* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WW2 Retaking Europe
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Forced labor of Germans in the Soviet Union wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
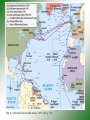
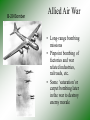
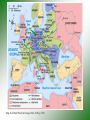
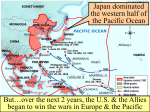
World War II Retaking Europe World War II • ALLIES: – Great Britain (and commonwealths of the British empire) • • • • Australia Canada India South Africa – Soviet Union (Russia) – United States of America – France (Free France) • [The French government had fallen to Nazi Germany in the spring of 1940 and was called ‘Vichy France’] • AXIS: – – – – Germany Italy Japan Miscellaneous conquered countries The Atlantic Charter • • • • August 1941 British Prime Minister: Winston Churchill U.S. President: Franklin D. Roosevelt (FDR) Declaration of Principles to guide the United States and Great Britain during the course of the war. – – – – – No territorial gain for US and Britain No territorial changes without peoples consent Territorial self-determination Safe boundaries in Europe Formation of an organization of world nations Americans enter the War • Battle of Britain (1940) German bombing of England • Nazi Germany controlled nearly all of western Europe • Nazi Germany had invaded the Soviet Union (USSR or Russia) • Japan attacked US naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaiian Islands Battle of the Atlantic • Food and supplies from U.S. to Britain destroyed by Nazi submarines = “wolf packs” • U.S. established convoy system • Development of “SONAR” to locate vessels underwater • Essentially victory for the Allies by 1942 Map 26.1 World War II in the North Atlantic, 1939–1943 (p. 752) North Africa Campaign • Germans invaded North Africa with goal of reaching oil fields of the Arabian peninsula • German General Erwin Rommel (“the Desert Fox”) • November 1942, Battle of El Alamein (Egypt) - British victory • Americans came in June of 1942 • Allies defeated Axis in North Africa by May,1943. • Casablanca (Morocco) Conference in January 1943 - Allies planned to deal with Europe first Allied victories - 1942 QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Allied Invasion of Italy • Allies invaded Sicily, July, 1943 • Mussolini removed as fascist leader of Italy (1943) • Brutal fighting • Heavy American losses • Famous battles: – Anzio – Monte Cassino • Allies captured Rome, May 1944 • Nazis surrendered in N. Italy, April 1945 War in the Soviet Union (USSR, Russia) • Nazis invaded USSR in June 1941 • Needed oil and food • Germans at first welcomed as liberators, later hated - executed Russian citizens • Germans almost captured Moscow, never did • Germans besieged Leningrad for 3 years • Battle of Stalingrad (Enemy at the Gates - movie) – USSR victorious – German casualties - 300,000+ – Russian casualties - est. 1.1 million Stalingrad QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. B-29 Bomber Allied Air War • Long-range bombing missions • Pinpoint bombing of factories and war related industries, railroads, etc. • Some ‘saturation’or carpet bombing later in the war to destroy enemy morale Invasion of Western Europe • Planned for spring of 1944 • Code named: OPERATION OVERLORD • More famously known as D-Day • June 6, 1944 D-Day, June 6, 1944 • Supreme Commander: General Dwight D. Eisenhower • 150,000 Allied troops invaded the French coast of Normandy • Heavily defended by Nazi soldiers and defenses (the Atlantic Wall) • Famous places: – Omaha Beach, Caen (France), Ste. Mere Eglise • Movies: – Saving Private Ryan – The Longest Day Hitting the Beach at Normandy (p. 771) D-Day, June 6, 1944 QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Liberation of France • French Resistance (to the Nazis) helped • August 25, 1944 Paris liberated • Most of Western Europe liberated by late 1944 Battle of the Bulge: (the Ardennes Forest) • December 1944 • Last desperate German counter-offensive • Temporarily isolated small units of the American Army • Largest battle in Western Europe • Casualties: – US - 80,000 – German - 100,000 Map 26.4 World War II in Europe, 1944–1945 (p. 769) End of World War II in Europe • March 1945 - Allies crossed Rhine River • Soviet troops advanced from the east, captured Berlin • USSR - lost 11,000,000 troops • Germany - lost 3,000,000 troops • April 25, 1945 - Russian and American troops met at the Elbe River in Germany Germany Surrenders • Hitler commited suicide, April 30, 1945 • German surrender, May 8, 1945 - Victory in Europe (V-E Day • Yalta Conference - Feb. 1945 • FDR died in April 1945 Vice-President - Harry Truman became president German Surrender (Victory in Europe) V-E Day QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. The Big Three at Yalta (p. 775) Yalta Conference (in the Soviet Union) • February, 1945 • FDR, Churchill, Stalin • Divided defeated Germany, divided Berlin into 4 zones • Stalin broke all his promises from Yalta: – dominated Eastern Europe (not free) – No free elections – Not enter war against Japan in the Pacific