* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Surface Anatomy - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
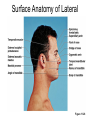
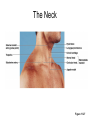
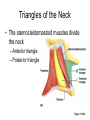
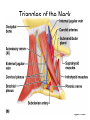
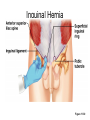
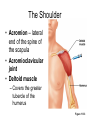
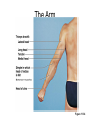
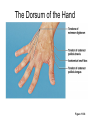
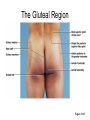
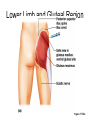
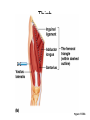
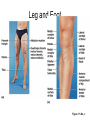
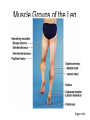
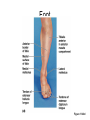
Surface Anatomy • Palpation – feeling internal structures through the skin • “Living anatomy” – provides information about – Palpation of arterial pulses – Skeleton, muscles, and blood vessels – Sounds of the heart and lungs – Where to give injections The Head • Cranium – selected structures felt through the skin – Superciliary arches – External occipital protuberance – Mastoid process – Temporalis muscle – at temple region – Frontalis muscle • Feel wrinkling of the forehead when eyebrows are raised Surface Anatomy of Lateral Aspect of the Head Figure 11.26 The Head • Face – selected structures felt through the skin – Lacrimal fossa – Root and bridge of the nose – Auricle of the ear – Zygomatic arch – Masseter muscle – Mandible – Temporomandibular joint The Neck • Skeletal landmarks – Spinous processes of cervical vertebrae • C7 is particularly prominent (vertebra prominens) – Hyoid bone – in the anterior, superior neck – Laryngeal prominence – the “Adam’s Apple” – Cricoid cartilage – inferior to the laryngeal prominence – Jugular notch – depression in the superior part of the sternum The Neck Figure 11.27 Muscles of the Neck • Sternocleidomastoid – most prominent neck muscle – Sternal head – Clavicular head • Deep to the sternocleidomastoid – Common carotid artery – Internal jugular vein • Trapezius – posterior aspect of the neck Triangles of the Neck • The sternocleidomastoid muscles divide the neck – Anterior triangle – Posterior triangle Figure 11.28a Triangles of the Neck Figure 11.28b The Trunk • The trunk consists of the – Thorax – Abdomen – Pelvis and perineum The Thorax • Sternum – portions felt through the skin – Manubrium, xiphoid process, and sternal angle • Midaxillary line – line from the center of the axilla onto the lateral thoracic wall • Midclavicular line – vertical line from midpoint of the clavicle to the groin Muscles of the Thorax • Pectoralis major • Serratus anterior The Anterior Thorax and Abdomen Figure 11.29 The Abdomen • Structures felt through the skin – Iliac crest – Anterior superior iliac spine – Inguinal ligament • Runs medially from anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle – Pubic crest Inguinal Hernia Figure 11.30 Muscles and other Abdominal Surface Features • Linea alba – The “white line” extending from xiphoid process to the pubic symphysis • Rectus abdominis – Linea semilunaris – lateral margin of rectus abdominis The Pelvis and Perineum • Four bony structures define the perineum – Pubic symphysis – Two ischial tuberosities – Coccyx The Back • Posterior median furrow – vertical groove along the midline • Spinous processes of vertebrae • Spine of the scapula – Medial end is opposite T3 • Medial border of the scapula The Back • Inferior angle of the scapula • Iliac crests – Supracristal line – intersects L4 • Sacrum – superior to cleft in the buttocks • Coccyx – posterior to the anus Surface Anatomy of the Back Figure 11.31a Muscles of the Back • Trapezius • Latissimus dorsi • Erector spinae Surface Anatomy of the Back Figure 11.31b Upper Limb and Shoulder • The Axilla – Base of the axilla – where armpit hair grows – Deep to the axilla – axillary lymph nodes and blood vessels – Anterior axillary fold – pectoralis major – Posterior axillary fold –latissimus dorsi and teres major Shoulder and Arm Figure 11.32a, b The Shoulder • Acromion – lateral end of the spine of the scapula • Acromioclavicular joint • Deltoid muscle – Covers the greater tubercle of the humerus Figure 11.33 The Arm • The region between the shoulder and elbow • Humerus – Palpated through skin along its entire length • Biceps brachii • Medial bicipital groove – The medial boundary of the biceps brachii • Triceps brachii The Arm Figure 11.34 The Elbow • Lateral and medial epicondyles of the humerus – Ulnar nerve – “funny bone” runs across medial epicondyle • Olecranon process of the ulna • Cubital fossa – (antecubital fossa) – Forms anterior surface of forearm The Anterior Surface of the Forearm and Fist Figure 11.35a Forearm • Bones – Ulna – palpate entire length • Styloid process and head – distal end • Radius – partly covered in muscle – Head of the radius – proximal end – Styloid process – distal end Muscles of the Forearm • Flexor muscles – anterior forearm – Flexor carpi radialis – Palmaris longus • This muscle is absent in about 30% of people • Extensor muscles – posterior forearm Other Structures of the Forearm • Anatomical snuff box bordered by – Extensor pollicis brevis – Extensor pollicis longus The Hand • Dorsum of hand – Dorsal venous network – Tendons of extensor digitorum • Palmar surface – Thenar eminence (not labeled on figure 11.35b) – Hypothenar eminence (see figure 11.17a–c ) – Pisiform bone The Dorsum of the Hand Figure 11.36 Gluteal Region • • • • Iliac crests Posterior superior iliac spine Sacroiliac joint Prominences of the buttocks – “Cheeks” of the buttocks – Formed from subcutaneous fat and the gluteal muscles The Gluteal Region Figure 11.37 Lower Limb and Gluteal Region • Natal cleft (gluteal cleft) – Vertical midline groove between “cheeks” • Gluteal fold – Horizontal fold below each “cheek” • Ischial tuberosities • Greater trochanter of the femur – Located at the lateral hip Lower Limb and Gluteal Region Figure 11.38a Thigh • Medial and lateral condyles of the femur • Patella • Three groups of muscles – Quadriceps femoris – anterior thigh • Vastus lateralis – injection site – Adductors – medial thigh – Hamstrings – posterior thigh Thigh Figure 11.38b The Thigh • The Femoral Triangle – Superior border – inguinal ligament – Inferior borders • Sartorius • Adductor longus • Popliteal fossa – Diamond-shaped hollow on posterior knee • Defined by borders of “hamstring” tendons and gastrocnemius Leg and Foot • Palpate patella to find the patellar ligament • Structures of the proximal leg – Tibial tuberosity – Lateral and medial condyles of the tibia – Head of the fibula • Structures of the distal leg – Medial malleolus – Lateral malleolus Leg and Foot Figure 11.40a, c Muscle Groups of the Leg • Posterior calf muscles – Gastrocnemius and soleus • Calcaneal tendon – inferior end of the soleus and gastrocnemius • Anterior compartment muscles – Tibialis anterior – Extensor digitorum – Fibularis Muscle Groups of the Leg Figure 11.41 Foot • Tendons on the dorsal surface of the foot – Extensor digitorum longus tendon – Extensor hallucis longus Foot Figure 11.40d