* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
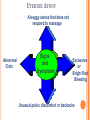
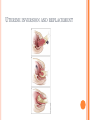
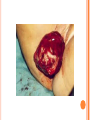
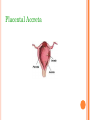
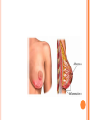
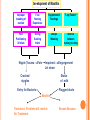
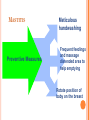
COMPLICATIONS OF POSTPARTUM POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Early Occurs when blood loss is greater than 500 ml. in the first 24 hours after a vaginal delivery or greater than 1000 ml after a cesarean birth *Normal blood loss is about 300 - 500 ml.) Late Hemorrhage that occurs after the first 24 hours MAIN CAUSES OF EARLY HEMORRHAGE ARE: Uterine Atony Lacerations Retained Placental Fragments Inversion of the Uterus Placenta Accreta Hematomas UTERINE ATONY **The myometrium fails to contract and the uterus fills with blood because of the lack of pressure on the open vessels of the placental site UTERINE ATONY PREDISPOSING FACTORS Prolonged labor Trauma due to Obstetrical Procedures Intrapartum Stimulation with Pitocin Overdistention of the Uterus Grandmultiparity Excessive use of Analgesia / Anesthesia UTERINE ATONY Most Key common cause of Hemorrhage to successful management is: PREVENTION! Nurse many times can predict which women are at risk for hemorrhaging. UTERINE ATONY A boggy uterus that does not respond to massage Abnormal Clots Signs and Symptoms Excessive or Bright Red Bleeding Unusual pelvic discomfort or backache NURSING CARE OF UTERINE ATONY Document Vaginal Bleeding Fundal massage / Bimanual Compression Assess Vital Signs (shock) Give medications--Pitocin, Methergine, Hemabate D & C, Hysterotomy/ectomy, Replace blood / fluids POST PARTUM HEMORRHAGE *LACERATIONS* PREDISPOSING FACTORS 1. Spontaneous or Precipitous delivery 2. Size, Presentation, and Position of baby 3. Contracted Pelvis 4. Vulvar, cervical, perineal, uretheral area and vaginal varices Signs and Symptoms 1. Bright red bleeding where there is a steady trickle of blood and the uterus remains firm. 2. Hypovolemia POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE *LACERATIONS* Treatment and Nursing Care 1. Meticulous inspection of the entire lower birth canal 2. Suture any bleeders 3. Vaginal pack-- nurse may remove and assess bleeding after removal 4. Blood replacement TEST YOURSELF ! You are assigned to Mrs. B. who delivered vaginally. As you do your post-partum assessment, you notice that she has a large amount of lochia rubra. What would be the first measure to determine if it is related to uterine atony or a laceration? RETAINED PLACENTAL FRAGMENTS This occurs when there is incomplete separation of the placenta and fragments of placental tissue retained. Signs Boggy , relaxed uterus Dark red bleeding Treatment D&C Administration of Oxytocins Administration of Prophylactic antibiotics HEMATOMA Major Symptom: PAIN- deep, severe, unrelieved, feelings of pressure Many times bleeding is concealed. Major symptom is rectal pain and tachycardia. Treatment: May have to be incised and drained. INVERSION OF THE UTERUS The uterus inverts or turns inside out after delivery. Complete inversion - a large red rounded mass protrudes from the vagina Incomplete inversion - uterus can not be seen, but Predisposing Factors: felt Traction applied on the cord before the placenta has separated. **Don’t pull on the cord unless the placenta has separated. Incorrect traction and pressure applied to the fundus, especially when the uterus is flaccid **Don’t use the fundus to “push the placenta out” UTERINE INVERSION AND REPLACEMENT TREATMENT AND NURSING CARE Replace the uterus--manually replace and pack uterus Combat shock, which is usually out of proportion to the blood loss Blood and Fluid replacement Give Oxytocin Initiate broad spectrum antibiotics May need to insert a Nasogastric tube to minimize a paralytic ileus Notify the Recovery Nurse what has occurred! Care must be taken when massaging Placental Accreta PLACENTA ACCRETA Signs: During the third stage of labor, the placenta does not want to separate. Attempts to remove the placenta in the usual manner are unsuccessful, and lacerations or perforation of the uterus may occur TREATMENT If it is only small portions that are attached, then these may be removed manually If large portion is attached--a Hysterectomy is necessary! LATE POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGE Most common cause is Retained Placental fragments Sub involution Treatment D&C Methergine ARE THESE EARLY, LATE, OR BOTH ? Uterine Atony _________________ Retained placental fragments _________________ Lacerations _________________ Inversion of the uterus _________________ Placenta accreta _________________ Hematoma _________________ POSTPARTUM INFECTIONS POSTPARTUM INFECTIONS Definition Infection of the genital tract that occurs within 28 days after abortion or delivery Causes Streptococcus Groups A and B Clostridium, E. Coli POSTPARTUM INFECTIONS Predisposing Factors 1. Trauma 2. Hemorrhage 3. Prolonged labor 4. Urinary Tract Infections 5. Anemia and Hematomas 6. Excessive vaginal exams 7. P R O M CRITICAL TO REMEMBER Signs and Symptoms of Postpartum Infection 1.Temperature increase of 100.4 or higher on any 2 consecutive days of the first 10 days post-partum, not including the first 24 hours. 2. Foul smelling lochia, discharge 3. Malaise, Anorexia, Tachycardia, chills 4. Pelvic Pain 5. Elevated WBC POSTPARTUM INFECTION TREATMENT AND NURSING CARE • Administer broad spectrum antibiotics • Provide with warm sitz baths • Promote drainage--have pt. lie in HIGH fowlers position • Force fluids and hydrate with IV’s 3000 - 4000 cc. / day • Keep uterus contracted, give Methergine • Provide analgesics for alleviation of pain • Nasogastric suction if peritonitis develops Test Yourself ! What is the classic sign of a Postpartum Infection? COMPLICATIONS OF POSTPARTUM INFECTIONS Pelvic Cellulitis Peritonitis Signs and Symptoms: Spiking a fever of 102 0 F to 104 0 F Elevated WBC Chills Extreme Lethargy Nausea and Vomiting Abdominal Rigidity and Rebound Tenderness PREVENTIVE MEASURES Prompt treatment of anemia Well-balanced diet Avoidance of intercourse late in pregnancy Strict asepsis during labor and delivery Teaching of postpartum hygiene measures keep pads snug change pads frequently wipe front to back use peri bottle after each elimination LOCALIZED INFECTION Infection of the Episiotomy, Perineal laceration, Vaginal or vulva lacerations Wound infection of incision site Signs: Reddened, edematous, firm, tender edges of skin Edges seperate and purulent material drains from the wound. Treatment Antibiotics Wound care CHECK YOURSELF Mrs. X. was admitted with endometritis and Mrs. Y. was admitted with an infection in her cesarean incision. Are both classified as a Puerperal Infection? What would be the major difference in presenting symptoms you would note on nursing assessment? POSTPARTUM CYSTITIS POSTPARTUM CYSTITIS • Prevention: • Monitor the patients urination diligently! • Don’t allow to go longer than 3 - 4 hours before intervening. • Treatment • Antibiotics -- Ampicillin • Urinary Tract Antispasmodics • Causes: • Stretching or Trauma to the base of the bladder results in edema of the trigone that is great enough to obstruct the urethra and to cause acute retention. • Anesthesia MASTITIS Marked Engorgement Pain Chills, Fever, Tachycardia Hardness and Redness Enlarged and tender lymph nodes MASTITIS Types: Mammary Cellulitis - inflammation of the connective tissue between the lobes in the breast Mammary Adenitis - infection in the ducts and lobes of the breasts Development of Mastitis Improper breaking of suction First Nursing Experience Supplemental Feedings "Lazy Feeder" Poor Positioning of Infant Strong Sucking Infant Abrupt Weaning Interval between nursing too long Nipple Trauma Pain Impaired Let down Cracked nipples Engorgement Stasis of milk Entry for Bacteria Plugged ducts Mastitis Treatment, Problem will resolve No Treatment Breast Abscess TREATMENT OF MASTITIS Rest Appropriate Antibiotics--Usually Cephalosporins Hot and / or Cold Packs Don’t Stop Breast Feeding because: If the milk contains the bacteria, it also contains the antibiotic Sudden cessation of lactation will cause severe engorgement which will only complicate the situation Breastfeeding stimulates circulation and moves the bacteria containing milk out of the breast MASTITIS Preventive Measures Meticulous handwashing Frequent feedings and massage distended area to help emptying Rotate position of baby on the breast COMPLICATION OF MASTITIS Breast Abscess Breast Feeding is stopped on the affected side, but may feed on the unaffected side. Treatment: Incision and Drainage THROMBOEMBOLIC DISEASE Predisposing Factors Slowing of blood in the legs Trauma to the veins Signs and Symptoms Sudden onset of pain Tenderness of the calf Redness and an increase in skin temperature Positive Homan’s Sign Treatment Heparin --it does not cross into breast milk Antidote: protamine sulfate Teach patient to report any unusual bleeding, or petchiae, bleeding gums, hematuria, epistaxis, etc. Complication Pulmonary Emboli POSTPARTUM PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Mental Health problems can complicate the puerperium. There are days when each new mother may feel inadequate, but the mother who has a constant feeling of inadequacy needs professional counseling. Pregnancy alone is not a cause of a psychiatric Illness; however, the psychological and physiological stressors relating to pregnancy may bring on an emotional crisis MOOD DISORDERS The Most common Mood Disorders are: Adjustment reaction with mood depression “baby blues” Postpartum major mood disorder “Postpartum Depression” Postpartum psychosis “BABY BLUES” 50-80% of moms are affected Self-limiting (up to 10 days) Cause Seems to be related to changes in progesterone, estrogen and prolactin levels Symptoms Tearful yet happy Overwhelmed Treatment POSTPARTUM MAJOR MOOD DISORDER “POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION” Risk factors: Primiparity History of postpartum depression Lack of social and relationship support Clinical Therapy: Counseling, support groups Medication (usually SSRI’s) Childcare assistance POSTPARTUM PSYCHOSIS Predisposing Factors: Similar to those of postpartum depression Assessment: Grandiosity Decreased need for sleep (insomnia) Flight of ideas Psychomotor agitation / hyperactivity Rejection of infant TREATMENT FOR MOOD DISORDERS Drug therapy (previous slide) Psychotherapy Explain importance of good nutrition and rest Some of her feelings may seem “unreasonable” Re-introduce the baby to the mother at the mother’s own pace How do the signs and symptoms of hematoma differ from those of uterine atony or a laceration? What laboratory study should the nurse suspect if the woman is on heparin anticoagulation? What is the significance of a board-like abdomen in a woman who has endometritis? Why is it important that the breast-feeding mother with mastitis empty her breasts completely? What is the KEY difference between postpartum blues and postpartum depression?