* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 32-innervation of abdomen & lymph drainage
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
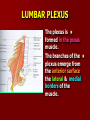
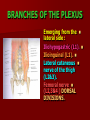
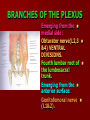
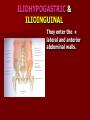
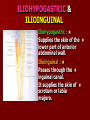
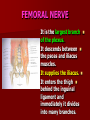
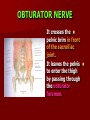
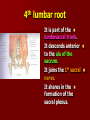
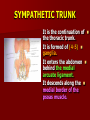
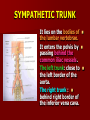
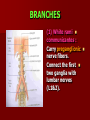
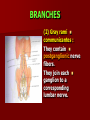
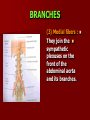
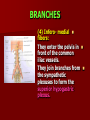
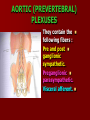
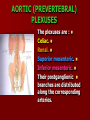
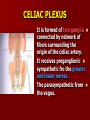
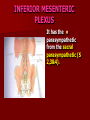
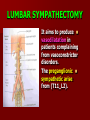
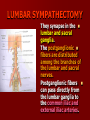
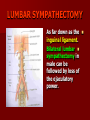
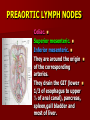
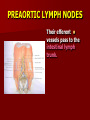
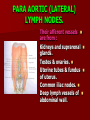
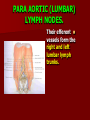
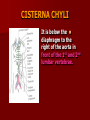
NERVE SUPPLY Somatic: Lumbar plexus. Autonomic : Sympathetic trunk. Aortic plexuses. LUMBAR PLEXUS It is the main nervous supply of the lower limb. It is formed from the anterior rami of the upper four lumbar nerves. It has a contribution from T12 (subcostal nerve). LUMBAR PLEXUS The plexus is formed in the psoas muscle. The branches of the plexus emerge from the anterior surface the lateral & medial borders of the muscle. BRANCHES OF THE PLEXUS Emerging from the lateral side : Iliohypogastric (L1). Ilioinguinal (L1). Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2&3). Femoral nerve (L2,3&4 ) DORSAL DIVISIONS. BRANCHES OF THE PLEXUS Emerging from the medial side : Obturator nerve(L2,3 &4) VENTRAL DIVISIONS. Fourth lumbar root of the lumbosacral trunk. Emerging from the anterior surface: Genitofemoral nerve (L1&2). ILIOHYPOGASTRIC & ILIOINGUINAL They enter the lateral and anterior abdominal walls. ILIOHYPOGASTRIC & ILIOINGUINAL Iliohypogastric : Supplies the skin of the lower part of anterior abdominal wall. Ilioinguinal : Passes through the inguinal canal. It supplies the skin of scrotum or labia majora. LATERAL CUTANEOUS NERVE OF THE THIGH It crosses the front of the iliacus muscle. It enters the thigh behind the lateral end of the inguinal ligament. LATERAL CUTANEOUS NERVE OF THE THIGH It supplies the skin on the anterior and lateral thigh to the level of the knee. FEMORAL NERVE It is the largest branch of the plexus. It descends between the psoas and iliacus muscles. It supplies the iliacus. It enters the thigh behind the inguinal ligament and immediately it divides into many branches. OBTURATOR NERVE It crosses the pelvic brim in front of the sacroiliac joint. It leaves the pelvis to enter the thigh by passing through the obturator foramen. th 4 lumbar root It is part of the lumbosacral trunk. It descends anterior to the ala of the sacrum. It joins the 1st sacral nerve. It shares in the formation of the sacral plexus. GENITOFEMORAL NERVE It descends in front of the psoas. It divides into a genital branch and a femoral branch. GENITOFEMORAL NERVE Femoral branch : Supplies a small area of the skin of the thigh. Genital branch : It enters the spermatic cord. It supplies the cremaster muscle. It is the nervous pathway for the cremasteric reflex. SYMPATHETIC TRUNK It is the continuation of the thoracic trunk. It is formed of (4-5) ganglia. It enters the abdomen behind the medial arcuate ligament. It descends along the medial border of the psoas muscle. SYMPATHETIC TRUNK It lies on the bodies of the lumbar vertebrae. It enters the pelvis by passing behind the common iliac vessels. The left trunk: close to the left border of the aorta. The right trunk : behind right border of the inferior vena cava. BRANCHES (1) White rami communicantes : Carry preganglionic nerve fibers. Connect the first two ganglia with lumbar nerves (L1&2). BRANCHES (2) Gray rami communicantes : They contain postganglionic nerve fibers. They join each ganglion to a corresponding lumbar nerve. BRANCHES (3) Medial fibers : They join the sympathetic plexuses on the front of the abdominal aorta and its branches. BRANCHES (4) Infero- medial fibers: They enter the pelvis in front of the common iliac vessels. They join branches from the sympathetic plexuses to form the superior hypogastric plexus. AORTIC (PREVERTEBRAL) PLEXUSES They contain the following fibers : Pre and post ganglionic sympathetic. Preganglionic parasympathetic. Visceral afferent. AORTIC (PREVERTEBRAL) PLEXUSES The plexuses are : Celiac. Renal. Superior mesenteric. Inferior mesenteric. Their postganglionic branches are distributed along the corresponding arteries. CELIAC PLEXUS It is formed of two ganglia connected by network of fibers surrounding the origin of the celiac artery. It receives preganglionic sympathetic fro the greater and lesser nerves. The parasympathetic from the vagus. INFERIOR MESENTERIC PLEXUS It has the parasympathetic from the sacral parasympathetic (S 2,3&4). LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY It aims to produce vasodilatation in patients complaining from vasoconstrictor disorders. The preganglionic sympathetic arise from (T11_L2). LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY They synapse in the lumbar and sacral ganglia. The postganglionic fibers are distributed among the branches of the lumbar and sacral nerves. Postganglionic fibers can pass directly from the lumbar ganglia to the common iliac and external iliac arteries. LUMBAR SYMPATHECTOMY As far down as the inguinal ligament. Bilateral lumbar sympathectomy in male can be followed by loss of the ejaculatory power. LYMPH DRAINAGE Lymph nodes : Preaortic. Para aortic (lumbar) Lymph vessels : Cisterna chyli. Thoracic duct. PREAORTIC LYMPH NODES Celiac. Superior mesenteric. Inferior mesenteric. They are around the origin of the corresponding arteries. They drain the GIT (lower 1/3 of esophagus to upper ½ of anal canal), pancreas, spleen,gall bladder and most of liver. PREAORTIC LYMPH NODES Their efferent vessels pass to the intestinal lymph trunk. PARA AORTIC (LATERAL) LYMPH NODES. Their afferent vessels are from : Kidneys and suprarenal glands. Testes & ovaries. Uterine tubes & fundus of uterus. Common iliac nodes. Deep lymph vessels of abdominal wall. PARA AORTIC (LUMBAR) LYMPH NODES. Their efferent vessels form the right and left lumbar lymph trunks. CISTERNA CHYLI It is below the diaphragm to the right of the aorta in front of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae. CISTERNA CHYLI It receives lymph from : Intestinal trunk. Right and left lumbar trunks. Lower part of the thorax. Its efferent is the Thoracic Duct.