting Fever and chills may also follow the bite or sting. Bite marks Care of Bites and Stings Ensure adequate ABC’s Inspect the site for stinger or bite marks Wash the area gently Remove jewelry from injured area If extremity, position just below level of heart If snakebite, consult medical direction Watch for development of allergic reaction SUMMARY Thermoregulatory Emergencies Drowning and Near-Drowning Bites and Stings