* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angles, Degrees, and Special Triangles
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
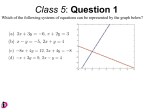
Finding an Equation from Its Graph Trigonometry MATH 103 S. Rook Overview • Section 4.5 in the textbook: – Introduction to Writing Trigonometric Equations – Writing equations when amplitude is modified – Writing equations when a vertical translation is applied – Writing equations when period is modified – Writing equations when a phase shift is applied – Writing equations in general 2 Introduction to Writing Trigonometric Equations Introduction to Writing Trigonometric Equations • We will only be concerned about finding equations of sine and cosine graphs • We start with the basic graphs of y = sin x or y = cos x and then “build them up” to y = k + A sin(Bx + C) or y = k + A cos(Bx + C) – i.e. We reference each change on the given graph to either y = sin x or y = cos x • Finding equations from graphs can be difficult so you MUST PRACTICE! 4 Writing Equations When Amplitude is Modified Writing Equations When Amplitude is Modified • If the minimum value m and maximum value M of the graph are values OTHER THAN -1 and 1 respectively: – The amplitude has possibly been modified – Calculate the value of A: 1 A M m 2 6 Writing Equations When Amplitude is Modified (Continued) – If the shape of the graph appears to be flipped “upside down” when compared to y = sin x or y = cos x: • The graph has been reflected over the x-axis • Calculate the value of A : 1 A M m 2 aa 7 Writing Equations When Amplitude is Modified (Example) Ex 1: Find an equation to match the graph: a) b) 8 Writing Equations When a Vertical Translation is Applied Writing Equations When a Vertical Translation is Applied • If the minimum value m DOES NOT match the opposite of the maximum value M: – A vertical translation has been applied – Find the amplitude: A 1 M m 2 – Calculate k = M – |A| • |A| represents where the graph would normally be • If M > |A|: – The graph was shifted up and k is positive • If M < |A| – The graph was shifted down and k is negative 10 Writing Equations When a Vertical Translation is Applied (Example) Ex 2: Write an equation to match the graph: 11 Writing Equations When Period is Modified Writing Equations When Period is Modified • If the graph DOES NOT have a period of 2π: – The period has been modified – Find the period • How long it takes for the graph to complete 1 cycle – Recall the formula for period: P 2 B – With a little algebra: B 2 P 13 Writing Equations When Period is Modified (Example) Ex 3: Write an equation to match the graph: 14 Writing Equations When a Phase Shift is Applied Structure of the Sine and Cosine Graphs • The sine graph has the following structure: 1 Starts at middle 2 Rises to max 3 Decreases to middle 4 Decreases to min 5 Rises to middle • The cosine graph has the following structure: 1 Starts at max 2 Decreases to middle 3 Decreases to min 4 Rises to middle 5 Rises to max 16 Writing Equations When a Phase Shift is Applied • If the graph DOES NOT have one of these structures starting at x = 0: – A phase shift has been applied – Find the value where a sine or cosine period begins • Remember the structure of each – Recall the formula to calculate phase shift: – With a little algebra: C Bp p C B 17 Writing Equations When Phase Shift is Modified (Example) Ex 4: Write an equation to match the graph – assume the period is 2π: 18 Writing Equations in General Writing Equations in General • To write an equation for a graph in general: – Take ONE step at a time – Decide whether the graph more closely resembles y = sin x or y = cos x – Calculate: • The value of A by utilizing the amplitude – If the graph is reflected over the x-axis, A will be negative • The vertical translation k • The value of B by utilizing the period • The value of C by utilizing the phase shift 20 Writing Equations in General (Continued) – Write the equation of the graph as either y = k + A sin(Bx + C) or y = k + A cos(Bx + C) • Often, there is more than one correct equation – Usually, one equation is more easier to find than the others • You can always check your answer by using a graphing calculator! 21 Writing Equations in General Ex 5: Write an equation to match the graph: a) b) 22 Summary • After studying these slides, you should be able to: – Find the equation in the form of y = k + A sin(Bx + C) or y = k + A cos(Bx + C) by examining a graph • Additional Practice – See the list of suggested problems for 4.5 • Next lesson – Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Section 4.7) 23