* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
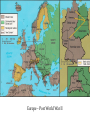
Objectives Know the key events that shaped the course of World War II in Europe Invasion of Poland (1939) • September 1, Germany and Russia invade Poland • September 3, Great Britain and France Declare War on Germany • Poland surrenders on 27 September • Period in inactivity termed ‘The Phony War” – French believed this signaled that Germany was preparing its static defenses (akin to WWI trench warfare) Invasion of France (1940) • April/June: Germany conquers Denmark and Norway in the north to secure its right flank and access to the Atlantic • May: Germany invades the Netherlands, Belgium enroute to its invasion of France • June 14: Germany marches into Paris • June 22: France surrenders and the Vichy government is established • Battle of Britain (“The Blitz”) begins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 43zVRey2XEs Operation Barbarossa • The Germans invaded the Soviet Union in the summer of 1941, and looked poised to take Moscow by October that year. • The German Blitzkrieg technique was as devastating in Russia as it had been in the rest of Europe. One week into the German invasion, 150,000 Soviet soldiers were either dead or wounded. • By October 1941, three million Soviet soldiers were prisoners of war. • War of Annihilation • September 1942 – February 1943: Battle of Stalingrad • Major Turning Point in European Theater • German Army attacking Stalingrad surrendered Feb 2, 1943. Allied Initial Stages: 1941 - 1942 • Having survived the Blitz and the evacuation of its army at Dunkirk, Great Britain needed time to gather her strength in Europe. • British initial strategy was to hold Africa (Suez Canal) while using Strategic Bombing to strike at German Industry. • While the United States enters the war following Pearl Harbor, she needs time to build-up her forces in Europe • The Second Front Debate • Operation Torch begins 8 Nov 1942 Invasion of Sicily and Italy • July 1943 American and British forces land in Sicily. Tough terrain and resistance initially slows Allied advances • 17 Aug – Sicily surrenders with fall of Messina • Italian government begins secret negotiations with Allies to sue for peace. Germany disarms the Italian military and digs in to defend Italy • With Sicily now secure, the Allies begin the invasion of Italy in Sep 1943 • Fighting up the spine of Italy is difficult, but on 4 June 1944 (two days prior to D-Day), U.S. forces enter Rome. • Italy finally surrenders on 2 May 1945 D-Day to Market Garden • While there was significant debate among the Allies on the timing of a cross-channel invasion of France, the D-Day invasion begins on June 6, 1944. • However, while maintaining securing a foothold is one thing, sustaining a drive into Germany is another. Operation Market Garden launched on 17 Sept 1944 was designed to relieve this concern The Beginning of the End • In a last ditch effort to stabilize the Western Front, Germany commits her last reserves of tanks and infantry. On 16 Dec 1944 German forces struck the lightly held sector in the Ardennes, cutting driving a wedge in the Allied lines and surrounding the U.S. 101st Airborne. • Short on fuel and pounded by U.S. aircraft and armor the last German offensive collapses by the end of January 1945. • Also in Jan 1945, Russia launches a large-scale offensive in Poland and East Prussia that carried their troops to within forty miles of Berlin. • German forces that survived the Battle of the Bulge had to be hurriedly shifted eastward to meet the growing Russian threat. • April 16, 1945 Russia has surrounded Berlin • Hitler commits suicide in his bunker on April 30th, with the formal surrender of Germany on 7 May 1945 (8 May declared as VE Day) Europe – Post World War II Objectives Know the key events that shaped the course of World War II in Europe