* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06Victory in Europe
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
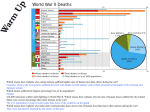
Turning the Tide The Allied Powers victory in Europe Objectives: 138. Describe the invasion of France at Normandy. 139. Define the Holocaust. 140. Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. 141. Recognize the accomplishments of the Yalta Conference. 142. Describe the events that led to German surrender and V-E Day. Objective 138: Describe the invasion of France at Normandy. Allied forces had gained momentum from defeating the Axis Powers in North Africa, naval success in the Atlantic, and the invasion of Italy. The invasion of France was named Operation Overlord. Objective 138: Describe the invasion of France at Normandy. The Allied forces were led into battle by General Dwight Eisenhower. Allied forces gave false clues to keep Germans guessing on location of invasion. Allies landed in Normandy on D-Day, June 6, 1944. Objective 138: Describe the invasion of France at Normandy. Germans secured the beach with concrete bunkers, tanks and mines. Difficult fighting commenced, and it took about a month for Allied troops to penetrate 20 miles into France. On August 25, 1944, the Allied forces had liberated Paris. Change in momentum - map While the invasions of Italy and France were successful , the Soviet Union had won the Battle of Stalingrad in the east, and began to push German forces back into Europe. As the Soviet Union, Great Britain, the United States, and the other Allied nations liberated more and more of Europe, they discovered what the Nazis had been doing in the concentration camps. Objective 139: Define the Holocaust. The Holocaust was Nazi Germany’s systematic slaughter of European Jews. Millions of Jews were put under German rule as Germany expanded throughout Europe. Approximately six million Jews were killed either at their capture, or in concentration camps. This treatment of Jews was called the “final solution of the Jewish question” by Hitler. Objective 140: Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. Transportation to the camp. Objective 140: Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. Jews were herded into railroad freight cars, usually packed in at least double what was provided for. There was standing room only for the entire trip, which could last several days. Water buckets would be passed around the train, but not everyone would get a drink. Passengers had not place to use the restroom. Many died in those few days from dehydration, disease or heat exhaustion. Objective 140: Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. Life in the camps Objective 140: Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. Those considered too weak to work were immediately taken into the “showers”, which were actually gas chambers. Afterwards, their bodies were cremated. Those fit to work would provide slave labor in the camps until they became too weak, at which point they would also be killed. Many were killed in mass firing squads, and buried in communal graves. Nazi doctors and scientists used prisoners for medical or science experiments, or used their bodies to make products. Dr. Josef Mengele Objective 140: Describe the conditions in German concentration camps. Death in the camps The Allied Powers by summer of 1944 had Meanwhile, the Allies had taken control the momentum in the war. of North Africa, invaded Italy and France, and were pushed the Axis Powers east. The Soviets had pushed Germany west, out of Asia. The time had come for the “big three” (Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin) to make plans for post war peace. Objective 141. Recognize the accomplishments of the Yalta Conference. What did each of the big three seek? Churchill – democratic systems for European nations that were liberated from Germany. Roosevelt – Soviet assistance in the Pacific War through an invasion of Japan. Stalin – Soviet sphere of influence in Eastern Europe. Objective 141. Recognize the accomplishments of the Yalta Conference. What did they agree to? Soviet Union would declare war on Japan three months after a German surrender. They discussed the return of liberated nations to self government. They agreed to divide Germany up after the war. They made plans for a new international peace organization, like the League of Nations. Objective 142. Describe the events that led to German surrender and V-E Day. September 1944: Allied crossed the German border. December 1945: Germany launched their final offensive against the Allies. At the Battle of the Bulge, after Germans created a bulge in the Allies’ lines, the Allies regrouped and pushed the Germans back rapidly. Objective 142. Describe the events that led to German surrender and V-E Day. In the spring of 1945, the Allied Powers were pressing further into Germany from both sides: the Soviet Union from the east, the British and Americans from the west. April 30, 1945: Hitler committed suicide in a bunker in Berlin. Objective 142. Describe the events that led to German surrender and V-E Day. Germany surrendered unconditionally on May 7, 1945. May 8, 1945 was known as V-E Day (Victory in Europe), as the end of the five years of fighting in Europe.