* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download European Theater
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Pearl Harbor (film) wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Magic (cryptography) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
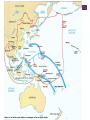
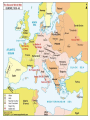
+ Warm Up: Use your notes to color the two alliances (Axis and Allies) on your World War II Maps. Create a key Remember sides! to color both + Objectives Content: Analyze primary sources from Pearl Harbor. Language: Explain the importance of the Invasions of Poland, France, and the Battle of Britain. + World War II + Theater During a time of war, the military uses the term “theater” to refer to a specific geographical area. We will cover two WWII theaters: European and Pacific. + Fronts The European Theater was broken up into the Western and Eastern Front because the European Theater was so big. + Germany Invades Poland September 1, 1939 + What happened? 1st use of “Blitzkrieg” Polish Army was defeated in a matter of weeks by Germans and Soviets. Britain and France declared War on Germany to honor their agreement to protect Poland’s borders + Importance Beginning of WWII + Germany invades France May 10-22 1940 + What happened? Days after Germany invades France, the German Army captures Paris French government agrees to disband + Importance Britain is now the only member of the Allies in Europe The invasion also helped strengthen the Nazi hold over Europe + Battle of Britain July 1940 + What happened? Air Raids by Germany against London & other major cities Germany wanted to destroy the Royal Air Force (RAF) & force Great Britain to surrender Germany believed they couldn’t carry out an invasion of Great Britain until the RAF was taken down + Importance First defeat of Hitler’s military forces + + Objectives Content: Analyze primary sources from Pearl Harbor and discuss the reliability of each. Language: Explain the causes and effects of the bombing of Pearl Harbor. + Pearl Harbor December 7, 1941 + Prior to the conflict, there was a gradual change in American foreign policy The United States was an isolationist country. Isolationists believe the United States should stay out of other country’s affairs, except in cases of selfdefense. + After Hitler invaded Poland, President Roosevelt announced the United States would remain neutral but he realized most Americans sympathized with the Allies. + The United States soon passed the Lend-Lease Act. This law, passed in 1941, allowed the United States to ship arms and supplies, without immediate payment, to nations fighting the Axis Powers. + There was also rising tensions developing between the United States and Japan because of Japanese aggression in East Asia. The U.S. cut off shipments of oil after Japan continued to invade China + On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the United States at Pearl Harbor without warning. Pearl Harbor is a navy base in Hawaii where the United States kept its Pacific Fleet + + + + In less than two hours, 19 American ships were sunk or seriously damaged, almost 200 American planes destroyed, and about 2,400 people were killed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vyoIpKGEw 8M&NR=1&feature=fvwp&safety_mode=tru e&persist_safety_mode=1 + On December 8, 1941, the United States declared war on Japan. Three days later, Germany declared war on the United States. + + Objectives Content: Defend which battle was the most important to World War II. Language: Explain the causes and effects of Japanese Internment. + Warm Up “Kenji” – Fort Minor http://youtu.be/I-L99_omies +Japanese American Internment There was a heightened Anti-Japanese fear in the United States as a result of the bombing of Pearl Harbor + While many Japanese Americans served in the armed forces, others were treated with distrust and prejudice, and many were forced into internment camps. As a result of this distrust, President FDR signed Executive Order 9066 1 2 3 4 5 6 + Executive Order 9066 It allowed the military commanders to designate “military zones” as “exclusion zones” from which “any or all persons could be excluded.” The power was used to exclude all Japanese from the Pacific Coast It directed the Army to relocate over 120,000 Japanese Americans to relocation camps. + + + + Between 110,000 and 120,000 Japanese were brought to these internment camps. Most of them were American citizens. + Battle of Midway June 1942 + What happened? Japan sent all of their military to Midway to launch a surprise attack on the U.S. Fleet U.S. Fleet was waiting for the Japanese to show up because of code breaker success U.S. defeated the Japanese in battle + Importance Turning point of war in the Pacific America begins to push Japan back + Battle of Stalingrad Begins August 1942, Ends February 1943 + What happened? Germany invaded the Soviet Union and moved into the city of Stalingrad Soviet Union sent 1 million well supplied soldiers to surround the city as winter approached. The Germans were unable to receive food and supplies and were forced to surrender. + Importance Turning point of the Eastern Front of the war. Soviet Union beings to push Germany back + D-Day June 6, 1944 + What happened? Paratroopers were dropped into Normandy, France to cut off supplies. Huge multinational coordinated sea to land invasion After sustaining heavy losses, Allied forces gained control of the coast + + + Importance Turning point of the Western Front of the war Great Britain and U.S. began to push Germany back