* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Hearing aid wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
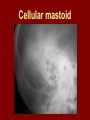
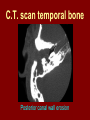
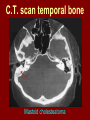
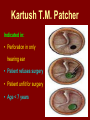
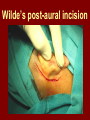
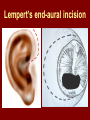
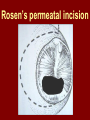
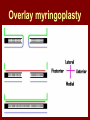
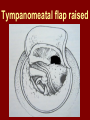
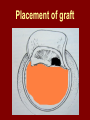
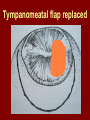
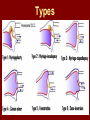
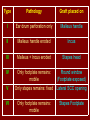
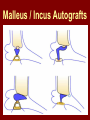
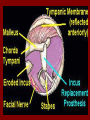
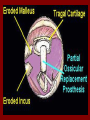
C.S.O.M.: Investigations & Treatment Dr. Vishal Sharma Investigations for T.T.D. • Examination under microscope • Ear discharge swab: for culture sensitivity • Pure tone audiometry • Patch test • X-ray mastoid: B/L 300 lateral oblique (Schuller) Done when cortical mastoidectomy is required in ear discharge refractory to antibiotics Uses of Audiometry • Presence of hearing loss • Degree of hearing loss • Type of hearing loss • Hearing of other ear • Record to compare hearing post-operatively • Medico legal purpose Patch Test Done when deafness = 40-50 dB • Do pure tone audiometry: for hearing threshold • Put Aluminum foil patch over T.M. perforation • Repeat pure tone audiometry: Hearing improved = ossicular chain intact & mobile Hearing same / worse = oss. chain broken or fixed Investigations for A.A.D. • Examination under microscope • Ear discharge swab: for culture sensitivity • Pure tone audiometry • X-ray mastoid: B/L 300 lateral oblique (Schuller) • CT scan: revision surgery, complications, children Uses of E.U.M. • Confirmation of otoscopy findings • Epithelial migration at perforation margin • Cholesteatoma & granulations • Adhesions & tympanosclerosis • Assesment of ossicular chain integrity • Collection of discharge for culture sensitivity Uses of X-ray mastoid 1. Position of dural & sinus plates: helps in surgery 2. Type of pneumatization: a. Cellular (80%): plenty of air cells b. Sclerotic (20%): small antrum, air cells absent c. Diploetic (<1%): bone marrow within few air cells 3. Cholesteatoma (cotton wool appearance) 4. Bone destruction: presence & extent 5. Mastoid cavity Dural & sinus plates Cellular mastoid Sclerotic mastoid Diploetic mastoid Attic bone erosion Causes for mastoid cavity • Cholesteatoma erosion • Mastoidectomy cavity • Tubercular mastoiditis • Coalescent mastoiditis • Malignancy • Eosinophilic granuloma • Mega-antrum • Large emissary vein C.T. scan temporal bone Posterior canal wall erosion C.T. scan temporal bone Mastoid cholesteatoma Treatment for Tubo-tympanic Disease Non-surgical Treatment • Precautions • Aural toilet • Antibiotics: Systemic & Topical • Antihistamines: Systemic & Topical • Nasal decongestant: Systemic & Topical • Treatment of respiratory infection & allergy • Tympanic membrane patcher Precautions • Encourage breast feeding with child’s head raised. Avoid bottle feeding. • Avoid forceful nose blowing • Plug E.A.C. with Vaseline smeared cotton while bathing & avoid swimming • Avoid putting oil & self-cleaning of E.A.C. Aural Toilet Done only for active stage – Dry mopping with cotton swab – Suction clearance: best method – Gentle irrigation (wet mopping) 1.5% acetic acid solution used T.I.D. Removes accumulated debris Acidic pH discourages bacterial growth Antibiotics Topical Antibiotics: Antibiotics: Ciprofloxacin, Gentamicin, Tobramycin Antibiotics + Steroid: for polyps, granulations Neosporin + Betamethasone / Hydrocortisone Oral Antibiotics: for severe infections Cefuroxime, Cefaclor, Cefpodoxime, Cefixime Antihistamines & Decongestants Antihistamines Systemic decongestants Chlorpheniramine Pseudoephedrine Cetirizine Phenylephrine Fexofenadine Topical decongestants Loratidine Oxymetazoline Levo-cetrizine Xylometazoline Azelastine (topical) Hypertonic saline Kartush T.M. Patcher Indicated in: • Perforation in only hearing ear • Patient refuses surgery • Patient unfit for surgery • Age < 7 years Surgical Treatment Indicated in inactive or quiescent stage • Myringoplasty • Tympanoplasty Indicated in active stage • Cortical Mastoidectomy • Aural polypectomy Methods to close perforation T.M. perforation < 2 mm Chemical cautery with silver nitrate Fat grafting Myringoplasty if these measures fail T.M. perforation > 2 mm Tympanic membrane patcher Myringoplasty Chemical cautery Approaches to middle ear Wilde’s post-aural incision Lempert’s end-aural incision Rosen’s permeatal incision Hearing Restoration Myringoplasty: • surgical closure of tympanic membrane perforation Ossiculoplasty: • surgical reconstruction of ossicular chain Tympanoplasty: • Surgical removal of disease + reconstruction of hearing mechanism without mastoid surgery Principles of hearing restoration • Intact tympanic membrane • Intact ossicular chain • Functioning receiving & relieving windows • Acoustic separation of these windows • Functioning Eustachian tube • Absence of sensori-neural hearing loss • Absence of active infection / allergy in middle ear cleft Myringoplasty Aims • Permanently stop ear discharge: dry, safe ear • Improve hearing: provided: 1. ossicles are intact + mobile; 2. absence of sensori-neural deafness • Prevention of: tympanosclerosis, adhesions, vertigo, S.N.H.L. (cochlear exposure to loud sound) • Wearing of hearing aid • Occupational: military, pilots • Recreation: swimming, diving Contraindications • Purulent ear discharge • Otitis externa • Respiratory allergy • Age < 7 yr (Eustachian tube not fully developed) • Only hearing ear • Cholesteatoma Methods Techniques: • Underlay: graft placed medial to fibrous annulus • Overlay: graft placed lateral to fibrous annulus Grafts used: • Temporalis fascia, Tragal perichondrium, Vein graft, Fascia lata, Dura mater Underlay myringoplasty Overlay myringoplasty Steps of underlay myringoplasty Tympanomeatal flap raised Placement of graft Tympanomeatal flap replaced Tympanomeatal flap replaced Why temporalis fascia? • Basal metabolic rate lowest (best survival rate) • Easily harvested by post-aural incision • Its an autograft, so no rejection • Same thickness as normal tympanic membrane • Large size graft can be harvested • Good resistance to infection Onlay Underlay Graft cholesteatoma No Blunting of anterior tympanomeatal angle Lateralization of graft No Delayed healing time (6 wk) 3-4 weeks No middle ear inspection Possible Difficult & takes more time Easier & quicker No Advantages of Local Anesthesia • Minimal bleeding • Hearing results can be tested on table • Facial palsy detected immediately • Labyrinthine stimulation detected immediately • No complications of General anesthesia Tympanoplasty Types Type Pathology Graft placed on I Ear drum perforation only Malleus handle II Malleus handle eroded Incus III Malleus + Incus eroded Stapes head IV V VI Only footplate remains: Round window mobile (Footplate exposed) Only stapes remains: fixed Lateral SCC opening Only footplate remains: mobile Stapes Footplate Malleus / Incus Autografts Thank You