* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animals - Trunity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
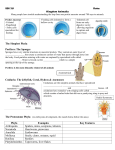
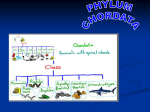
Animals – Unit 1 Living Things Called Animals Content Learning Goals • Students will be able to explain why some living things are considered “animals” and how scientists tell them apart. Living Thing Plant Animal Language Learning Goals Be able to define: • Classify • Traits • Scientific Name Traits • The certain way an animal looks or acts Classify • To put into groups based on traits When is a living thing an animal? When it has these traits: • It moves by itself • Eats food • Needs water and oxygen Scientific Name • The name all scientists use to describe an animal Examples: 1. Canis familiaris 2. Felis catus 3. Equus caballus 4. Homo sapien Animals – Unit 2 A Look at the Animal Kingdom Content Learning Goals • Students will learn about phyla and classes of animals. They will be able to identify 7 animal phyla, 5 classes of vertebrates. • Be able to recognize 50+ animals and which phyla or class they belong to Language Learning Goals Be able to define: • Phylum or Phyla • Class • Memorize the names of 50+ organisms in the animal kingdom. Phyla • Group of animals with some similar traits (scientist’s category to classify animals) • Now we’ll look at seven phyla. They go from very simple animals to those that are highly complex. Animals Porifera Coelentrate Worm Mollusk Arthropod Echinoderm Vertebrate Porifera Phylum • • • • • • Have pores (holes) “Porifera” means “having holes” Sponges Very simple animals Bodies are empty sacks The inside of the body is called the body cavity Sponge Coelenterate Phylum • Jellyfish, sea anemone and coral • “stinging cell animals” • Tentacles are like arms. They are used for stinging Jellyfish Sea Anemone Coral Worm Phylum • Parasites – animals that live inside the bodies of other animals • Segments – small sections • Digestive System – mouth, intestines and anus • Circulatory System – Heart and blood vessels that move blood through the body Worm Mollusk Phylum • Means “soft body” • Clams, octopus, squid, snails and slugs Clam Octopus Snail Slug Arthropod Phylum • • • • Have Legs with joints Spider, bee, crayfish, ant, fly Hard outside covering – “exoskeleton” Bee Segments – Head, Thorax, Abdomen Spider Bee Fly Butterfly Ant Echinoderm Phylum • Sea urchin, starfish, sand dollar • Hard covering…echino means “spiny” and derm means “skin”, so echinoderms have spiny skin. • Many have five-part body patterns • Tube feet – like suction cups Starfish Sand dollar Vertebrate (Sub) phylum • Animals with backbones • Dogs, birds, snakes and humans • Skeleton inside the body (including a skull covering a brain) • Subphylum of “Chordates” – (most chordates are vertebrates, so people usually just use the term “vertebrate”) Class • Group of animals in the same phyllum Phylum Subphylum Class • In vertebrates, this includes: Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles, Birds and Mammals Chordates Vertebrates Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds Mammals Fish Three types: • Fish with bony skeletons (trout) • Fish with cartilage (sharks) • Fish without jaws (lamprey) • All have gills to breathe and fins to move in the water. Fish Shark Lamprey or “Eel” Amphibians • They like water and have gills to breathe just like fish • BUT unlike fish, they grow up and live on the land. • They lay eggs in water that have no shells. • They have skin that dries out so they stay in wet places, but not always in the water. Frog Salamander Reptiles • They don’t need water, but some like it • They have waterproof skin and scales • They lay eggs with leathery shells Snake Turtle Crocodile Lizard Birds • They have feathers, beaks, wings and scales on their feet • Wings are for flying and sometimes for swimming. Some birds can’t fly • They lay eggs with hard shells Bird Chicken or Rooster (Chick) Turkey Duck Mammals • • • • They are covered in hair They nurse their young Most give birth instead of laying eggs Most live on land, but some are in the sea Dog (Puppy) Cat (Kitten) Rabbit (Bunny) Cow (Calf) Pig Horse (Foal) Donkey Sheep (Lamb) Goat Monkey Mouse Lion Tiger Cougar Bear Elephant Giraffe Deer Elk Moose Dolphin Whale Review • Activity