* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Freedmen's Colony of Roanoke Island wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Forty acres and a mule wikipedia , lookup
Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
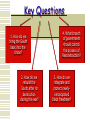
Chapter 8 The Reconstruction Era 1865-1877 Key Questions 1. How do we bring the South back into the Union? 2. How do we rebuild the South after its destruction during the war? 4. What branch of government should control the process of Reconstruction? 3. How do we integrate and protect newlyemancipated black freedmen? Reconstruction The Federal government had to figure out how the 11 states would rejoin the Union, rebuild the southern economy, and promote the rights of former slaves. The South’s Economy After the War About ¼ of southern white men between the ages of 20 and 40 died in the war. 3 million newly freed slaves were now without homes and jobs. The land was utterly destroyed. “Forty Acres and a Mule”? Ten Percent Plan In 1863, Lincoln issues the proclamation of amnesty and reconstruction. (10% Plan)) It said that when a 10% of the state’s voters took the loyalty oath, the state could set up a new government. If the state’s constitution abolished slavery and gave African Americans an education, then the state would regain representation in Congress. Lincoln also wanted to pardon former confederates and give them compensation for lost property. He did not require a guarantee for social/political equality for African Americans. Radical Republicans such as Thaddeus Stevens and Charles Sumner were against the plan because they thought African Americans should have full citizenship (voting), severe punishments for the South and they supported Williams Sherman’s plan to take the South’s land and give it to freed men. The Wade-Davis Bill Congress rejected the 10% plan but passed the Wade-Davis Bill. The bill stated that a majority of state’s prewar voters swear allegiance and guarantee African American equality before restoration could begin. Lincoln pocket vetoed this by withholding his signature beyond the 10 day deadline. Freedmen’s Bureau (1865) Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands. Many former northern abolitionists risked their lives to help southern freedmen. Called “carpetbaggers” by white southern Democrats. Carpetbaggers: Term coined by Southern Whites to describe Northern businessmen and politicians who came to the South after the Civil War to work on Reconstruction projects or invest in Southern infrastructure. Freedmen’s Bureau Seen Through Southern Eyes Plenty to eat and nothing to do. Freedmen’s Bureau Primitive Welfare Agency. Provides food, clothing, medical care, and education to both freedmen and white refugees. Union General Oliver O. Howard headed the bureau. He later founded Howard University In D.C. Taught an estimated 200,000 blacks how to read. Freedmen’s Bureau School Freedmen’s Bureau AKA – The Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands. Goal was to provide food, clothing, healthcare and education to black and white refugees. Helped reunite families, get fair working contracts Andrew Johnson Assumed the presidency when Lincoln was assassinated. He gave pardons and land to anyone who pledged allegiance and the states needed to accept the 13th and have a state constitution that got rid of slavery. He was a supporter of state’s rights but not of African American suffrage or rights He wanted “Government for white men” Black Codes! Black Codes – Laws that sought to limit the rights of African Americans and keep them as landless workers. They required that they work in only a few occupations such as servants or farm laborers. The vagrancy laws stipulated that if blacks weren’t working they could be arrested and sent to work as prison labor. Congress was mad at this and tried to pass a bill that would allow the Freedman’s Bureau the right to punish the S. if they didn’t give blacks rights but Johnson vetoed it. Civil Rights act of 1866 – Federal government would be able to guarantee civil rights over state laws…Johnson vetoed this as well but Congress overturned the veto. Congressional/Radical Reconstruction Radicals and moderates passed the 14thAmendment – Guaranteed citizenship to African American’s and states can’t pass laws that take away citizens rights. Any state that refused to let blacks vote might lose seats in the House by black pop. Also, leading confederate officials couldn’t hold state or federal office. Military Reconstruction Act 1867 Johnson vetoed this also but it was overturned. Divided the 10 states that hadn’t been readmitted into 5 military districts governed by former Union generals . Map on page 275 These states had to write a constitution that allowed blacks to vote and accept the 14th Amendment. Impeach Johnson Congress thought Johnson was abusing his power so they passed the Tenure of Office Act which said the president needed Senate approval to remove people from office. He tried to fire Radical Republican...Edwin Stanton...and the House impeached (remove) him for his actions. The Senate let him off, by one vote. In the Election of 1868, (R) Ulysses S. Grant won th 15 amendment Passed in 1869 and ratified in 1870 You can’t deny voting rights to any male based on race, color or pervious condition of servitude (slavery). Excludes Women of Course! Republican Governments By 1870, all of the Southern states had rejoined the Union. Republicans dominated the South. Blacks began serving in politics. Both MS and SC had a black Speaker of the House. Some served in the U.S. Congress. Some Southerners were not eligible to vote because they did not take the oath of allegiance. Yankee Go Home Scalawags: Southern white men who had been denied involvement in southern governments before the Civil War, but now joined the Republican Party. They teamed up with northern whites and blacks who came to the South looking for prosperity. Southerners called them “Carpetbaggers” because they carried carpet suitcases. Jim Crow Era Begins Women worked in medical facilities, orphanages, and shaped the public school system. Got the public school system up and running but it was expensive because of segregation (2 of everything)!! Tax supported system Government Business as Usual Besides illiteracy, the South (and other parts of the nation) were experiencing corruption in politics. They would lend money to Rail Roads to get them built and sometimes the loans were stolen or mishandled. Some of the black politicians got blamed (even though it wasn’t their fault) Reconstruction Gains Blacks started utilizing the Freedmen’s Bureau schools and by 1866, 150,000 attended. Also, black colleges were set up. Blacks found comfort in churches which were set up all across the South. They b/c school site, employment agencies, community center and political rallying points. Southern Economy - Land Post Civil War: 90% of the land was owned by 50% of the people. After the war there were a lot of people looking for land. 3 choices – 1) Sharecropping – A landowner gave a sharecropper a place to live, seeds, tools in return for a share of the crop and he told them what to plant…land owner got supplies on credit from a supplier 2) Sharetenancy – farm worker chose what crop to plant and bought his own supplies 3) Tenant Farming – The tenant paid the owner rent, managed his own crop and chose where to live. Rise of the KKK 1. 2. 3. 4. Some Southerners resented that blacks began to gain rights. The Ku Klux Klan was formed in 1866 as an organization to terrorize black and white sympathizers, carpetbaggers. They tried to prevent people from going to the polls… Grandfather Clause White Primaries Poll Taxes Literacy Tests In response, the government passed the Enforcement Acts/KKK acts which made it a federal offense to interfere with the right to vote. Many members were indicted. Corruption Grant gave high level jobs to his friends who then stole. His VP, Schuyler Cofax was implicated in stealing from Union Pacific RR. Boss Tweed was stealing millions. “The Tweed Ring.” Grant still won in the Election of ‘72 but confidence in political officials was going down. Also in 1873 a big bank failed due to all the loans to Railroad companies…now the North’s economy was in trouble as well. Reconstruction’s End 1871 troops were with withdrawn from the South 1872 – freedmen’s bureau was shut down. 1874 – Radical Republican Sumner died Southern whites began to gain back more power by uniting Democrats and Republicans to exclude blacks…they were called the “redeemers” Election of 1876 (R) Rutherford B Hayes v. (D) Samuel Tilden Tilden got 51% of the vote and carried all Southern states but Republicans claimed there were miscounts in 3 southern states where the Republicans controlled the counts. When they recounted they found enough mistakes to give Hayes the win. Southern D. were mad and Congress stepped in Compromise of 1877 – Hayes wins: 1)troops out of the S. 2)southerner gets cabinet position. 3)subsidies ($) to build RR and ports in South. The Whiskey Ring (R) were caught in 1875 for stealing millions of $ in tax revenue on liquor. 110 convictions came out of it and $3 mil was recovered. This led to the downfall of reconstruction