* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The War of 1812
Battle of Tippecanoe wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Lundy's Lane wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Crysler's Farm wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Frenchtown wikipedia , lookup
Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Bladensburg wikipedia , lookup
Battle of North Point wikipedia , lookup
Battle of York wikipedia , lookup
Burning of Washington wikipedia , lookup
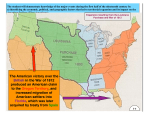
The American Nation Chapter 10: The Age of Jefferson 1801–1816 Section 1: A Republican Takes Office Section 2: The Louisiana Purchase Section 3: New Threats from Overseas Section 4: The Road to War Section 5: The War of 1812 Chapter 10, Section 5 The War of 1812 •How was the United States unprepared early in the war? The United States Was Not Prepared for War Chapter 10, Section 5 • The United States Navy had only 16 ships. The British had a huge fleet. • The United States Army was small and ill equipped. Many officers knew little about warfare. • The government relied on volunteers, who were poorly trained and had little experience in battle. Many deserted. Chapter 10, Section 5 The War of 1812 •What successes did Americans have in the West? The War of 1812 in the West Chapter 10, Section 5 The invasion of Canada General William Hull led American troops into Canada. The Canadians made it look like their forces were large and included experienced British troops. The Americans retreated. Battle of Lake Erie Captain Oliver Hazard Perry designed and built his own ships. Perry’s fleet met a British fleet on Lake Erie. The Americans won the battle. Battle of the Thames General William Henry Harrison’s troops pursued a British force and their ally Tecumseh toward Canada. The Americans won a victory at the Battle of the Thames. Tecumseh died in the battle. Battle of Horseshoe Bend Andrew Jackson and American troops defeated the Creeks. The Americans won the battle. Chapter 10, Section 5 The War of 1812 •How did the final battles of the war progress? The Final Battles of the War of 1812 Chapter 10, Section 5 Bladensburg, Maryland British troops marching toward Washington, D.C., met American troops about 30 miles from Washington. The British scattered the Americans. Washington, D.C. The British set fire to the White House and other buildings, then set off for Baltimore. Baltimore, Maryland The British bombarded the harbor but were unable to take Fort McHenry. They withdrew. Francis Scott Key wrote “The StarSpangled Banner” about this battle. New Orleans The British attacked the city. Andrew Jackson led a strong force of frontiersmen and Choctaw Indians. Citizens of New Orleans, including African Americans, joined his forces. British losses were heavy. The American forces won a victory at the Battle of New Orleans. Chapter 10, Section 5 Chapter 10, Section 5 The War of 1812 •Why did New Englanders protest against the war? New Englanders Protest the War Chapter 10, Section 5 • The British blockade hurt New England’s sea trade. • New Englanders feared that the United States might win land in Florida and Canada, which would become new states. That would make the South and the West more influential than New England. • Delegates from New England states met at the Hartford Convention, in Hartford, Connecticut. They threatened to leave the Union if the war continued. • While the Hartford Convention was still meeting, news of a peace treaty arrived. • The Treaty of Ghent ended the War of 1812. It was named after the city in Belgium where it was signed. In the treaty, Britain and the United States agreed to go back to the way things were before the war. Chapter 10, Section 5 Section 5 Assessment When the British reached Washington, D.C. in 1814, they a) b) c) d) met in person with James Madison. set fire to the White House and other buildings. skirmished with American troops and then retreated. found documents that helped them win the war. The treaty that ended the War of 1812 a) gave Britain use of the Port of New Orleans. b) said Britain had to stop forcing American sailors into service. c) returned conditions between Britain and the United States to the way they had been before the war. d) made Britain recognize American neutrality. Chapter 10, Section 5 Section 5 Assessment When the British reached Washington, D.C. in 1814, they a) b) c) d) met in person with James Madison. set fire to the White House and other buildings. skirmished with American troops and then retreated. found documents that helped them win the war. The treaty that ended the War of 1812 a) gave Britain use of the Port of New Orleans. b) said Britain had to stop forcing American sailors into service. c) returned conditions between Britain and the United States to the way they had been before the war. d) made Britain recognize American neutrality.