* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science – Visual Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
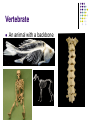
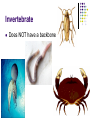
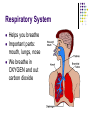
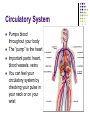
Science – Visual Study Guide Chapter 4 – Lessons 1-4 Mr. Rowe & Ms. Hallock VERTEBRATES AND INVERTEBRATES Vertebrate An animal with a backbone Invertebrate Does NOT have a backbone Vertebrates – 5 Groups Mammals Hair on most of its body Females feed milk to their young Vertebrates – 5 Groups Fish Covered with scales Breathe with gills Vertebrates – 5 Groups Reptiles Has dry scales or tough plates Slithers across ground or crawls on short legs Vertebrates – 5 Groups Amphibians Moist skin without scales, hair, or feathers Breathes with lungs as an adult, gills when young Lives in water AND on land Vertebrates – 5 Groups Birds Covered with feathers Has wings, scaly legs and a beak Females lay eggs Some fly – not ALL! Invertebrates Here are some examples: be able to name at least 3 animals without backbones Invertebrates Arthropods are the biggest group! They include: Insects Arachnids (spiders) Crustaceans (crabs & shrimp) Centipedes & Millipedes There are more INVERTEBRATES in the world – about 95% of all animals do NOT have backbones! SYMMETRY MOST animals have SYMMETRY! That means that the parts of their bodies match up with other parts around a midpoint or a line. Examples: ENDOSKELETON AND EXOSKELETON EXOSKELETON Shell on the OUTSIDE of an animal’s body Protects them from getting SQUISHED! Keeps them from drying out Think: Knight in shining armor! ENDOSKELETON Think ENDO = INDOOR Skeleton (bones) on the INSIDE of their bodies Helps them stand up and walk WARM AND COLD BLOODED ANIMALS WARM BLOODED Some animals are warm-blooded Mammals Birds That means their body temperature stays the same all the time. They get energy from food they eat. COLD BLOODED Some animals are cold blooded Fish Reptiles Amphibians This means they need the SUN to keep them warm. They are whatever temperature they are in their environment. WHAT ALL ANIMALS MUST DO… In order to be called an animal, an organism must do 6 things: Be made up of many CELLS In order to be called an animal, an organism must: MOVE on their own In order to be called an animal, an organism must: GROW and DEVELOP In order to be called an animal, an organism must: REPRODUCE (have babies) In order to be called an animal, an organism must: React to changes in their environment Birds fly south for the winter Bears hibernate in the winter In order to be called an animal, an organism must: Get energy by eating food In order to be called an animal, an organism must: Get rid of wastes IMPORTANT FACTS Humans are VERTEBRATES! Humans have an ENDOSKELETON! Humans are WARM-BLOODED! Humans constant body temperature is 98.6! LIFE CYCLE Life Cycle The stages of growth and change that make up an animal’s life Birth Growing Having babies Death LIFE SPAN Life Span How long an animal can usually live in the wild Example: a moth lives about a week Snake can live 20 years Parrot can live 80 years METAMORPHOSIS Metamorphosis Frogs and many insects like butterflies go through it It’s a cycle where an animal looks different at each stage BODY SYSTEMS Respiratory System Helps you breathe Important parts: mouth, lungs, nose We breathe in OXYGEN and out carbon dioxide Circulatory System Pumps blood throughout your body The “pump” is the heart Important parts: heart, blood vessels, veins You can feel your circulatory system by checking your pulse in your neck or on your wrist Skeletal System Made up of our BONES Helps us to stand, stay upright, and move around We have 206 bones in our bodies! Muscular System Made up of muscles. We have 640 muscles in our bodies! They push and pull on bones to help us move. Nervous System Made up of our BRAIN, SPINAL CORD, and nerves Also our 5 senses (how we take in information) Messages about what we feel travel from our bodies to our brains and our brain sends back messages about how to react (move away if something is hot) Digestive System IMPORTANT PARTS: mouth, throat, stomach, small and large intestine Helps us to break down food after we eat and use the vitamins in it to keep us healthy