* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz Cards C1 Topic 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
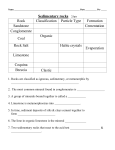
1) Name the three types of rock. Answer Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 2) Name two examples of sedimentary rocks. (2) Answer Limestone Chalk Sandstone C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 3) Describe some features of sedimentary rocks (2) Answer • Contain fossils • are layered • easily broken away by wind, rain and waves C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 4) Describe how sedimentary rocks are formed? (4) Answer. • Formed from layers of sediments (silt, animals, plants). • Over millions of years pressure from layers above, • squeezes out the water and compresses them. • Finally cemented together C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 5) How are metamorphic rocks formed? (3) Answer. • Formed by action of heat • and pressure. • Formed from sedimentary rocks (or igneous). C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 6) Give an example of metamorphic rock and what is formed from. Answer • Marble formed from, • Limestone or chalk C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 7) Name the two types of igneous rocks giving examples. (2) Answer Extrusive eg; basalt Intrusive eg; Granite C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 8) Describe the difference between in appearance between extrusive and intrusive igneous rocks. • Intrusive rock: Contain large crystals • Extrusive rocks: Contain small crystals C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 9) Describe how extrusive igneous rocks are formed (2). Molten magma pushes out of crust, cools quickly, above ground, forming small crystals C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 10) Describe how intrusive igneous rocks are formed (2). a) Molten magma pushes up into the crust, cools slowly underground forming big crystals C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 11) Give some uses of limestone (3) Answer 1) Building material, bricks, cement and concrete 2) Making glass 3) Neutralising of acidic soil and rivers due to acid rain C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 12) Describe how cement is made (2). Answer Limestone heated in a kiln with powdered clay . C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 13) How is concrete made ? Answer Mix cement with sand, water and gravel C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 14) How is glass made? Answer Heat, sand and sodium carbonate until it melts. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 15) Describe some of the problems with quarrying limestone. (4) Answer 1) Makes ugly holes permanently effecting the scenery. 2) Noise pollution from explosions and transporting limestone. 3) Destroys habitats. 4) Dust pollution explosion pollution from. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 16) Give some advantages of quarrying limestone. (3) Answer • Provides products like houses, roads, paints and medicine. • Used to neutralise acidic soil and water ways. • Used in power station chimneys to neutralise acidic gases (SO2 which causes acid rain). • Brings money, jobs and local improvements (e.g roads) into the local environment. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 17) What is the name of the chemical that limestone is made from (2). Answer Calcium carbonate . C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 18) What is the chemical formula of calcium carbonate? Answer CaCO3 . C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 19) When calcium carbonate is heated it is thermally decomposed into what two products. (2) Calcium Oxide + Carbon dioxide C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 20) What is the word equation for the thermal decomposition calcium carbonate? (2) Answer Calcium Carbonate ---Calcium Oxide + CO2 C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 21) What is the balanced equation for the thermal decomposition calcium carbonate? (2) Answer CaCO3 ----- CaO + CO2 C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 22) What are the balanced symbol equation for the thermal decomposition of a) Copper Carbonate b) Zinc Carbonate Answer a) CuCO3 ----- CuO + CO2 b) ZnCO3 ----- ZnO + CO2 C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 23) How is thermal stability of different metal carbonates determined? (3) Answer (any of the three following point) • Heat the carbonate in a boiling tube, • Pipe off the gas given off (CO2) into limewater. • The CO2 will turn the limewater milky. • Least stable carbonate will decompose faster and the lime water will turn milky more quickly. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 24) How is Calcium hydroxide formed? Answer Add water to calcium oxide C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 25) How is Limewater produced from calcium hydroxide? Answer • Dissolve calcium hydroxide (solid) in water. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 26) What is the conservation of mass? Answer • A reaction conducted in a sealed tube, the total mass before and after the reaction do not change. C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman 27) What is the formula for the following acids a) Hydrochloric acid b) Sulphuric acid c) Nitric Acid Answer a) HCl b) H2SO4 c) HNO3 C1 TOPIC 2 M. Rahman