* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Preswex: History
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Operation Green (Ireland) wikipedia , lookup
Écouché in the Second World War wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Britain (film) wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
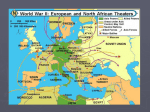
3rd Year History •WORLD WAR II •Invasion of Poland SS dressed up 29th of August • 1st September GB and France declare war. • Blitzkrieg • Luftwaffe, then Panzers then motorised infantry. Poland defeated in 5 weeks. • •Phoney War >Denmark and Norway • • • • Fighting on sea only until…. Spring 1940 Denmark defeated by Germans in a day. Norway invaded to protect neutral Sweden’s iron ore getting to Germany. Quisling installed as nazi puppet in Norway. •France • • • • • Wrong to think the Ardennes would send the Germans through Belgium (Maginot Line). Dunkirk 300,000: British and French troops evacuated in ‘Operation Dynamo’ France surrendered in the same railway carriage as Germans had. Vichy France and Occupied France. Resistance movement. •Operation Sea Lion and The Battle of Britain German plan = Sea Lion • Churchill ‘We shall never surrender’. • RAF Spitfire and Hurricanes and Radar Vs Luftwaffe. • The Blitz: Civilian cities targeted allows RAF recover. • •North Africa Libyan Oil crucial to war. • Italy incompetent. • Rommel’s Afrika corp successful at first. • Montgomery and El Alamein a turning point. • •Operation Barbarossa • • • • • June 1941: 3 pronged attack on Leningrad, Moscow and Kiev. Russian retreat. Scorched earth policy. Stalin’s ‘Great Patriotic War’ German troops and machines not able for Russian winter. Stalingrad (control of Caucasus oil fields) big turning point. •USA Joins the War • • • • USA had supplied food and weapons to GB. Allied convoys had tried to fend off U-Boat ‘Wolfpacks’. Japan’s Empire. Dec 1941 Pearl Harbour. US navy lucky as only 18 ships sunk. Eventually Alllied ships, weapons (depth charges), sonar, code-breaking and air reconnaissance won. •Allied Bombing & Allied Advance 1942-1945 • • • • • US Flying Fortresses and GB Lancasters bombed German cities and factories. German retaliation with V1 and V2. GB and US troops up through Italy. Russians push Germans back. Battle of the Kursk (biggest tank battle) •Operation Overlord (D-Day) D-Day 6 June 1944 Normandy (shallow) Utah, Omaha, Juno, Gold and Sword. • Mulberry Harbours. Gliders and parachutes. • Pluto the pipeline. • Battle of the Bulge • Hitler’s suicide and VE day 15th August 1945 • •Defeat of Japan US helped by Austalia and GB. • Island hopping. Aircraft carriers. Kamakazi. • Battles of Midway, Coral Sea and Iwo Jima. • Hiroshima and Nagasaki. • •Why the Allies Won • Bigger armies • USA wealth and weapons ‘the arsenal of democracy’ • Oil •Results of WW2 Destruction (Marshall Aid) • Nuremberg trials • Germany divided • Cold War • Super powers • European Unity •