* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - 20th Century History
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Italian resistance movement wikipedia , lookup
Operation Torch wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
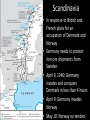
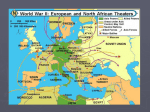
World War II: In Europe The War in Europe in Forty Minutes September 1939 • September 1: Germany invades Poland • September 3: Britain, France, Australia, NZ declare war on Germany • Superior airpower and armor (tanks) quickly surround Polish forces and eliminate them • Soviets attack from the East • September 27 Warsaw surrenders Scandinavia • In response to British and French plans for an occupation of Denmark and Norway • Germany needs to protect iron ore shipments from Sweden • April 9, 1940: Germany invades and conquers Denmark in less than 4 hours • April 9: Germany invades Norway • May 10: Norway surrenders The Phony War and the Low Countries • What have the Allies been doing since Sept of 1939? • Raising armies, blockading Germany, and the French have been in their fortresses on the French border, the famous, impervious…Maginot Line! • What could the Germans do?..Schlieffen Plan Part II • May 10, 1940- Germany attacks Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands • May 15, The Netherlands surrenders • May 26 Germans surround British and French forces at Dunkirk. British miraculously escaped. Fall of France and Vichy • May 27 Belgium surrenders • June 10: Italy declares war on Britain and France • June 14: Germans enter Paris • June 22: France and German Armistice. New French government established. Called Vichy France and declared neutral • June 28 Charles DeGaulle recognized as head of Free French Battle of the Atlantic • Britain again blockaded Germany • Germany responded by submarine warfare..sound familiar? • In 1942, 452 ships were sunk by the Germans and England was almost starved into surrender • By the end of the war Germany had sunk 2,177 ships and killed more than 30,000 sailors • By 1944, destroyers, planes, greater ship production and the breaking of the German code, had mostly ended the battle with a victory for the Allies War in North Africa • August 1940: Italy attacks British colonies in Africa (Egypt) • After brief successes Italians are pushed back, losing half of Libya and all of Ethiopia • In 1941 Hitler sends Rommel • British pushed out of Libya and far back into Egypt • By 1942, Germans had out run their supplies (British control of the Mediterranean) and are forced out of Egypt and Libya and back into Tunisia Battle of Britain • After the fall of France, Hitler’s next goal was the invasion of Britain • To do so he needed to defeat the British air force (RAF) • Beginning in July of 1940 Germans began bombing campaign of Britain and all Allied ships in the English Channel • German bombing killed more than 43,000 civilians • Britain eventually wins due to superior radar and fewer pilot losses (shot down British pilots live to fly again) • Beginning in 1940, Britain responded by bombing German cities Yugoslavia and Greece • 1940 and 1941 Romania, Hungary, and Bulgaria join the Axis • Oct. 1940: Italy declares war on Greece, invades and then is drive far back into Albania • British troops arrive in Greece • March 1940 Yugoslavia joins Axis, then coup overthrows the govt. Yugoslavia quits Axis • Germany invades Yugoslavia and Greece Operation Barbarossa • June 22, 1941: German surprise attack on the USSR • Most of the Soviet air force is destroyed on the ground • By late July Germans were bombing Moscow • By August they had surrounded Leningrad (St. Petersburg) • In September the first snows begin to fall slowing further German advances Operation Torch • Nov 1942: British, American and Free French forces land in North Africa • Some Vichy French forces fight them, others surrender • Germany invades Vichy France • By May of 1943 all Axis forces in North Africa have been neutralized Leningrad & Stalingrad • Leningrad was surrounded by German forces for 900 days • 632,000 people died including soldiers and civilians • Germans were finally stopped at Stalingrad • Hitler and Stalin both refused to allow their armies to retreat and poured as many resources as possible • Battle of attrition which Stalin won • Germans lost 841,000 men • Soviets lost 1.1 million • It was the first major battle the Germans lost in World War II The Soviet Advance-Kursk to the Ukraine 1943 • After Stalingrad the German army was in retreat • In an attempt to stop the advancing Soviets they met at Kursk • Germans lost • Casualties: German 170,000, Soviets unknown • The Germans were to never regain the initiative as the Soviets pushed them back into the Ukraine and beyond The Invasion of Italy and Italy switches sides…imagine that! • July 1943 US, British, and Canadian forces invade Sicily (the football of Italy) • Allied forces made it about half way up the boot • King Victor Emmanuel deposed Mussolini and Italy joined the Allies • Mussolini was imprisoned The Rescue of Mussolini and the Gustav line • September 1943 Mussolini was rescued from prison in a raid by German special forces led by Otto Skorzeny • Mussolini was placed in charge of northern Italy a new country called the Italian Social Republic • Strong German resistance in the mountains, especially at Monte Casino, kept the Allies from advancing further North. D-Day • June 6, 1944 • US, British, and Canadian forces landed on the beaches of Normandy in France • Had the Allies failed the war might have turned out differently • By August the Allies were approaching Paris Liberation of Paris • By August 25, Paris was liberated • The Allies allowed DeGaulle to lead the entry • By the beginning of September Brussels and Antwerp had been liberated Battle of the Bulge • German final last gasp • Attempt to break Allied lines and recapture the Low Countries and make a treaty with the Allies • Germans expected to be able to join the Allies to fight the Soviets • Lack of fuel and airpower leads to German defeat Soviets in Poland and the Warsaw Uprising • August 1944: Allies ask Polish Resistance to stage an uprising in Warsaw to help the advancing Soviet army • Soviet army stops its advance and allows Germans to deal with Polish Uprising • This allows Soviets to put in place a pro-Communist government since all the other resistance fighters had been dealt with by the Germans Hitler’s Suicide and the End of the War • August 1944: Romania and Bulgaria fall to the USSR • January 1945 Hungary falls to USSR • April 1945 Soviets enter Berlin • Hitler commits suicide in his bunker • Soviet and Allied forces meet at the Elbe River • May 8, 1945 War in Europe ends