* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Excretory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
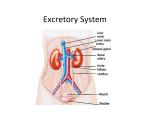
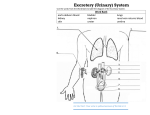
Excretory System Excretory System Function: The excretory system eliminates nonsolid wastes from the body. • Nonsolid wastes are eliminated through lungs, skin, and kidneys. • Lungs exhale carbon dioxide and water vapor. • Sweat glands in skin release excess water and salts. skin lungs kidneys ureters urethra urinary bladder Excretory System • The ureters are tubes that carry urine from the pelvis of the kidneys to the urinary bladder. skin lungs • The urinary bladder temporarily stores urine until it is released from the body. • The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. • The outer end of the urethra is controlled by a circular muscle called a sphincter. kidneys ureters urethra urinary bladde Excretory System Function of the Kidney • The principal function of the kidney is to filter blood in order to remove cellular waste products from the body. • At any given time, 20 % of blood is in the kidneys. Humans can function with one kidney. • If one ceases to work, the other increases in size to handle the workload. Excretory System The kidneys help to maintain homeostasis by cortex filtering the blood. The kidneys are fist-sized, bean shaped structures. – two layers: medulla and cortex – filtering units called nephrons – renal artery and renal vein medulla renal artery renal vein ureter (to bladder) Excretory System The kidney can also excrete other waste products, such as : • 1) urea a nitrogenous waste produced in the liver from the breakdown of protein. It is the main component of urine • 2) uric acid usually produced from breakdown of DNA or RNA • 3) creatinine waste product of muscle action. Excretory System Kidneys have three basic functions in maintaining homeostasis. –remove waste from blood –help to maintain electrolyte, pH, and fluid balances –release key hormones Excretory System Nephrons clean the blood and produce urine. • Nephrons are the filtering units in the kidneys. • They clean and rebalance the blood to produce urine. to body • There approximately 1 loop of Henle million nephrons in each kidney from body to body from other nephrons Excretory System • Nephrons clean the blood in a three-step process. • The first step is filtration of the blood. • Glomerulus: Network of capillaries Glomerulus 1 FILTRATION Water, electrolytes, amino acids, glucose, urea, and other small molecules diffuse out of the blood, creating the filtrate. • Bowman’s Capsule: Encases the glomerulus Bowman’s capsule • The body’s entire volume of blood is filtered every 45 min Excretory System • The first step is filtration of the blood. • The second step is reabsorption of materials. from body to body loop of Henle 2 REABSORPTION As the filtrate enters the rest of the tubule, most of the materials are reabsorbed into the blood. Materials collecting not reabsorbed make duct up the urine, which flows into the loop of Henle. from other nephrons Excretory System • The first step is filtration of the blood. • The second step is reabsorption of materials. • The third step is excretion of materials. from body 3 collecting duct to body loop of Henle from other nephrons EXCRETION In the loop of Henle, water can be reabsorbed one final time to reduce the volume of urine. The remaining urine flows into a collecting duct that leads to the ureter. Excretory System Injury and disease can damage kidney functions. • A kidney transplant can replaced damaged kidney. – recipient and donor tissue must match – drugs prevent tissue rejection The daughter and son in this photo donated a kidney and liver tissue to their mother. Excretory System • Dialysis can be used to filter and clean the blood. Excretory System Disorders of the Excretory System UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) • Is a very common disorder. If the bladder has become infected, it is known as cystitis. If the urethra is infected., it is called urethritis. • Symptoms include painful urination burning sensation), frequent urination (even if no urine present) and bloody or brown urine. • This can lead to chills, fever, nausea, vomiting and upper abdomen tenderness. Excretory System NOTE : • If left untreated, all UTI’s can lead to permanent kidney damage and possible kidney failure. • The general treatment is by antibiotics. • Also, a person should drink lots of water. Excretory System Kidney Infections • Result when an infection reaches the kidneys and becomes known as pyelonephritis. • Common causes can be infection from elsewhere in the body or obstruction of the prostate gland (usually in older men). • For children, infection can be caused by the tube that drains urine from the kidneys and the bladder. Excretory System Kidney Stones • Crystals formed from minerals in urine. • They can be found in the kidney, ureter or bladder. • 80% of those stricken are males. • The most common crystals are: – Calcium Oxalates – Uric acid Excretory System Kidney Stones (cont) • Symptoms include severe back or abdomen pain, blood in the urine, nausea and vomiting. • Diagnosis involves a complete medical examination, including X-rays. • Treatment may vary from letting the stones pass through the urinary tract to ultrasound shock to disintegrate the stones to a small size that can be passed through the urinary tract. • Really large stones require surgery for removal. Excretory System Kidney Stones (cont) • Ways to avoid kidney stones: • Increase liquid intake • Limit sodium intake • Limit animal protein • Limit foods high in oxalate (spinach, strawberries, nuts, dark chocolate, brewed tea)