* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mollusca_Day_1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
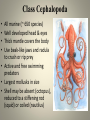
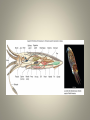
Molluscs Phylum: Mollusca • Kingdom: Animalia • Mollusca = “soft bodied” • Over 100,000 species in this phylum • Examples: snails, slugs, clams, oysters, squid, octopus, nautilus & cuttlefish, chitons Characteristics of All Mollusks • Soft-bodied invertebrate covered with protective mantle (may or may not form a hard, calcium carbonate shell) • True fully-lined coelom (body cavity) • Cephalization – distinct head with sense organs and brain • Muscular foot – used for movement (modified into tentacles/arms for squid and octopus) Characteristics -cont.• Scraping mouth-like structure called the radula • Free-swimming larval stage called trochophore • Body organs called visceral mass lie below mantle • Most have separate sexes that cross-fertilize eggs • Bilateral symmetry Characteristics -cont.• Have circulatory, respiratory, digestive (1-way with mouth and anus), excretory, nervous & reproductive systems • Gills between the mantle and visceral mass are used for gas exchange 4 Classes • Cephalopoda (squid, octopus, nautilus, cuttlefish) • Pelecypoda/Bivalvia (clams, oysters, mussels, etc) • Polyplacophora (chitons) • Gastropoda (snails, slugs, nudibranchs, conchs, abalone, etc) Class Cephalopoda • • • • All marine (~ 650 species) Well developed head & eyes Thick mantle covers the body Use beak-like jaws and radula to crush or rip prey • Active and free swimming predators • Largest mollusks in size • Shell may be absent (octopus), reduced to a stiffening rod (squid) or coiled (nautilus) Cephalopoda • Foot adapted into arms with suckers • Closed circulatory system • Highly developed nervous system • Separate sexes with internal fertilization Squid • Large complex brain • 8 arms/ 2 longer tentacles to catch prey • Uses jet propulsion to move by forcing water out their excurrent siphon • Can squirt an inky substance into water to temporarily blind predators Squid • Chromatophores in skin help change squid color for camouflage • Have internal shell called pen • Female lays eggs in jellylike material & protects them until hatching Squid • Largest mollusk is a giant squid • Can grow up to 40-50ft including tentacles • Hunted by sperm whales and suction marks on whales show they fight Giant Squid http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uLRY1cNxL1 I piglet squid http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/news/animals-news/marine-censusgraphics-vin/