* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap 25 – Excretory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
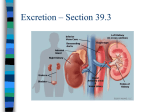
Chapter 25 Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko All organisms must EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT CO2 eliminate waste O2 respiratory system Food Mouth products!! Eliminates CO2 ANIMAL digestive system Digestive eliminates system solid wastes Nutrients and excess H+. Respiratory system Interstitial fluid Heart Circulatory system Body cells Urinary system Intestine Anus Unabsorbed matter (feces) Metabolic waste products (urine) Functions of the Excretory System -- Maintains salt/water balance -- Eliminates metabolic wastes, drugs, toxins -- Indirect regulation of blood pressure and pH Osmoregulation = The Balance of water and solute levels in body fluids. Osmoconformers (marine invertebrates) – have body fluids with a [solute] = to [seawater] Osmoregulators (land animals, freshwater animals, saltwater fish) – have body fluids with [solute] that differ from environment – must actively regulate water movement Osmoregulation strategy depends on animal’s habitat!! © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Osmoregulation = Balance of solutes and water Freshwater fish Passive water gain through gills Salts actively Taken up by gills – gain water by osmosis (mainly through gills), – take in salt by active transport through their gills and in food – excrete excess water in dilute urine. Excretion of dilute urine from kidneys FRESH WATER (hypotonic environment) Osmoregulation strategy depends on animal’s habitat!! © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Osmoregulation = Balance of solutes and water Saltwater fish – lose water by osmosis from the gills and body surface, – drink seawater, and – use their gills and kidneys to excrete excess salt. Passive loss of water through gills Drinks seawater SALT WATER (hypertonic environment) Salts actively excreted by gills © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Excretion of concentrated urine Osmoregulation = Balance of solutes and water Land animals – risk of dehydration – lose water by evaporation and waste disposal – gain water by drinking and eating – conserve water by – efficient kidneys. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Disposal of Nitrogenous and metabolic wastes Metabolism produces toxic by-products. Nitrogenous wastes = breakdown products of proteins and nucleic acids. Animals dispose of nitrogenous wastes in different ways. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. The Human Urinary System The urinary system – forms and excretes urine and – regulates water and solutes in body fluids. Nephrons = functional units of kidneys –extract a fluid filtrate from the blood, and –refine the filtrate to produce urine. Animation: Nephron Introduction DETAILED STRUCTURE OF A NEPHRON Processing of Urine in 4 Stages Filtration – Blood enters kidney via renal artery --> various capillary beds (GLOMERULUS) – Each capillary bed wraps around nephron – Blood filtered through capillary bed by force of blood pressure – Proteins and RBCs remain in blood – Filtrate contains: Water, salts, glucose, amino acids, urea collected by Bowman’s capsule From Bowman’s Filtration renal capsule artery Nephron tubule H2O, other small molecules Reabsorption Secretion Excretion Urine Interstitial fluid Capillary © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. To renal vein Processing of Urine in 4 Stages Reabsorption – proximal and distal tubules return – Glucose, salt, and amino acids to blood by active transport – Water follows by osmosis Secretion – Substances in the blood are transported into the urine by active transport at PCT and DCT Excretion From Bowman’s Filtration renal capsule artery Nephron tubule H2O, other small molecules Reabsorption Secretion Excretion Urine Interstitial fluid Capillary © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. To renal vein Processing of Urine Glomerulus – Filters Urine by force of blood pressure – Filtrate captured by Bowman’s Capsule PCT and DCT – Active transport or secretion of substances to and from blood Loop of Henle – Concentration of urine and reabsorption of water – Active transport of Na out – Water follows by osmosis Collecting Duct – Further concentration of urine and reabsorption of water – Responds to ADH © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. PROXIMAL TUBULE NaCl Nutrients HCO3– H2O K+ H+ NH3 CORTEX DESCENDING LIMB OF LOOP OF HENLE Filtrate Contains: H2O Salts (NaCl and others) HCO3– H+ Urea Glucose; amino acids Some drugs DISTAL TUBULE H2O NaCl K+ H+ ASCENDING LIMB OF LOOP OF HENLE NaCl H2O OUTER MEDULLA NaCl COLLECTING DUCT Key Active transport Passive transport HCO3– Urea NaCl INNER MEDULLA H2O Animation: Bowman’s Capsule and Proximal Tubule Animation: Collecting Duct Animation: Effect of ADH Animation: Loop of Henle and Distal Tubule Figure 25.8_1 Bowman’s capsule Proximal tubule Nutrients H2O NaCl HCO3 Blood Cortex Filtrate composition H2O Salts (NaCl and others) HCO3 H Urea Glucose Amino acids Some drugs Some H drugs and poisons Medulla Reabsorption Secretion Filtrate movement Figure 25.8_2 Proximal tubule Nutrients H2O NaCl HCO3 Cortex 1 Some H drugs and poisons Distal tubule H2O NaCl HCO3 K H 3 Collecting duct Medulla Interstitial Loop of fluid Henle 2 NaCl NaCl H2O NaCl Urea H2O Reabsorption Secretion Filtrate movement Urine (to renal pelvis) Hormonal Control of Kidneys Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) – Produced by pituitary gland Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus Thirst Hypothalamus Drinking reduces blood osmolarity to set point ADH Pituitary gland – Released in response to decreased blood volume – Regulates the permeability of collecting duct to water – High ADH; nephrons reabsorb water from the urine, returning it to the blood H2O reabsorption helps prevent further osmolarity increase STIMULUS Increase in solute concentration In blood; decrease blood Collecting duct Volume; Decreased blood pressure – Leads to increased blood volume and blood pressure Homeostasis: Proper blood pressure Solute levels © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Kidneys and Acid-Base Balance pH is regulated by – Secretion of acidic and basic organic compounds – reabsorption of HCO3– and – secretion of H+. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc.