* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to PEO
Racial stereotyping in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Aversive racism wikipedia , lookup
Sexual racism wikipedia , lookup
Employment discrimination wikipedia , lookup
International Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Racial Discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Employment Non-Discrimination Act wikipedia , lookup
Mentalism (discrimination) wikipedia , lookup
Racism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Employment discrimination law in the United States wikipedia , lookup
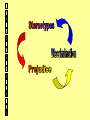
This slideshow has been designed for use by students on Introductory level and Intermediate 2 level Care courses. It will familiarise users with issues relevant to the ideas and practice of promoting equal opportunities. Objectives of this package This package provides an introduction to some of the issues associated with promoting an equality of opportunity. On completion, you will have an understanding of the meaning of prejudice, stereotyping and discrimination and how they relate to one another. You will be aware of ways in which people may be disadvantaged by discrimination and also of how it may affect them. You should also have an awareness of the main points of the key legislation in this area. Promoting Equal Opportunities “Care workers are generally concerned with trying to provide the resources and services that individuals need to improve the quality of their day-to-day lives. The principles and values of care provision show us that everyone should be valued equally and treated equally.” But are people all treated equally and fairly? Click here for Activity 1 Talking In The Street Copyright: Getty Images Racial Unrest Area Copyright: Getty Images Inflammatory Graffiti 1968 Copyright: Getty Images In the previous exercises, you have been looking at the idea of people not being “treated equally”. Another way of talking about that kind of treatment is to talk about “discrimination”. You will probably be familiar with this term and you may even use it yourself. But what exactly is “discrimination”? Barnardo’s Boys Copyright: Getty Images Malnutrition Copyright: Getty Images Click here to look at a definition of “discrimination” Left on Crutches Copyright: Getty Images Where does discrimination come from? From the definition of discrimination we have looked at, we can see that it is about how we treat people. That is to say, it is about how we behave; it’s about what we do. Inflammatory Graffiti 1968 Copyright: Getty Images Follow this link for an activity to identify things that people do that could be considered to cause discrimination. Racial Unrest Area Copyright: Getty Images “Why do people discriminate against others?” (1) From the list of examples that you made in the last activity, you will have seen that not only is discrimination fairly common but it can be done by anyone and not only by people that might be thought of as “bad” or “evil”. Follow this link for a study group exercise that looks at why this might be. Malnutrition Copyright: Getty Images “Why do people discriminate against others?” (2) Look back at your answers in the previous activity. Generally, what we can see is that people will behave in a discriminatory way because of what they believe about others and because of their attitudes towards them. Where these beliefs and attitudes tend to be negative, people are more likley to behave in a negative way – that is to say, they are more likley to discriminate against the group that they have negative beliefs or attitudes about. Beliefs, attitudes and behaviour. Our attitudes, our beliefs and our behaviour are all closely linked and related, as the diagram shows: When people have a set of negative beliefs about other individuals and the groups that they belong to, we called those beliefs “stereotypes”. When they have a set of negative attitudes about these individuals and groups, which are formed when they “prejudge” them, forming an opinion of them before they even know them, we tend to call these attitudes “prejudice”. In the same way that we have already seen that beliefs, attitudes and behaviours are all linked, we can now see that stereotyping, prejudice and discrimination are all linked in the same way. “Why do people discriminate against others?” (2) Look back at your answers in the previous activity. Generally, what we can see is that people will behave in a discriminatory way because of what they believe about others and because of their attitudes towards them. Where these beliefs and attitudes tend to be negative, people are more likeley to behave in a negative way – that is to say, they are more likeley to discriminate against the group that they have negative beliefs or attitudes about. Legislation One of the main ways in which we can tackle discrimination is by making it illegal. In the UK, we currently have a number of pieces of legislation (laws) which do exactly this. The purpose of these laws is to try to make sure that everyone is treated equally, that everyone should have the same opportunities and not be disadvantaged because of their gender, skin colour, disability or any other factor. The main pieces of legislation that make discrimination illegal are as follows: • The Race Relations Act 1976 • The Sex Discrimination Act 1975 • The Disability Discrimination Act 1995 Read each of these short guides and then try the legislation Asylum Seekers and Refugees Follow this link to read more about the “Myths of Asylum Seeking” Once you have read that report, try this