* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Warm-Up Question
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Swedish neutrality wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
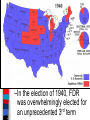
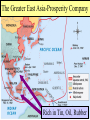
■Essential Question: –What factors led the United States to shift from isolation in the 1920s & 1930s to an active war participant by 1941? ■Warm-Up Question: –What caused World War 2? –How do these factors compare to the reasons for the outbreak of World War 1? American Isolationism & Foreign Policy in the 1920s & 1930s Foreign Policy in the 1920s & 1930s ■After WWI, the U.S. assumed a selective isolationist foreign policy –Americans wanted to maintain the economic boom of the 1920s & were desperate for an answer to the depression in the 1930s –But, the U.S. did play an active role in attempts at international disarmament & economic stability In 1924, Hoover negotiated a reduction in The U.S. Foreign Debt Commission Foreign Policy: Economic Policy German debt, anportion extended canceled a large of time theseperiod debts, to but repay debts, &some U.S. the loans to help Germany ■In the 1920s, most divisive insisted that of the money be repaid make payments issue to France & England international was war debts: The Dawes Plan helped stabilize the the German –European nations owed U.S. economy, allowed Germany to repay the $10 billion; Attempts to reclaim Allies, and helped France & England repay these debts ledUnited to anti-American their debts to the States sentiment in Europe –When Germany could not repay $33 billion in reparations, the U.S. negotiated the Dawes Plan European Debts toHyper-inflation the U.S. in Germany by 1923 Foreign Policy: Economic Policy ■But the Great Depression made post-war recovery in Europe difficult in the 1930s: –The Hawley-Smoot Tariff in 1930 limited European attempts to sell their goods in the U.S. –The U.S. was unable to provide loans, leaving Germany unable to repay reparations & Europe unable to repay its war debts The USA, England, Japan, Italy, & France Foreign Policy: International Peace But, The neither Nine-Power the NineTreaty or Four-Power reaffirmed Acts England, USA, Japan, France signed the Foursigned the Five-Power Treaty & agreed to limit had provisions the Chinese to enforce Open-Door these Policy agreements ■The USA never joined the League Power Treaty to collective construction ofagreeing battleships & aircraft security carriers of Nations, but did play a role in attempts to avoid future wars: –At the Washington Disarmament Conference in 1921, world leaders agreed to disarmament, free trade, & collective security –In 1928, almost every nation, including the USA, signed the Kellogg-Briand Pact, renouncing war as a tool of foreign policy Foreign Policy: International Peace ■These agreements did not last: –Japan needed raw materials to continue its industrial expansion –Japan began to create an Asian empire by attacking Manchuria in 1931 & China in 1937 –In both occasions, the League of Nations reprimanded Japan but chose no punitive measures Totalitarian Regimes: Hideki Tojo & Emperor Hirohito In 1937,Japan Japanese pilots bombed the USS Panay, Invades Manchuria a U.S. gunboat stationed in China, killing 3 Americans. The U.S. accepted Japan's apology & promise against future attacks Unlike the USS Maine or Lusitania, few Americans called for war against Japan Totalitarian Regimes: Benito Mussolini Totalitarian Regimes: Hitler The Munich Pact “Peace in our time” Rome-Berlin-Tokyo Axis Foreign Policy: International Peace ■In the 1930s, FDR & Congress were too preoccupied with the Great Depression to adequately plan for new world conflicts involving totalitarian dictators ■The rising threat of war in Europe & Asia strengthened Americans’ desire to avoid involvement in another world war Foreign Policy: Citizen Attitudes ■In the 1920s & 1930s, most Americans wanted to avoid another “meaningless war” –Munitions makers & bankers were labeled “merchants of death” & were blamed forRoad to Historian Walter Millis’ America’s WarAmerican blamed Wilson & British propaganda involvement in WWI for “duping” the U.S. into WWI –Passivism swept across college campuses; Students staged “walk-outs” & anti-war rallies Veterans of FUTURE Wars The “Lost Generation” All Quiet on the Western Front portrayed WWI as brutal The Neutrality of 1935 banned The Act Neutrality Acts arms sales to nations at war & warned citizens to sail on belligerent ■The not “merchants of death”ships charges The were Neutrality 1936Dakota banned Senator led Act by of North loans to any warring nation Gerald Nye from 1934 to 1936: The Neutrality Act of 1937 made –Reaction to the Nye Committee the 1935 & 1936 acts permanent report led to popular support to avoid making the same mistakes that led America to enter WW1 –Congress passed 3 neutrality acts to avoid future wars The Clouds of War (3.37) ■Essential Question: –How did the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor alter the course of World War 2? ■Reading Quiz Ch 25A (888-904) The Road Towards American Intervention From Neutrality to Undeclared War But…FDR was able to get $1 billion ■As Europe headed toward war, from Congress to expand the U.S. navy FDR openly expressed his favor for intervention & took steps to ready the U.S. for war –In 1937, FDR unsuccessfully tried to convince world leaders to “quarantine the aggressors” –Everything changed in 1939 with the Nazi-Soviet Pact & the German invasion of Poland The War Comes to Europe (9.11) From Neutrality to Undeclared War “The destroyer-for-bases deal is the most ■When WW2 began in“merchants 1939, of Still attempting to avoid more important action in the reinforcement of death” in the banking our national defense thataindustry has been&taken Congress imposed cash carry since the Louisiana Purchase” policy to aid the Allies: —FDR –The U.S. would trade with the FDR responded with all-out aid to Which eased the rigid restrictions of Allies but would not offer loans theNeutrality Allies but Acts did not call for warto the of 1935-1937 –The U.S. would not deliver allow the US to aid England & France American products to Europe ■In addition, FDR traded 50 old Still destroyers attempting towith avoidEngland losing American for 8 lives at sea by German submarines naval bases in Western Europe From Neutrality to Undeclared War “The future of western Isolationistscivilization Interventionists is being decided Groups like the ■ Were appalled by the■battlefield upon of Europe” Committee to —CDAAA chair, William this departure from Allen White Defend America by neutrality & FDR’s Aiding the Allies involvement of the called for unlimited U.S. in foreign war aid to England ■ Their “fortress of ■ They argued that America” idea St. Louis that Dispatch headline: the events in argued “Dictator Roosevelt Europe did impact Germany was not Commits Act of War” a threat to the U.S. the security of U.S. From Neutrality to Undeclared War ■By 1940, “interventionists” had the majority of American public sentiment on their side: –in 1940, Congress appropriated $10 billion for preparedness –FDR called for America’s first ever peacetime draft –In the election of 1940, FDR was overwhelmingly elected for an unprecedented 3rd term From Neutrality to Undeclared War ■By 1940, England remained the only active opposition to Hitler but was running out of money ■FDR called for a Lend-Lease Act: –U.S. can sell or lend war supplies to Allied nations –Congress put $7 billion to allow England full access to U.S. arms U.S. Cash and Carry Program Lend-Lease Supply Routes From Neutrality to Undeclared War ■England desperately needed help escorting U.S.-made supplies through the u-boat infested Atlantic –FDR allowed for U.S. patrols in the western half of the Atlantic –German attacks on U.S. ships in 1941 led to an undeclared naval war between USA & Germany U.S. Cash and Carry Program From Neutrality to Undeclared War ■In 1941, FDR & Churchill met to secretly draft the Atlantic Charter: –The U.S. & Britain discussed a military strategy if the USA were to enter the war –They discussed post-war goals of free trade & disarmament ■In 1941, Germany broke the Nazi-Soviet Pact & invaded Russia From Neutrality to Undeclared War ■FDR brought U.S. to the brink of war & opened himself to criticism: –In Sept 1941, polls showed 80% of Americans supported remaining neutral in WW2 –FDR had to wait for the Axis to make a decisive move…which Japan delivered on Dec 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor The U.S. Enters World War 2 (3.49) Showdown in the Pacific ■Japan took full advantage of the European war to expand in Asia: –Attacked coastal China –Seized French & Dutch colonies in East Indies & Indochina –Signed the Tripartite Pact with Germany & Italy in 1940 ■FDR retaliated against Japan with fuel, iron, & oil sanctions The Greater East Asia-Prosperity Company Rich in Tin, Oil, Rubber Showdown in the Pacific ■In 1941, the U.S. & Japan were This wastoreally a stall tactic resolve intended unable diplomatically to hide Japanese military preparations their differences, so the USA: for an the attack onJapan Pearlwanted Harboran end U.S. wanted –Froze all Japanese assets USA Japanese removed to sanctions & in a free from China hand to China –Banned all oil sales to Japan ■Hideki Tojo sent an envoy to negotiate for a resolution…but secretly ordered an attack on the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor On Dec 7, 1941, the U.S. naval fleet in the Pacific was crippled by the attack; 8 battleships were sunk & 2,400 Americans were killed Showdown in the Pacific ■After Pearl Harbor: –Congress declared war against Japan on Dec 8, 1941 –Italy & Germany declared war on the U.S. on Dec 11, 1941 ■American public opinion The U.S. now was faced now a possible war… fully behind the war2-ocean effort to defeat the fascist threat in Europe …but Germany was still seen as theagainst primary Japan danger & to seek revenge