* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download vectored
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
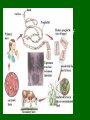
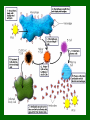
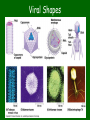
Pathogens & Immunity • Text Chapter 6- 7- 8 What is a pathogen • Anything that causes harm to your body – Bacteria, virus, protista and fungi are all kingdoms that contain common pathogenic organisms – Animals (mosquitos, tapeworms) and plants (poison ivy, poison oak) are larger pathogenic organisms Pathogenic Fungus Animal pathogens Roundworms, heartworm & tapeworms Transmission of pathogens • Contaminated food, water • Bodily fluids via unprotected sex, sharing of needles during drug use • Mother to unborn child • • Airborne – Attach to dust or water droplets Vectors • Mosquitoes – West Nile Virus, Malaria • Houseflies, tse tse fly (African Sleeping Sickness) • Ticks – Lyme disease (bacteria) • Animals - Rabies (virus) How do they work? • Transmitted or vectored by a number of ways… • Propagated • Spread person to person • Common source • All get sick from one source point, i.e. contaminated water How to stop a pathogen… • Prevent entry to body – Good hygiene, insect repellent, boil water, throughly cook food, do not engage in risky behaviors • Promote a rapid immune response – Healthy lifestyle – diet, sleep, exercise • Medicines – Anitibiotics, antivirals, fungicides • Vaccines – Teach your immune system to recognize invaders The immune response • Antigen – nametags for all cells and cell-like organisms • Host – the organism or cell that is under attack; has a particular receptor site for antigens • Antibody – a protein made by the body to prevent attachment of pathogen to host cell vaccine • A little bit of virus (weakened or dead) that “teaches” your body to make antibodies • Your body remembers how to fight pathogens by “memory B cells” Viruses T4 Bacteriophage • NO! Is it Alive? – Do not perform the 6 characteristics of life • 1. cells • 2. organization • 3. energy use • 4. homeostasis • 5. growth & development • 6. reproduction Influenza Virus What is a Virus? • Obligate intracellular parasite – Piece of DNA or RNA covered with a capsid • Protein “coat” Classification of Viruses • No Kingdom! • classify based on the host they invade – Plants, animals, bacteria • Genetic material – DNA or RNA – RNA viruses are called retrovirus • morphology Viral Shapes How do Viruses work? Must have host Lytic or virulent cycle • 1. Finds specific host – antigen “name tags” matches a host “docking station” 2. Injects its nucleic acid into host cell 3. Host cell becomes a viral “factory” to make new viruses 4. Host cell bursts releases viruses, kills host Lysogenic or Temperate Cycle • Some viruses enter host and become dormant – Inactive • Can become activated by another virus – Example – cold sore viruses made active by common cold Beneficial Virus?! • Control of other diseases • Useful in Genetic Engineering as a vector of new DNA – Gene therapy to cure genetic disorders – Ie. Cystic fibrosis Effects of Viruses • Harmful pathogenic HIV – AIDS Pandemic • Human Immunodeficiency Virus – Causes Auto Immune Disorder Syndrome (AIDS) – Spread through blood, semen, vaginal fluid, and breast milk – Attacks immune system – Helper T cells, which controls the rest of your immune system Spread of HIV 25 million dead to date Control of HIV • Education! • Protection – Vaccines – Interferon • Keep it dormant – control trauma, stress • Boost immune system