* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 01D)EA~1
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
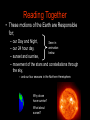
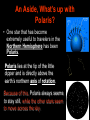
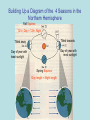
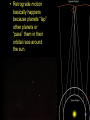
Earth and Other Planetary Motion (4.01-06) Reading together • As you look up at the sky, you will notice that the stars and planets are not always in the same position each night. • “Polaris”, however, is always directly above the North Pole of the Earth. • The Earth rotates underneath Polaris each day. This happens at the same time as Earth revolves around the Sun. Figure it out: Revolve or Rotate, which is which? Reading Together • These motions of the Earth are Responsible for; – – – – our Day and Night, Seen in animation our 24 hour day, below. sunset and sunrise, movement of the stars and constellations through the sky, – and our four seasons in the Northern Hemisphere. Why do we have sunrise? . What about sunset? 1. Effects of Earth’s Rotation • Rotation means the movement of the Earth around its axis. (like a wheel rotates on an axel) • The Earth rotates every 24 hours • Gives us morning and night • Makes the sun, moon, stars and constellations appear to rise in the East and set in the West • Stars close to Polaris will not rise and set, just rotate in the sky. Imagine you lived on this ball, why would the sun rise in the East? An Aside, What’s up with Polaris? • One star that has become extremely useful to travelers in the Northern Hemisphere has been Polaris. Polaris lies at the tip of the little dipper and is directly above the earth’s northern axis of rotation. Because of this, Polaris always seems to stay still, while the other stars seem to move across the sky. Eyes on Polaris More Aside Star Shapes - Constellations • When people looked up at the night sky they looked for meaning and patterns, but also for practical tools. • They began to develop the concept of the constellations. 1. Some constellations were used for story telling (Hercules, Orion’s Belt). 2. Some constellations were used for giving directions and navigating both the sea and land at night. 2. Effects of Earth’s Revolution • Revolution means the orbit or revolving of the Earth around the Sun. • The Earth’s orbital period is 365 ¼ days or 1 year. • Reasons why we see different stars and constellations in winter and summer (What is above us in the night changes). Why do we have those pesky leap years?!? Can you SEE the reason above? • Our 4 seasons are due to the tilt of the Earth on its axis as it revolves or orbits around the sun. Correcting ideas about seasons. In your margin notes • The reason for summer is not that the Earth is any closer to the sun. • The reason for summer is that when the earth is tilted towards the sun, the sun’s light strikes the Earth directly. • During winter the light is spread out over the Earth’s surface more since the earth is tilted away from the sun. The same amount of light spread out over a larger surface means the surface is colder. Northern winter Northern Summer Building Up a Diagram of the 4 Seasons in the Northern Hemisphere Fall Equinox 12 hr. Day = 12hr. Night Tilted towards Tilted away Day of year with most sunlight Day of year with least sunlight Spring Equinox Day length = Night length 3. Effects of other Planets’ Orbits • All the other planets orbit around the sun, at different speeds and distances from the Sun • They APPEAR to move past one another and sometimes fall back relative to one another (this is called retrograde motion) but this is due to their different speeds and positions in our Solar System. • They APPEAR to move through different constellations, but they are actually much closer than the stars. Mars is a great example of a planet that shows retrograde motion. The word Planet is derived from a Greek word that called these “stars” with “weird” motion, THE WANDERERS. • Retrograde motion basically happens because planets “lap” other planets or “pass” them in their orbital race around the sun. Reminder of basic ideas Rotation of the Earth on its axis 1. Time to complete one rotation is 24 hours 2. Causes day and night 3. Sun rises in the east and sets in the west 4. Polaris is above the axis of rotation Revolution of the Earth around the sun 1. Time to complete one revolution is 365.25 days 2. Causes the seasons 3. Causes retrograde motion Questions: SUN