* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dementia & Delirium in Surgical Patients - E-Ageing: E
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
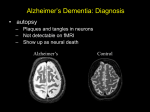
Dementia & Delirium in Surgical Patients Damian Harding Department of Geriatric Medicine February 2008 Introduction Surgical patient population has changed.. Introduction Surgical patient population has changed.. More older patients Patients have more co-morbidities.. More likely to experience patients with dementia, and to encounter delirium/ acute confusion in surgical patients. Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Dementia Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Dementia: “acquired loss of cognitive function due to an abnormal brain condition” Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Dementia: “acquired loss of cognitive function due to an abnormal brain condition” Usually progressive Includes functional decline Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Dementia: “acquired loss of cognitive function due to an abnormal brain condition” Usually progressive Includes functional decline Memory loss and cognitive impairment are NOT features of normal aging! Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Prevalence of all dementias in the >65 yr population is 6-8% Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Prevalence of all dementias in the >65 yr population is 6-8% Prevalence in >85yr population is 30% Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Prevalence of all dementias in the >65 yr population is 6-8% Prevalence in >85yr population is 30% Estimated annual cost reaches US$100 billion (2001) Direct care to individual Lost wages by caregivers Dementia Definitions and Epidemiology Prevalence of all dementias in the >65 yr population is 6-8% Prevalence in >85yr population is 30% Estimated annual cost reaches US$100 billion (2001) Direct care to individual Lost wages by caregivers Significant emotional and personal costs Types of Dementia At least 50-60% of people with dementia have Alzheimer’s Disease Types of Dementia At least 50-60% of people with dementia have Alzheimer’s Disease Commonest types of dementia include: Types of Dementia At least 50-60% of people with dementia have Alzheimer’s Disease Commonest types of dementia include: Alzheimer’s Disease Vascular (multi-infarct) dementia Lewy body Dementia Alcoholic dementia (depression and pseudo-dementia) Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits (including memory loss) Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits (including memory loss) Functional impairment Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits (including memory loss) Functional impairment Clear consciousness* Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits (including memory loss) Functional impairment Clear consciousness* Change from previous level (>6 months duration) Alzheimer’s Disease Neurodegenerative disease associated with: Cognitive deficits (including memory loss) Functional impairment Clear consciousness* Change from previous level (>6 months duration) Median survival from diagnosis: 5-6 years Alzheimer’s Disease is associated with specific changes in brain anatomy, chemistry and physiology Alzheimer’s Disease is associated with specific changes in brain anatomy, chemistry and physiology Neurofibrillary tangles* Amyloid plaques Loss of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity and of cholinergic projection neurons in Nucleus basalis of Meynert* Alzheimer’s Disease is associated with specific changes in brain anatomy, chemistry and physiology Neurofibrillary tangles* Amyloid plaques Loss of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity and of cholinergic projection neurons in Nucleus basalis of Meynert* Multifactorial genetic component Alzheimer’s Disease is associated with specific changes in brain anatomy, chemistry and physiology Neurofibrillary tangles* Amyloid plaques Loss of cortical choline acetyltransferase activity and of cholinergic projection neurons in Nucleus basalis of Meynert* Multifactorial genetic component CT/MRI may be normal or show generalized atrophy/ focal atrophy in medial temporal lobe *correlates with disease severity Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Aphasia Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Aphasia Word-finding difficulties Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Brush teeth, dress, comb hair Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Brush teeth, dress, comb hair Agnosia Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Brush teeth, dress, comb hair Agnosia Failure to recognise objects/ familiar faces Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Brush teeth, dress, comb hair Agnosia Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Failure to recognise objects/ familiar faces Frontal executive dysfunction Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Cognitive Amnesia Aphasia Brush teeth, dress, comb hair Agnosia Word-finding difficulties Apraxia Misplace/ lose objects. Repeat same question. Failure to recognise objects/ familiar faces Frontal executive dysfunction (Capacity to consent for treatment) Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Delusions, hallucinations Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Delusions, hallucinations Mood problems Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Delusions, hallucinations Mood problems Behavioural changes Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Delusions, hallucinations Mood problems Behavioural changes Apathy Overactivity/ agitation (wandering) Aggression Personality changes Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Mood problems Behavioural changes Delusions, hallucinations Apathy Overactivity/ agitation (wandering) Aggression Personality changes Abnormal sleep Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Mood problems Behavioural changes Delusions, hallucinations Apathy Overactivity/ agitation (wandering) Aggression Personality changes Abnormal sleep Reduced appetite Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Features: Non-Cognitive Psychotic symptoms Mood problems Behavioural changes Delusions, hallucinations Apathy Overactivity/ agitation (wandering) Aggression Personality changes Abnormal sleep Reduced appetite Incontinence Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Biological Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Biological Social Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Biological Social Psychological Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Depends on stage of disease Multifactorial and multidisciplinary Management of Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementias Depends on stage of disease •Multifactorial and multidisciplinar y Day therapy/ day hospital Day centres Respite care Social worker Alzheimer’s Association Community (Silver Chain) support Psychologist Psychiatrist Geriatrician GP Dietician OT Physiotherapy Care for Patients with Dementia Admitted for Surgery Care for Patients with Dementia Admitted for Surgery Admission Assessment Care for Patients with Dementia Admitted for Surgery Admission Assessment Implementation of Care Care for Patients with Dementia Admitted for Surgery Admission Assessment Implementation of Care Discharge considerations Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Take history from patient and carer Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Take history from patient and carer What is patient’s usual level of function? (ADLs) Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Take history from patient and carer What is patient’s usual level of function? (ADLs) Patient’s usual daily routine Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Take history from patient and carer What is patient’s usual level of function? (ADLs) Patient’s usual daily routine Are patient and carer currently coping at home? Care for Patients with Dementia: Admission Assessment Take history from patient and carer What is patient’s usual level of function? (ADLs) Patient’s usual daily routine Are patient and carer currently coping at home? (Is patient at risk of elder abuse?) Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Day/ night cycle Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Day/ night cycle Remind patient of day/ time/ place/ why here Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Day/ night cycle Remind patient of day/ time/ place/ why here Allow family/ carers to stay longer/ use of phone/ photograph prompts Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Day/ night cycle Remind patient of day/ time/ place/ why here Allow family/ carers to stay longer/ use of phone/ photograph prompts Consider use of visual prompts “This is the bathroom”/ “I had knee surgery 2 days ago”/ “My nurse is..” Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Environmental Patient orientation Day/ night cycle Remind patient of day/ time/ place/ why here Allow family/ carers to stay longer/ use of phone/ photograph prompts Consider use of visual prompts “This is the bathroom”/ “I had knee surgery 2 days ago”/ “My nurse is..” Low level lighting at night Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Physical Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Physical Ensure patient receives usual medications Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Physical Ensure patient receives usual medications Beware of increased effects of abnormal physiology causing agitation/ drowsiness Care for Patients with Dementia: Implementation of Care Physical Ensure patient receives usual medications Beware of increased effects of abnormal physiology causing agitation/ drowsiness Beware of new drugs and their doses: Anaesthesia Analgesia (and bowels) Anti-emetics Fluids (and electrolytes) Care for Patients with Dementia: Discharge considerations Attention to function (ADLs) and ability to return to previous environment Attention to function (ADLs) and ability to return to previous environment If not sure: arrange OT, physiotherapy, geriatric medicine review Attention to function (ADLs) and ability to return to previous environment If not sure: arrange OT, physiotherapy, geriatric medicine review Patient may benefit from ongoing restorative care Attention to function (ADLs) and ability to return to previous environment If not sure: arrange OT, physiotherapy, geriatric medicine review Patient may benefit from ongoing restorative care Patient may require increased long term level of care Attention to function (ADLs) and ability to return to previous environment If not sure: arrange OT, physiotherapy, geriatric medicine review Patient may benefit from ongoing restorative care Patient may require increased long term level of care Ensure good communication to patient and carers (reduce stress and confusion)