* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
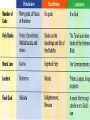
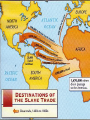
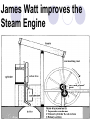
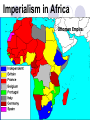
SOL Preparation for World History Getting ready for the SOL There are less than 80 questions on the SOL Exam They are multiple choice questions Some include maps & graphs You have unlimited time in which to complete the test Answer all questions, leave no question unanswered The secret is in preparation, what is important to know People and events shape our history We will identify as many important people and events as possible in order to be prepared to respond successfully on the SOL Let’s Begin Be sure to use a highlighter to identify key information Make notes and page references to you text book to access more details Follow the slides and link the person or event with important knowledge The slides, like the test follow a chronological sequence We will do a practice test when we have finished 5 Great World Religions Judaism Christianity Islam Hinduism Buddhism Christianity and Islam 2 largest religions of the world Christianity- Jesus & the Bible Islam- Allah &the Koran, the prophet Mohammed. 5 Pillars of Faith Mono-theistic religions Life after death or heaven Geographical distribution of world’s major religions Judaism (in Israel & North America) Christianity (Europe, North & South America) Islam (Middle East, Africa, & Asia) Hinduism (Concentrated in India) Buddhism (East and Southeast Asia) World Religions Renaissance Not since the times of Greece and Rome, had there been such a period of magnificence…the Dark Ages lasted for 800 years until the great wealth created by trade led to a period known as the Renaissance Salvation by Martin Luther faith alone Bible is ultimate authority All humans equal before God Pre-destination John Calvin Faith revealed by living a righteous life, work ethic Expansion of the Protest Church Reformation (rise of Capitalism) At first the Reformation divided countries of Europe Religious intolerance led to war Gradually, religious toleration emerged, but first came the Counter Reformation of the Catholic Church Edict of Nantes Allows religious freedom to flourish in France st 1 example of religious toleration, ideas will spread across Europe over the next few hundred years Henry VIII of England Reformation led by a Monarch Creates the Church of England Johannes Gutenberg Leonardo da Vinci Laws of Planetary Motion Copernicus (heliocentric theory) to Kepler (LPM) to Galileo Sun is the center of the universe Galileo Proves Kepler’s work His ideas rock the Catholic Church Used telescope Spanish Armada William Shakespeare and the Globe Theater European thinkers express new ideas Age of Enlightenment brought together ideas of the Renaissance & the Scientific Revolution New attitudes are shaped about society and individuals The Enlightenment Applied reason to the human world, not just the natural world Stimulated religious tolerance Fueled democratic revolution around the world Voltaire Religious toleration should triumph over religious fanaticism:the separation of church and state Columbian Exchange Diseases Disease kills a large segment of the indigenous population of America Spanish in America The Spanish conquest of the Americas reflect the influence of Spain on language, customs, & culture on another people God, Glory, and Gold slavery Civilization of Africa Ghana- gold and salt European trading post along coast Slave trade Plantation System Agricultural system in the South. Cash crops like tobacco & cotton fuel slavery Mercantilism An economic practice adopted by European colonial powers in an effort to become selfsufficient; based on the theory that colonies existed for the benefit of the mother country Declaration of Independence July 4, 1776 - Philadelphia Absolutism Divine Right Theory – power given to a King by God This concept will clash with the ideas of the new modern philosophers of the 1600’s Louis XIV & Peter the Great Absolute Monarchs Louis XIV Peter The Great Glorious Revolution A “bloodless” revolution Greater power of Parliament in England An example of shared power of the monarch and the people American & French Revolution Napoleon- Codes James Watt improves the Steam Engine Transportation Locomotive is an important form of transportation that changes life in Europe Robert Fulton’s steamboat speeds ocean travel Commerce & Communication is enhanced (food supply improves) Henry Bessemer Process to make steel Steel is cheaper to produce People whose ideas and inventions change the world Sir Isaac Newton Eli Whitney Henry Bessemer Match their breakthroughs Louis Pasteur Edward Jenner Karl Marx Isaac Newton Theory of Gravity Laws of Motion Writers advocate liberty and reason Adam Smith, 1776 writes The Wealth of Nations, explains a free economy & Laissez Faire policies Law of Self Interest-competition & supply and demand Factories Mercantilism Food supply Congress of Vienna “The Sword” Giuseppe Garibaldi Fought in the effort to unite Northern and Southern Italy Otto von Bismarck and German Unification Led Germany Realpolitik all means are justified to achieve and hold power Imperialism in Africa Ottoman Empire Carving up China U.S. in China Open Door Policy of free trade in China with out conflict Revolution in Russia Rise of Communism led by Lenin…the Soviet Union formed Continued by Joseph Stalin 5-year plans for agriculture and industry The Big Four at Wilson’s 14 the Treaty of points Versailles League of Nations War Guilt Clause World-wide depression follows WW I Manhattan Project & the Atomic Bomb Project to develop the atomic bomb in New Mexico World War II D-Day, Europe is liberated Island hopping across the Pacific Marshall Plan to rebuild Europe MacArthur rebuilds Japan Cold War The Berlin Airlift The Marshall Plan Truman Doctrine – policy of containment NATO & Warsaw Pact Berlin Wall erected in 1961 English domination of India ends after World War II Gandhi & the idea of civil disobedience frees India of British rule after 200 years Communist Leaders Stalin leads Soviet Union Mao rules China Split Spy planes discover that the soviets have placed missiles in Cuba (1962) Kennedy orders a blockade Soviets agreed to remove missiles if the U.S. would agree not to invade Cuba and if they removed missiles from Turkey United Nations Apartheid Apartheid, policy of racial segregation formerly followed in South Africa. The word apartheid means “separateness” in the Afrikaans language. Fall of the Soviet Union 1989, satellite nations forced democratic elections Berlin Wall comes down East & West Germany reunited World’s Hot Spots The Middle East Persian Gulf Ongoing Middle East conflict Oil OPEC European Common Market Progress toward greater unity among the 12 member states of the European Community was mixed during 1991. Nevertheless, leaders of the member states, at a summit meeting in Maastricht, the Netherlands, in December, succeeded in agreeing on two treaties that committed them to monetary union by the end of the decade and gave the Community a clear political profile for the first time. World Geography Geographic features Rivers Mountains Oceans How they influence world history