* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 15asteroids4s
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
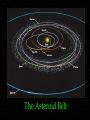
Asteroids Astronomy 311 Professor Lee Carkner Lecture 15 Quiz #2 Monday Quiz 2 same format as quiz 1 ~20 multiple choice/matching ~4 short answer Covers lectures 9-15 bring pencil and calculator No class Friday Rocks in Space Asteroid -Meteoroid -Meteor -- the flash of light when a meteoroid hits the Earth’s atmosphere sometimes called a falling or shooting star Meteorite -- Types of Meteorites Meteorites are classified based on their composition Two major types are irons and chondrites Chondrites are the most common type of meteorite But, irons are much easier to find What are the properties of chondrites and irons and how can you identify them? Iron Meteorites Composed of iron and nickel Often show Widmanstatten patterns when etched with acid Widmanstatten Paterns Chondrite (Stony) Meteorites Composed of silicates Contain chondrules, small glassy inclusions of material that were heated and quickly cooled Carbonaceous chondrites Chondrules The Missing Planet In the 18th century astronomers noticed that there was a gap between Mars and Jupiter with no planets In 1801 G. Piazzi found a faint moving star in the gap This is the asteroid belt The Asteroid Belt Asteroid Myths Are the asteroids debris from a planet that exploded? Is the asteroid belt dangerous to travel through? Asteroid Facts Size: Orbit: Asteroid Belt 2-3.5 AU, some have eccentric Earth crossing orbits Description: Formation of the Asteroid Belt If Jupiter did not exist, a fifth terrestrial planet might have formed at 2.8 AU Jupiter’s gravity: Trojans and NEOs Many asteroids are found outside of the asteroid belt Trojan asteroids have been captured in Jupiter’s Lagrange points Some asteroids cross the Earth’s orbit and are called Near Earth Objects (NEO) Studying Asteroids Several asteroids have been observed at close range In 2005 the Japanese mission Hayabusa studied asteroid Itokawa and tried to collect a sample for return to Earth Asteroid Features Only Ceres, Pallas and Vesta (the 3 largest asteroids) have enough gravity to form a sphere Asteroids show many craters During the heavy bombardment period asteroid collisions must have been frequent Composition of Asteroids Asteroids are divided into three major groups based on composition S Type C Type M type Formation of Asteroids M and S type asteroids are found in the inner asteroid belt where temperatures are higher Formation of Meteoroids Some asteroids became large enough to differentiate These asteroids were then broken up by collisions Asteroids that never differentiated formed chondrites What Use is an Asteroid? Mining Space Habitats Spaceships Providing Material for Life in Space Summary Asteroids are small bodies that orbit the Sun Most are in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter (2-3.5 AU) Jupiter’s gravity prevented the asteroids from forming a planet Description: Small (most less than 1 km) Max size is few hundred km Irregularly shaped Heavily cratered Summary: Meteoroids Iron made of metal formed from core of asteroids (M type) Achondrites (Stony) made of rock with no inclusions made from crust of asteroids (S type) Chondrites (Stony) made of rock with small inclusions made from undifferentiated asteroids (S and C type)