* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download VIRUSES - Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
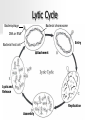
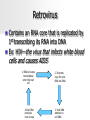
VIRUSES Viruses Are Not Cells! There are several structural and functional differences between cells and viruses The structural differences include: – No nucleus – No cell membrane – No organelles The functional differences include: – – – – Do Do Do Do not not not not grow respire develop reproduce Viral Structure Viruses are made up of 2 parts: – Capsid—a protein coat which enables the virus to bind to a cell – Nucleic acid—either DNA or RNA Some viruses have an additional protective coating called an envelope Replication vs. Reproduction Viruses do not reproduce Viruses replicate Reproduction requires cell division and replication does not A virus requires a host for it to replicate A host is a living cell that provides all the materials a virus needs to replicate Classification of Viruses Shape: allows viruses to attach to only a few kinds of cells; like two pieces of a jigsaw puzzle – Filovirus—has no distinct shape – Polyhedral virus—multifaceted geometric shape – Binal virus—has a polyhedral capsid and a helical tail – Helical virus—tightly coiled DNA or RNA inside a long, narrow capsid Classification of Viruses (cont.) Host: – Plant virus – Animal virus – Bacterial virus—these are also called bacteriophages Lytic Cycle Bacteriophage Bacterial chromosome DNA or RNA Entry Bacterial host cell Attachment Lysis and Release Replication Assembly Lysogenic Cycle Entry: Lysis & Release: Assembly: Not pictured Prophage Replication: Retrovirus Contains an RNA core that is replicated by 1st transcribing its RNA into DNA Ex: HIV—the virus that infects white blood cells and causes AIDS 1. RNA & reverse transcriptase enter the host cell 4.Viral DNA produces new viruses 2. Enzymes copy the viral RNA into DNA 3. Viral DNA attaches to cell DNA Nonviral Particles Viroid: – No capsid – Contains RNA – Cause plant diseases Prion: – Protein molecule with no RNA or DNA – Cause animal diseases (i.e. mad cow disease)