* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AUDITORY BRAINSTEM EVOKED RESPONSE (ABR)
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Auditory processing disorder wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
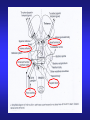
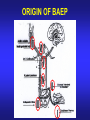
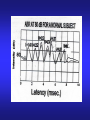
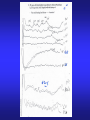
AUDITORY BRAINSTEM EVOKED RESPONSE (ABR) DR. Fawzia AlRouq PHD. (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) What is evoked potential? Electrical potentials that occur in the group of neuron in response to stimulation of a sense organ which can be recorded by surface electrodes is known as Evoked Potential. eg. SEP, ABR and VEP Introduction • Auditory brainstem response (ABR) is a neurologic test of auditory brainstem function in response to auditory (click) stimuli. • It’s a set of seven positive waves recorded during the first 10 seconds after a click stimuli. They are labeled as I - VII PHYSIOLOGY • Auditory brainstem response (ABR) typically uses a click stimulus that generates a response from the hair cells of the cochlea, the signal travels along the auditory pathway from the cochlear nuclear complex to the inferior colliculus in mid brain generates wave I to wave V. ORIGIN OF BAEP Origin of each wave Wave Origin I Cochlear nerve II Dorsal & Ventral cochlear nucleus III Superior olivary complex IV Nucleus of lateral lemniscus V Inferior colliculus VI Medial geniculate body VII Auditory radiation(cortex Objectives • At the end of this session the students should be able to: Acquire the principles involved in the test. Identify & describe the genesis of the brainstem potentials in order to use them to study brainstem conductions in health & disease. Construct evoked response audiograms to identify conductive & sensorineural hearing loss. Requirements • • • • • Clinical averager Ear phone Silver cup electrodes Electrode jelly Patient leads Electrode placement (Montage) • Cz (at vertex) (recording electrode) • Ipsilateral ear lobule or mastoid process (reference electrode). • Contra lateral ear lobule (act as a ground) Procedure • Subject lying supine with a pillow under his head. • Room should be quite. • Clean the scalp & apply electrode. • Check the impedance. • Apply the ear phone (red for the right ear & blue for the left ear) • Select the ear in the stimulator & apply masking to the opposite ear. Contd.. • • • • • Stimulation rate : 11/sec. Repetition : 2000 Find out the threshold of hearing. ABR should be done at around 80dB. Start averaging process & continue until the required repetition accomplished. • Calculate the peak – interpeak latencies for the ABR waves. Normal values • Peak latency of a wave = less than the next higher no. wave • Or just add 1 to that wave, latency will be less than that. eg. Latency of wave 1 is less than 2. Wave Latency I <2mSec. II <3 m.sec III <4 m.sec IV <5 m.sec V <6 m.sec VI <7 m.sec Identification of waves • Identify wave V which is the most persitent wave. It comes as IV-V complex, and wave V comes to the base line. • Go in reverse order, wave IV, III, II, & I. • Also observe their latencies, eg. latency of wave I will be less than 2mSec. Calculation & Analysis • Write down the absolute peak latencies for the waves • Find out the interpeak latencies of I – III, III – V and I – V. Interpretation • Wave I : small amplitude, delayed or absent may indicate cochlear lesion • Wave V : small amplitude, delayed or absent may indicate upper brainstem lesion • I – III inter-peak latency: prolongation may indicate lower brainstem lesion. • III – V inter-peak latency: prolongation may indicate upper brainstem lesion. • I – V inter-peak latency: prolongation may indicate whole brainstem lesion. Shortening of wave the interval with normal latency of wave V indicate cochlear involvement. APPLICATIONS • Identifying the hearing loss • Classification of type of deafness (conductive or sensorineural) Contd… • Identification of retro choclear patholgy Auditory brainstem response (ABR) audiometry is considered an effective screening tool in the evaluation of suspected retrocochlear pathology such as an acoustic neuroma or vestibular schwannoma. NEWBORN SCREENING • Several clinical trials have shown auditory brainstem evoked response (ABR) testing as an effective screening tool in the evaluation of hearing in newborns, with a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 9698%. IN SURGERY • Intraoperative monitoring • Auditory brainstem response (ABR), often used intraoperatively, provides early identification of changes in the neurophysiologic status of the peripheral and central nervous systems. This information is useful in the prevention of neurotologic dysfunction and the preservation of postoperative hearing loss. For many patients with tumors of CN VIII or the cerebellopontine angle, hearing may be diminished or completely lost postoperatively, even when the auditory nerve has been preserved anatomically. EVOKED RESPONSE AUDIOMETRY • The procedure of evoked response audiometry is same as that of ABR. • Here the evoked response is obtained with different intensities of click stimuli. • First start with a stimulus intensity of 80 dB. • Put the record in memory • Change the stimulus intensity to 60 dB. • Put the record in memory. Cont… • Continue the test with stimulus intensity of 40 dB, & 20 dB. • In all these tracings identify wave V and find out its latency at all intensities of stimuli. • Plot latency – intensity graph for wave V. Interpretation • Normal : There is a shaded area for the normal person. If your points fall in this area then the person is having normal hearing. • Conductive Deafness: the latency – intensity graph plotted will be above & parallel to the shaded area. • Sensorineural Deafness: the graph plotted will be irregular & not forming a curve. CASES