* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US Involvement in World War 2
Mittelbau-Dora wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Collaboration with the Axis Powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
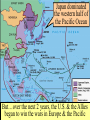
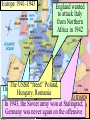
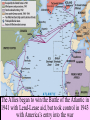
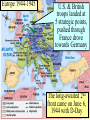
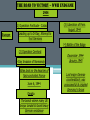
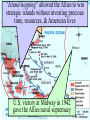
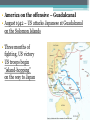
Warm-up (in notebook) 1. What was the cash-carry program? Lend-lease program? 2. How did FDR push the US towards war? 3. What was the significance of Pearl Harbor? How was the US Navy affected? ■Essential Question: –What role did the U.S. play in winning the wars in Europe & the Pacific? When the U.S. entered WW2 in late 1941, Japan dominated Germany controlled victory seemed remote the western half of almost all of Europe the Pacific Ocean Germany pressed into Russia Axis armies controlled Northern Africa & threatened But…over the next 2 years, the U.S. & the Allies the Suez Canal began to win the wars in Europe & the Pacific Europe 1941-1943 England wanted to attack Italy from Northern Africa in 1942 The USSR “freed” Poland, The U.S.Hungary, wanted Romania to attack across In 1942, troops To U.S.-Anglo win the European In 1943, the Sovietbegan armycampaign, wonItalian at Stalingrad; Nazi-controlled the 2campaign different Germany was never & again on was the offensive France by 1943 Stalin ANGRY plans were proposed “Europe First” Strategy • Allies battle U-boats in the Atlantic • German “Wolf packs” sink merchant ships • Convoys, radar help Allies Battle of Stalingrad Germany attacked Russia, June 1941 Germany was defeated by 1943 TURNING POINT of the war; Germany retreating (90,000 troops captured) The Battle of Stalingrad - Background • Germans begin “Operation Barbarossa” on June 22, 1941. • Invasion of Russia goes very quickly. By December Germans are on the verge of taking Moscow. • Russian winter halts German advance. Germans dig in, lines stabilize by spring, 1942. German Goals • Capture Stalingrad • Move southeast and capture Crimean oil fields • Use the capture of Stalingrad as propaganda in war effort Russian Response • Stalin orders all Russians who are able to fight to defense of Stalingrad. • Soviets run short on supplies • Soviet soldiers ordered not to retreat under any circumstances. • Result is fierce urban fighting. ▫ Factories and buildings become fortresses for Russians ▫ Germans call fighting in Stalingrad “rattenkrieg” War of the rats The Eastern Front The Battle of Stalingrad • Aug. 21, 1942 – Feb. 2, 1943 • One of the bloodiest battles in human history • Between 1.5 and 2 million people killed during battle. • Over 50000 Russian civilians killed during bombing raids. ▫ Ordered not to evacuate by Stalin, in order to increase the morale of defenders. Turning Point of the War • German Army eventually surrounded by Russian Army, trapped at Stalingrad. • Germans lose an entire army. • 90000 Germans captured. ▫ Only 5000 survive Russian prison camps • Germans forced to give up push for Crimean Oil fields • After Stalingrad Germans gain no new territory. The Allies began to win the Battle of the Atlantic in 1941 with Lend-Lease aid, but took control in 1943 with America’s entry into the war ■Allied invasion of North Africa ■ Operation Torch ■ Key Leaders: – Gen. Dwight Eisenhower – Gen. George Patton ■ May 1943 – German & Italian troops surrender in Tunisia • Allied invasion of Italy • July 1943 – British & American armies invade Sicily • Mussolini overthrown • Allies defeat Italy • Sept 1943 – Italy surrenders War in Europe ■ Operation Torch (November 1943) ■ Casablanca Conference (1943)—unconditional surrender of Axis ■ Battle of Atlantic—won by U. S. in 1943 ■ Sicily invaded on July 10, 1943 ■ September 1944, Italy mainland invaded ■ Anzio landings on January 22, 1944 ■ Rome fell on June 4, 1944 • British & American bombers batter Germany • To relieve pressure on Stalin & the Soviet Union, Allied bombers attack German cities • Target political & industrial centers • Tuskegee Airmen – African American squadron, protected bombers from enemy pilots • 1,500+ missions, zero causalities Carpet Bombing of German Cities • Allies begin large scale daylight bombing raids on German cities. • Designed to demoralize German citizens and destroy production capacity of Germany. • Millions of buildings destroyed, possibly as many as 500,000 German civilians killed. Europe 1944-1945 U.S. & British troops landed at 5 strategic points, pushed through France drove towards Germany The long-awaited 2nd front came on June 6, 1944 with D-Day Allied ingenuity helped win the war: Hedgerows in Normandy U.S. soldiers were trained to problem-solve rather than wait for orders The Road to Victory – WWII Endgame 1944 (1) Operation Fortitude - Calais Europe Leading up to D-Day; Attempt to fool Germans (3) Liberation of Paris August 1944 (4) Battle of the Bulge (2) Operation Overlord D-Day Invasion of Normandy Allies land on the beaches of Nazi-controlled France June 6, 1944 Omaha The beach where many US troops landed & faced heavy German resistance December 1944January 1945 Last major German counterattack; was unsuccessful & crippled Germany’s forces Operation Fortitude • Fictitious army created under command of Gen. Patton • Used phony, inflatable tanks & weapons made of cardboard • Also, fake scripted radio messages • Fooled Hitler & German intelligence, paved the way for an invasion of Normandy The liberation of Europe • Soviet forces move westward, liberating the Balkans. • Allied forces move eastward liberating France, and the low countries • In April 1945 Soviets and Americans link up at the Elbe River. Operation Overlord and After ■ Teheran Conference—Cross-channel invasion ■ June 6, 1944—landings in Normandy (5,000 U. S. casualties on Day One) ■ Paris fell August 25, 1944 ■ Battle of the Bulge, Dec. 16, 1944—January 26, 1945 ■ March 7, 1945, Bridge at Remagen seized ■ May 7, 1945, Germany surrendered Ike with Paratroopers before D-Day Operation Overlord (D-Day) – June 6, 1944 – Allied invasion of France Normandy Landing (June 6, 1944) German Prisoners Higgins Landing Crafts American troops following their landing on “Omaha” beach Yalta Conference in February 1945 ■TheTo“Big 3” met Yalta to & recognize theat independence discuss post-war given sovereignty of nationsEurope in Eastern Europe the eminent defeat of Germany: –Stalin refused to give up Eastern Europe but he did agree to “self-determination” –Stalin agreed to send Soviet troops to the Pacific after the German surrender if the USSR could keep Manchuria Soon after the Yalta Conference in Feb 1945, FDR died…and Harry Truman became president April 12, 1945 – FDR Dies Harry Truman (“Give ‘em Hell Harry”) In late April 1945, the Allies broke through the Eastern & Western Fronts forcing both Italy & Germany to surrender Hitler and Eva die together in suicide Führerbunker “Island-hopping” allowed the Allies to win The Doolittle Raid on Tokyo on April strategic 18, islands investing precious 1942without was a morale boost time, resources, & American lives U.S. victory at Midway in 1942 gave the Allies naval supremacy • Fighting in the Philippines • Allied forces attacked by Japan • Gen. Douglas MacArthur forced to evacuate • Allied troops surrender, captured, forced to march over 60 miles (Bataan Death March) • The Doolittle Raid • US planes bombed Tokyo in retaliation for Pearl Harbor; boosted US morale • Battle of Coral Sea • Japan attacks New Guinea; Allied forces (US & Australia) defeat the Japanese • Momentum shifts toward the US, confidence rising • Turning Point in the Pacific – Battle of Midway • Japan hopes to capture Midway, an American naval base in the Pacific • US commander Chester Nimitz intercepts the Japanese plans • June 4, 1942 – Japan attacks, but US is victorious • TURNING POINT: Japan retreats, US on the offensive • America on the offensive – Guadalcanal • August 1942 – US attacks Japanese at Guadalcanal on the Solomon Islands • Three months of fighting, US victory • US troops begin “island-hopping” on the way to Japan War in the Pacific ■Island Hoping and Leapfrogging ■January 1943, New Guinea Invaded ■Tarawa invaded, Nov. 20, 1943 ■Marianas secured on June 19, 20, 1944 ■Battle of Leyte Gulf, October 25, 1944 The Japanese refused to play by according to the Geneva Convention “rules” of war Iwo Jima – February 19, 1945 Bloodiest Battle in Marine Corp History (6812 die) The German surrender in May 1945, allowed World War II in the Pacific the U.S. to turn its full attention towards Japan Victories at Saipan in 1944 & Iwo Jima & Okinawa in 1945 allowed for bombings on Japan Okinawa (April 1, 1945) – largest invasion in history, 300 miles from Japan – defended by 300,000 Japanese (Kamikaze Missions) Americans bomb Japan ■ Tokyo and other Japanese cities firebombed by U.S. ■ Estimates of civilian deaths in Tokyo range from 90,000 to over 100,000 ■ Most Japanese buildings constructed from wood. War in the Pacific ■ U. S. plans to invade Japan: Operations Coronet and Olympic, but war casualties rise ■ Firebombing raids on Tokyo, March 1945 ■ Decision to use Atomic Bomb ■ August 6, 1945—Hiroshima; August 9, 1945, Nagasaki ■ Japanese sue for peace on August 14, 1945 ■ Formal Surrender on U. S. Missouri, September 2, 1945. How did we get Atomic Bombs? ■ Manhattan Project – 1942-1946 ■ J. Robert Oppenheimer, physicist – “Father of the Atomic Bomb” The Decision to Drop the A-Bomb –The U.S. military favored a fullscale invasion of Tokyo by 1946 –The Japanese refused to surrender thus far & were arming civilians for an Allied invasion –At the Potsdam Conference in July 1945, Truman gave the order to use the atomic bomb (we will address this Thursday) Enrico Fermi at the University of Chicago Triumph & Tragedy in the Pacific ■In August 1945, the USA forced Japan to surrender by dropping 2 atomic bombs ■Effect of the atomic bomb: –Revenge for Pearl Harbor –Showed the USSR that the USA had the ultimate weapon (began the Cold War nuclear arms race) Affects of the atomic bomb ■ Intense heat created by blast causes blindness. Incinerates everybody and everything in a 1 kilometer radius (0.6 miles). ■ Shockwave destroys all wooden buildings in 2 kilometer radius (1.2 miles) . ■ Radiation exposure kills people near ground zero. Many other people within a 2-3 mile radius develop various forms of cancer. ■ Bombs are estimated to have killed more than 200,000 people. Nagasaki Hiroshima Hiroshima – August 6, 1945 “Little Boy” - Dropped on Hiroshima Nagasaki – August 9, 1945 “Fat Man” – Dropped on Nagasaki The aftermath of the A-Bomb The Road to Victory – WWII Endgame 1945 Europe Pacific Hitler commits suicide by gunshot April 30, 1945 Battle of Iwo Jima Feb. 9, 1945 Battle of Okinawa April 1, 1945 Atomic Bomb – Hiroshima August 6 Atomic Bomb – Nagasaki August 9 V-J Day (Victory in Japan) September 2, 1945 V-E Day (Victory in Europe) May 8, 1945 Balance Sheet ■23 million soldiers and 33 million civilians died world wide ■War cost approximately $1,000,000,000,000 ■9 million Soviets died in Battle ■U. S. lost 294,000 servicemen in combat, 600,000 wounded, and 114,000 others killed in war related accidents. VJ Day: The War ends!