* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE H.E.L.P. PROJECT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
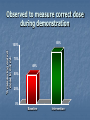
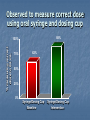
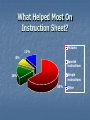
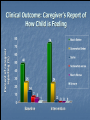
THE H.E.L.P. PROJECT The Health Education and Literacy for Parents ROR AND HEALTH LITERACY ROR proved to have positive impact on families Any intervention aimed at improving language & literacy development in children should also address parental literacy skills Health Education & Literacy for Parents (HELP) Project Based on ROR Model Parent educators and trained volunteers approach parents in clinic waiting area Provide short term educational interventions, which include several “activities” Gives Parents Strategies to improve family & child’s health, growth & development “Plain language” handouts with illustrations that support these strategies A sense that they are “learners” –they can learn new things with supportive help H.E.L.P. Goals Improve parents’ ability to read & understand health care instructions Instruct parents to use written materials to focus on child’s overall health Help parents better communicate with Pediatrician Motivate parents to continue their own education Waiting Area Health Literacy Intervention Learn more about you child’s medicine activity Understanding and “Decoding” Your Child’s Prescription “What do you use to give your child liquid medicine?” Medication Instruction Sheet (MIS) Medication Log (Self-Monitoring) Questions to Ask Pediatrician/Pharmacist Medical Diaries to Record Medications of e Collaborative Resources New York Poison Control Center Literacy Assistance Center Hotline Quality Improvement Project (QIP) Evaluation of H.E.L.P. Intervention Sheets Aim of QIP Evaluation To measure the effectiveness of these forms: Does knowledge of medication usage improve? Does adherence increase ? Is there improvement in child’s clinical status? QIP Evaluation Design Ongoing Convenience sample in Pediatric Clinic and Pediatric Dental Clinic Baseline and Intervention Groups Background and Follow-up Questionnaires Enrollment & Eligibility Pediatrician notifies evaluator when patient receives liquid antibiotic prescription Parents are invited to participate in the evaluation if they meet the following criteria: Child (patient) under 12 years of age Able to speak English or Spanish Have access to a telephone at home Procedures Baseline Group (n=50) Intervention Group (n=42) Standard practice Pediatrician or Pediatric Dentist provide intervention: Medication Sheets and Dosing Instrument Both groups: Measure dosing accuracy, administer background questionnaire Follow-up questionnaire administered over the telephone four to seven days later Outcome Measures Dosing Accuracy Medication Knowledge Medication Adherence Satisfaction with Intervention Procedures Patient Clinical Outcome Demographics Baseline Intervention (n=50) (n=42) 84 % 90 % 78 % 72 % 91 % 90 % 81 % 67 % Mean (SD) age of patient, yrs 3.92 (2.8) 3.55 (2.7) Mean (SD) # Children in Home 2.35 (1.1) 2.67 (1.5) Respondent: Relation: Mother Caregiver: non-US born Background: Hispanic/Latino Language: Spanish DOSING ACCURACY Observed to measure correct dose during demonstration 88% % measuring correct dose to 0.2 mL 100% 75% 49% 50% 25% 0% Baseline Intervention Observed to measure correct dose using oral syringe and dosing cup 88% % measuring correct dose to 0.2 mL 100% 75% 62% 50% 25% 0% Syringe/Dosing Cup Baseline Syringe/Dosing Cup Intervention % measuring correct dose to 0.2 mL Observed to measure the correct dose at baseline: kitchen spoons verses oral syringe and dosing cup 100% 62% 75% 50% 28% 25% 0% Kitchen spoons Syringe and Dosing Cup FOLLOW UP CALL: MEDICATION KNOWLEDGE Medication Knowledge Baseline Intervention Named Prescribed Medication 84% 95% Knew Proper Preparation 90% 100% Knew Proper Medication Storage 92% 98% Knew Reason for Medication 92% 100% FOLLOW UP CALL: MEDICATION ADHERENCE Adherence: Tracking System Baseline Intervention Kept track medicine given 62 % 93 % Correct 24 hr. dose freq. Gave medication at correct time Not missing doses prior day 90 % 90 % 86 % 100 % 100 % 100 % Adherence: Use of Intervention Materials 91% used Medicine Instruction Sheet 94% used Medication Log Sheet FOLLOW UP CALL: SATISFACTION WITH INTERVENTION Satisfaction: Did the Medicine Instruction and Log Sheets Help? % helped by intervention sheets to use medicine correctly 100% 92% 83% 75% 50% 25% 0% Medicine Instruction Sheet Medication Log Sheet What Helped Most On Instruction Sheet? Pictures 11% 8% Spanish instructions Simple instructions 16% 65% Other Which Pictures Helped the Most? Dosing pictograms 25% Shake well 14% 42% 19% All Other FOLLOW UP: PATIENT CLINICAL OUTCOME SUMMARY Results will be used to: Develop the intervention for other medications Expand intervention to other clinics at Bellevue Hospital Train medical and nursing staff to use intervention Medication Information and Log Sheets Dosing instrument given with each prescription Parent education in proper use of oral syringe H.E.L.P Project Contact Information Linda van Schaick (212) 562-3165 E-mail: [email protected]