* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 13
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Wehrmacht forces for the Ardennes Offensive wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Hürtgen Forest wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
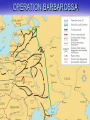
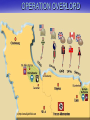
GC unit 11 Part 1 World War II The US position Still viewed all of this as a “European problem” – Isolationism – The Neutrality Acts – Eventually these were relaxed and we began to aid the allies Lend lease Act Destroyers for naval bases – July 1941 Japanese occupy Indo-China at the expense of the French (US leads a world wide oil embargo and sent aid to the Chinese) Pearl Harbor December 7th 1941 Hitler’s Conquests in Europe Blitzkrieg (Panzer divisions of 300 tanks) – Infantry and air support April 1940 he attacked Denmark and Norway Then the Netherlands (2 days) and Belgium (2 weeks) Hitler avoided the Maginot Line by invading France through Luxembourg on June 10th 1940 – The Miracle of Dunkirk: 300,000 saved but all equipment was lost (DeGaulle and the Free French) – Germans reach Paris on June 14th 1940 and set up the Vichy government under Henri Petain The Battle of Britain From August of 1940 until March of 1941 Hitler bombed England to soften them up for invasion (15,000 killed in London in 2 months) – British bomb Berlin and caused the Luftwaffe to shift focus to London – Hitler shifts focus to London (allows British industry to produce) – RAF used radar and US help to fight off the attacks – Churchill took power in May of 1940 (good relationship with FDR and the US) THE BATTLE OF THE ATLANTIC WHEN? 1942-43 WHERE? N. ATLANTIC SEA LANES WHO? – GERMAN U-BOAT FORCE (WOLFPACKS) – U.S. / BRITISH NAVIES & MERCHANT SHIPS WHAT? – GERMANS ATTEMPT TO CUT OFF FLOW OF SUPPLIES FROM U.S. TO BRITIAN – ATTACKS START CLOSE TO U.S. SHORE – COMBAT EVENTAULLY MOVES FURTHER INTO THE ATLANTIC – U.S. USES SONAR & RADAR TO HINDER GERMANS RESULTS? – HEAVY LOSSES ON BOTH SIDES – BY MID-1943, ALLIES HAVE WON CONTROL OF THE ATLANTIC WW II GERMAN U-BOAT OPERATION BARBAROSSA THE EASTERN FRONT June 22, 1941: – Operation Barbarossa / Germany invades Russia – Why? Lebensraum: Definition – Living Space for Germans Nazi Racial Theories – Slavic (Russians, Poles, etc.) considered inferior to Germans – Russia’s Jews needed to be eliminated – Wanted to force GB to sign a treaty by eliminating an important potential ally Resources: Land, Food, Oil Communist “threat” / desire to destroy “Bolshevism” Hitler’s mistrust of Stalin STALINGRAD When? October 1942 February of 1943 Where? Stalingrad (Southern Russia) Why? – German attempt to capture / occupy oil fields in S. Russia – Then Germans can control important Volga River supply route What happens? – – – – – Aug.-Oct.: German 6th Army seizes Stalingrad Oct.-Nov.: Russians surround / cut off Germans Nov.-Feb.: German Army starved / casualties high Feb: German 6th Army surrenders 91,000 prisoners ***Russian casualties (military & civilian): 1,250,000 (more than US in the entire war) STALINGRAD: Turning point in European Theatre THE NORTH AFRICAN & ITALIAN CAMPAIGN WHEN? Nov.’42-1944 WHO? ALLIES: – U.S. FORCES: DWIGHT D. EISENHOWER – BRITISH: BERNARD MONTGOMERY – GERMAN AFRIKA KORPS: ERWIN ROMMEL ***ROMMEL: “THE DESERT FOX” WHY IMPORTANT? – CONTROL OF MEDITERRANEAN SEA – ALLIES THOUGHT IT WAS “SOFT UNDERBELLY” OF EUROPE BATTLE OF EL ALAMEIN: – TURNING POINT IN NORTH AFRICA – BRITISH VICTORY RESULTS? – ALLIES FORCE AXIS TO USE UP VALUABLE RESOURCES – MUSSOLINI LOSES POWER IN ITALY ; LATER KILLED – ALLIES CONTROL MEDITERRANEAN Italy Surrenders July 1943 allies invaded Sicily to open a second front in Europe – Mussolini had been deposed and arrested in the Spring of 1943 – Italians surrender to British and US not USSR – Germans divert troops to bail out Italy, rescue Mussolini and restore him as the leader in German controlled N. Italy OPERATION OVERLORD JUNE 6, 1944 GOAL: – ALLIED INVASION OF NORTHERN EUROPE – MASSIVE AMPHIBIOUS & AIRBORNE INVASION – TO ESTABLISH AN ALLIED ”BEACHHEAD” IN N. FRANCE WHO? ALLIES (156,000 TROOPS, 4,000 LANDING CRAFT, 6000 SHIPS, 11,000 PLANES) – U.S.: ARMY AIRBORNE, AIR CORPS, INFANTRY, RANGERS U.S. NAVY, U.S. COAST GUARD – BRITS.: ARIBORNE, R.A.F., INFANTRY NAVY – CANADIANS: INFANTRY – FREE FRENCH: INFANTRY, NAVY WHERE? NORMANDY BEACHES, FRANCE GERMANS EXPECTED ATTACK TO ARRIVE IN DIFFERENT PART OF FRANCE WHY? GEORGE S. PATTON USED AS “DECOY” HITLER WOULD NOT ALLOW REINFORCEMENTS MOVED TO NORMANDY OPERATION OVERLORD THE FALL OF GERMANY LATE 1944: GERMANY IS ON VERGE OF DEFEAT DEC., 1944: GERMANS TRY ONE LAST GAMBLE TO WIN WAR: – ARMORED / INFANTRY OFFENSIVE IN WEST – BATTLE OF THE BULGE – GERMANS LOSE CAN’T REPLACE LOSSES 120,000 KIA/MIA, 600 TANKS, 1600 PLANES APRIL, 1945: SOVIETS SEIGE BERLIN BATTLE OF BERLIN: – HITLER COMMITS SUICIDE – UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER – THIRD REICH HAS ENDED MAY 8, 1945: V-E DAY War in the Pacific December 7th 1941 Pearl Harbor US declares war on Japan – Japan scores early victories until the Battle of Coral Sea (1st Naval battle where ships did not see each other) – Turning point was Battle of Midway June 6th 1942 US destroyed 4 Japanese Carriers (Chester Nimitz) – Island Hopping – Douglas MacArthur and the Philippines – Harry Truman (The Manhattan Project) Hiroshima and Nagasaki (Aug 1945) V-J Day Aug 15th 1945