* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of VoIP - ITU
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
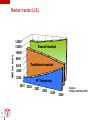
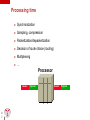
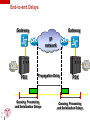
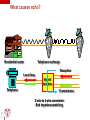
Introduction to Voice Over IP Technology www.iitelecom.com © Internation Institute of Telecommunications inc., 2000-2004 Why integrate voice over IP? To reduce the costs? To maximize bandwidth usage To use a single network? Telephony on Intranet and Internet To create new commercial applications? To integrate voice mail, email and fax Call Centers – CTI (Computer Telephony Integration) – Telephony on Internet Integration of voice-data-images? 2 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 VoIP traffic on the network Traffic: voice, video… Isochronous traffic – Fixed intervals Throughput – Constant (voice) – Variable (video) Short delays The IP network: Asynchronous mode of transfer – Process by which the data can be transmitted at unspecified intervals. – Generate variable and unforeseeable delays – T T T T T 3 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Designed for non isochronous traffic The traffic adaptation to the network 4 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 3 performance factors Name three factors which will influence the ambulance delay : 5 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 3 performance factors Transpose these 3 factors in a network environment and relate them to packet latencies at a LAN exit point LAN LAN 6 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Router Router Constraints / Solutions Sampling Delays Delay variation/jitter Echo Compatibility/interworking Inter local area networks (QoS) With the PSTN – Signaling and supervision – Added value services Information security 7 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Define packets Signal compression RTP/UDP QoS Priority – RSVP – ToS/Diffserv Field – IPv6 Dimensioning/capacity Equipment Gateway, gatekeeper What are the challenges? 8 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 The signal must be transported via various network types – A great number of technologies and standards are used – Interworking and interconnections between various technologies and equipment The applications, the services, the technologies and the standards evolve quickly – Proprietary solutions versus standards Maintain the quality of the voice signal – Toll Quality or equivalent To preserve the current telephone services – Call transfer, call on hold, caller ID, etc. Interworking between the traditional voice network and the IP network – Seamless services – Addressing, classification – Quality of service, MTBF, MTTR – Security and confidentiality Billing Operations and management Who are the stakeholders? Users (residential, commercial) Internet service providers Carriers Equipment vendors Technology (platform, chip, software) Industry standards (ANSI, ITU, IEEE, IETF) 9 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Market trends (U.S.) Million lines 14000 12000 10000 Overall market 8000 6000 4000 Traditional market 2000 2001 2002 10 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 IP Telephony 2003 2004 2005 Source: Phillips InfoTech 2002 2006 In the year 2000, some figures… VoIP will account for 75 % of the world voice services in 2007. * The number of IP Centrex lines should grow from 13,000 in 2001 to 10 million in 2008. The number of standard Centrex lines in 2001 was estimated at 16,5 million. * The market for IP PBX should reach 3,9 billion dollars in 2005, which represents 20 % of the traditional PBX market. ** The companies will migrate their voice service from traditional networks towards IP networks at a rate which will generate a world market for IP PBX of 16,5 billion dollars from here to 2006. *** 90 % of the companies operating in multiple sites will migrate towards IP systems for the transport of the voice in the next 5 years. **** 25 % of Internet users will adopt IP Telephony PC-TO-TELEPHONE in 2006. **** * ** *** **** ***** 11 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Frost & Sullivan Synergy research Allied Business Intelligence Phillips Group Ovum In the year 2000, some figures… (cont’d) * 12 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Unified messaging applications will bloom in 2004 and 2005. The expenditure related to these applications should reach 3.5 billion dollars in 2005 with an annual growth rate of 32.1 % * TIA (Telecommunication Industry Association) Questions? ? 13 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 The protocol suite Analog to digital sampling Ethernet Checksum (FCS) 4 bytes Voice sample N O 1 compression Voice sample N O 2 n bytes Voice sample N O 3 packetization 14 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 RTP Header 12 bytes UDP Header 8 bytes IP Header 20 bytes Ethernet/LLC header 18 bytes Packets construction Packetization Continuous signal conversion into individual packets Packetization Size of a packet payload 15 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Which will be the payload size (in bytes) of a 20ms voice signal packet when using a 64 Kb/s PCM? – The packet size has a significant effect on the quality of service – Delay – Echo – Delay variation Packet size versus tolerable delay Did you see the storm yesterday? 16 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 He cuts me all the time 200 - 250 ms is tolerable Overlaps if higher > 250ms How is your sister? Delay Sources Serialization time Propagation time Processing time “Processing delay” Time to sit in memory “Queuing delay” 17 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Serialization time Time necessary for the transmission of the first to the last bit of a given packet. Called transmission delay Delay = L/C C [ bps ] 10 10 01 10 11 00 01 0 L [ bits ] Time (ms) Packet Length Circuit speed (kbps) (Bytes) 18 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 56 128 256 1 536 60 8,6 3,8 1,9 0,3 500 71,4 31,3 15,6 2,6 1 500 214 93,8 46,9 7,8 4 000 571 250 125 20,8 Propagation time T1 T 2 Delay = T 1 + T 2 [ms] 19 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Processing time Synchronization Sampling, compression Packetization/depacketization Decision of route choice (routing) Multiplexing … Processor Header 20 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Payload Header Payload Queuing / Time to sit in memory Header Payload Header Header Payload Payload Header Memory Queuing delay 21 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Payload End-to-end Delays Gateway Gateway IP network PBX Propagation Delay Queuing, Processing and Serialization Delays 22 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 PBX Queuing, Processing and Serialization Delays What is echo? Do I hear echo ? Hello! Hybrid junction Hybrid junction PSTN Hello! One way delay; if higher than 20 - 30 ms, a person distinguishes the echo. 23 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 How can we cancel echo? What causes echo? Residential sector Telephone exchange Reception Local loop Hybrid Junction Telephone Transmission 2 wire to 4 wire conversion Bad impedance matching 24 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Echo is always present Echo varies according to the delay and the power of the return signal. Return signal , reduction of power Echo is undetectable (dB) Echo poses a problem Delay (ms) 25 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 How to eliminate/minimize echo? Decrease the return signal – – Advantage: • An easy solution Disadvantages: • Human intervention • Reduction of the signal power for the person who speaks Installation of echo cancellers – – Advantage: • Eliminate the return signal (echo) Disadvantage: • Costs Reduction of the delays 26 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Voice compression Objectives: – To reduce bandwidth usage. – To reduce packet size Compression algorithms are used for video and voice. Disadvantages: – Reduction in voice quality – Introduction of delay (echo) Bandwidth (kbit/s) Not acceptable Toll Quality Quality commercial 64 PCM (G.711) Cellular 32 ADPCM 32 (G.726) 24 ADPCM 24 (G.726) 16 ADPCM 16 (G.726) 8 27 IIT 101 LD-CELP 16 (G.728) © IITelecom, 2004 0 CS-ACELP 8 (G.729) MPC-MLQ 5,3 (G.723.1) Quality Mean Opinion Score (MOS) Evaluation of the sound quality with various compression methods on a scale of 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent) A result of 4,0 is considered “Toll Quality” Test conditions: – – – With background noise, several people discussing at the same time; Individuals speaking various languages, men and women; Etc. 4.1 4 3.9 3.8 3.7 MOS 3.6 3.5 3.4 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 G.723.1 MPC-MLQ 5,3 kbit/s G.729a CS-ACELP 8 kbit/s G.728 LD-CELP 16 kbit/s G.729 CS-ACELP 8 kbit/s 28 G.726 ADPCM 32 kbit/s G.711 PCM 64 kbit/s 3.3 Silence suppression Automatically deactivated for fax/modem Background noise generated at the destination -31 dbm Voice signal power Meter Bandwidth Economy -54 dbm Time Voice Signal 29 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Silence Voice Signal Large DATA packets affect voice Gateway Gateway WAN 56 kbit/s Voice 1 500 bytes data Voice Data Packet Serialization time: PBX Voice Voice 1 500 bytes data PBX 214 ms Voice 1 500 bytes data Voice Voice packets 60 bytes every 20 ms 30 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Voice packets 60 bytes every 214 ms Solution - Fragmentation Gateway Gateway WAN 56 kbit/s 500 Voice 500 Voice Data packet Serialization time PBX Voice Voice 1 500 bytes data IIT 101 60 bytes every 20 ms © IITelecom, 2004 71,4 ms PBX Voice 1 500 bytes data Voice Voice packets 31 500 Voice packets 60 bytes every 71,4 ms Packet construction The packetization The sample The sample 12 bytes RTP 8 bytes UDP 20 bytes IP LLC/802.3 32 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 22 bytes Appendix - Acronym list 33 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Acronym list 3GPP Third Generation Partnership Project CIR Committed Information Rate ABR Available Bit Rate CM Cable Modem ACF Admission Confirm CMIP Common Management Information Protocol ACM Address Complete Message CMTS Cable Modem Termination System ADPCM Adaptive Differential Pulses Code Modulation CO Central Office ADSM Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line CoPS Common open Policy Server AF Assured Forwarding CoS Class of Service ALI Automatic Location Identifier CPL Common Programming Language ANI Automatic Number Identifier CPU Central Processing Unit ANM Answer Message CRTP Compressed Real-Time Protocol ANSI American National Standard Institute CS-ACELP Conjugate Structure Adaptive Code Excited Linear Prediction ARP Address Resolution Protocol CSRC Contributing Source ARQ Admission Request CTD Click-To-Dial ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange CTI Computer Telephony Integration ASN Abstract Symbol Notation dB Decibel ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode dBm Decibel relative to 1 milliwatt BGP Border Gateway Protocol DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol bps Bits Per Second DiffServ Differentiated Services CA Call Agent DNS Domain Name Server CAC Connection Admission Control DOCSIS Data Over Cable Interface Specifications CAN Campus Area Network DS Differentiated Services CAR Committed Access Rate DSCP Differentiated Services Code Point CBWFQ Class-Based Weighted Fair Queuing EF Expedited Forwarding CGI Common Gateway Interface EGP Exterior Gateway Protocol CIC Circuit Identification Code EIGRP Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol 34 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Acronym list (cont'd) ERP Enterprise Resource Planning ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network ETSI European Telecomm Standards Institute ISUP Integrated Services Digital Network User Part FCS Frame Check Sequence ITSP Internet Telephony Service Provider FEC Forward Equivalence Class ITU International Telecommunication Union FRF Frame Relay Forum ITU-T ITU - Telecom FRTS Frame Relay Traffic Shaping JPEG Joint Photographic Expert Group FTP File Transfer Protocol kbps Kilobits Per Second GK Gatekeeper LAN Local Area Network GTS Generic Traffic Shaping LDP Label Distribution Protocol HFC Hybrid Fiber Coax LD-CELP Low-Delay Code Excited Linear Prediction HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol LER Label Edge Router Hz Hertz LIB Label Information Base IAM Initial Address Message LLC Logical Link Control ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol LLQ Low Latency Queuing IDC International Dated Corporation LS Location Server IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers LSR Label Switch Router IETF Internet Engineering Task Force MAC Media Access Control IGP Interior Gateway Protocol MAN Metropolitan Area Network IHL Internet Header Length MAP Mobile Application Part INAP Intelligent Network Application Profile MCR Minimum Cell Rate IntServ Integrated Services MCU Multipoint Control Unit IP Internet Protocol MDCP Media Device Control Protocol IPv4 IP version 4 Megaco Media Gateway Control IPv6 IP version 6 MG Media Gateway IPDC IP Device Control MGC Media Gateway Controller 35 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Acronym list (cont'd) MGCP Media Gateway Control protocol PCM Pulse Code Modulation MIB Management Information Base PHB Per-Hop Behavior MIME Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension POP3 Post Office Protocol version 3 MIPS Million Instruction Per Second POTS Plain Old Telephone Service MMUSIC Multiparty Multimedia Session Control PPP Point-to-Point Protocol MOS Mean Opinion Score PQ Priority Queuing MPLS Multi Protocol Label Switching PS Proxy Server MP-MLQ Multipulse Multilevel Quantization PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network ms Millisecond QoS Quality of Service MTBF Mean Time Between Failure RARP Reverse ARP MTP Message Transfer Part RAS Registration Admission Status MTTR Mean Time To Repair RFC Request For Comment NAT Network Address Translation RMON Remote Monitoring NCS Network-based Control Signaling RPC Remote Procedure Call NFS Network File System RS Registration Server NNTP Network News Transfer Protocol RSVP Resource Reservation Protocol OLC Open Logical Channel RTCP Real-time Control Protocol OMAP Operational, Management and Admin Process RTP Real-time Protocol OPX Off Premise Extension SCCP Signalling Connection Control Part OSPF Open Shortest Path First SCP Signal Control Point OSI Open System Interconnection SCTP Stream Control Transmission Protocol PAN Personal Area Network SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy PBH Per-Hop Behavior SDP Session Description Protocol PBX Private Branch Exchange SGCP Simple Gateway Control Protocol PCR Peak Cell Rate SIGTRAN Signalling Transport 36 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004 Acronym list (cont'd) SIP Session Initiation Protocol VPN Virtual Private Network SLA Service Level Agreement WAN Wide Area Network SLIP Serial Line Internet Protocol WFQ Weighted Fair Queuing SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol WRED Weighted Random Early Drop SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol SONET Synchronous Optical Network For additional acronyms, SS7 Signaling System 7 http://www.csrstds.com SSP Switching Service Point SSRC Synchronisation Source STHML Safe Hypertext Transfer Protocol STP Signal Transfer Point SVC Switched Virtual Circuit TCAP Transaction Capabilities Application Part TCP Transport Control Protocol TDM Time Division Multiplexing TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol TIA Telecommunication Industry Association ToS Type of Service TTL Time To Live UA User Agent UDP User Datagram Protocol URL Uniform Resource Locator VAD Voice Activation Detection VBR-rt Variable Bit Rate - Real-time VoIP Voice over IP 37 IIT 101 © IITelecom, 2004