* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hitler
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
German occupation of Czechoslovakia wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
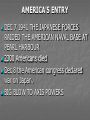
The second world war its causes and main events Causes of the war 1 The treaty of Versailles very harsh terms lopsided and biased Not properly negotiated 2 The failure of league of nations had no power had no army of its own was a toy in the hands of the victorious countries The rise of dictatorships FASCISM- ITALY- NAZISM - GERMANY – COMMUNISM- USSRFascism Spain MUSSOLINI (1922) HITLER (1932) STALIN (1928) FRANCO People developed faith in one man one party rule 3 The Rearmament of Germany German rearmament began after Hitler left 1932-4 Geneva Disarmament Conference stating that as the powers would not disarm to his level, he would rearm Germany to their level. By 1935 rearmament was well underway. This involved conscription and munitions factories. First term of the treaty was broken 4 The Remilitarization of the Rhineland (1936) Hitler marched 30,000 troops into Cologne on 7th March 1936. France, with 250,000 troops mobilised, remained passive because Britain would not support her. Britain took the view that Germany was ‘marching into her own back yard.’ 5 The Rome- Berlin Axis (October 1936) Originally Mussolini did not want to be Hitler’s ally The Rome-Berlin Axis in 1936. Mussolini and Hitler strengthened their alliance a. The Anti-Commintern Pact (1937) with Japan. The Pact of Steel (May 1939). The axis powers were formed. 6 Britain’s policy of Appeasement (May37- March 39) Chamberlain became British Prime Minister in 1937, He followed the policy of appeasing Germany, believing that all Hitler wanted to do was unite German speaking people. Chamberlain had misinterpreted Hitler’s aims. (We have the benefit of hindsight.) 7 Munich Agreement (29th September, 1938) Hitler could take the Sudetenland the following day without a plebiscite Hungary and Poland could take border districts from Czechoslovakia Britain and Germany would never go to war. HITLER GOING FOR THE SIGNING OF MUNICH PACT 8 Hitler Gained the Sudetenland (29th September, 1938) Hitler Gained the Sudetenland (29th September, 1938) The Sudetenland was lost by Austria in the Treaty of St. Germain Czechoslovakia gained 3 million German speaking people. The Sudeten German leader, Konrad Henlein, demanded a union with Germany 9 The Fall of Czechoslovakia (March 1939) So far Hitler had only taken German speaking territory, so Chamberlain could still appease Hitler. In March 1939, Hitler threatened to bomb Prague, so the Czechs surrendered. Chamberlain realised appeasement had failed, so he began to rearm Britain and guarantee peace in Poland. Nazi – Soviet pact August 1939 Secret negotiations by Stalin Hitler suddenly announced the pact Hitler Stalin The non-aggression pact was surprising. Hitler and Stalin were seen as natural enemies. When Hitler talked of taking over new land for Germany, many thought that he meant Russia. Hitler also hated Communism, the form of government in Russia German Invasion of Poland (1st September, 1939) German tanks invaded West Prussia and Posen on the 1st September 1939 using blitzkrieg tactics. (This is a lightning, sudden attack coordinating air, then land forces). Poland was in a danger of being removed from the map of europe. German army marching into Poland Europe in 1938 Germany attacks Poland Phony war /Sitzkrieg/sitting war Sept 1st 1939 attack on Poland beginning of the 2nd world war April 9th 1940 the phony war ended when Hitler attacked Denmark German forces move to Poland ,France and Austria. By June 1940, France had surrendered to the Germans Battle of Britain September 1940-May 1941: the Blitz For the following nine months, the German air force (Luftwaffe) launched repeated bombing raids on British towns and cities. This was known as the BLITZ and was an attempt to bomb Britain into submission. AMERICA’S ENTRY DEC 7 1941 THE JAPANESE FORCES RAIDED THE AMERICAN NAVAL BASE AT PEARL HARBOUR 2300 Americans died Dec 8 the American congress declared war on Japan. BIG BLOW TO AXIS POWERS Battle of Stalingrad The extent of Axis controlled area grows Second front opened up