* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download American History Unit II- US Foreign Affairs - Waverly
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
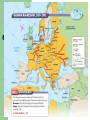
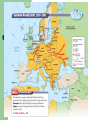
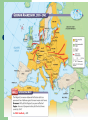
10th American History Unit IV- A Champion of Democracy Chapter 13 – Section 2 Europe Erupts Into War Europe Erupts in War The Main Idea Far from being satisfied by the actions of France and Great Britain, Germany turned to force and triggered the start of World War II. Reading Focus • How did Germany’s actions in 1939 trigger the start of World War II? • Where did German forces turn after overrunning Poland in 1939? • What developments increased tensions between the United States and Japan in East Asia? World War II Begins (01:03) The Start of World War II Neville Chamberlain believed that his policy of appeasement—or giving in to aggressive demands to maintain peace—had prevented the outbreak of war. Rival British politician Winston Churchill condemned Chamberlain’s policy of appeasement and said it would lead to war. Churchill was correct; Hitler was not appeased by gaining the Sudentenland. In 1939 Hitler gained more land by force, made alliances that he hoped would help him in the future, and attacked Poland. War Comes to Europe The Munich appeasement made Hitler want more. Signs as Non-aggression pact with Russia- which secretly gave Germany western Poland. Sept. 1, 1939 Hitler invades Poland. Sept. 3, 1939 England and France declare war on Germany. Sept. 17, 1939 Stalin’s armies move into Eastern Poland. Nationalism and the Rise of the Axis Powers (00:51) Hitler’s Actions in 1939 Czechoslovakia Alliances Poland • In March Hitler sent troops into what remained of Czechoslovakia. • Established a pact with Italy • On September 1, 1939, Hitler invaded Poland. • Czechoslovakia fell without putting up a fight. • Established a nonaggression pact with Stalin’s Soviet Union • Chamberlain finally realized that Hitler could not be trusted. • Stalin agreed not to stop Hitler’s expansion and Hitler agreed not to attack Stalin. • Appeasement had failed. • This pact shocked many in Europe. • The German military used the blitzkrieg, or “lightening war.” • Poland fought back to no avail. • By the end of the month, Poland was in German hands. Blitzkrieg The German method of attack known as blitzkrieg, or lightning war, was made possible by technological advances. The development of tanks that could move rapidly; the use of airplanes, bombs, and paratroopers; and coordinated radio communication allowed German troops to make rapid offensive moves that overwhelmed other European countries. The blitzkrieg was successful in the early years of the war but was ineffective in later years, as the Allies began to use tanks and planes in a similar manner. The New Warfare Blitzkrieg- Lightening war. Strike with lightening speed- planes, tanks, trucks, even motorcycles. Quickly overwhelm the enemy. Airpower made it all possible- striking at the very heart of defenseless nations, transformed warfare April 9, 1940 Hitler ends “phony war” and invades Denmark and Norway. One month later her rushes into Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg, thus bypassing the Maginot line. June 14, 1940 German soldiers march into Paris and France surrenders. Phoney War Germans on one side, The French behind the Maginot line The British moving into France. “Phoney War”. Only thing happening was the Soviet attack on Finland, Finns fought bravely but lost. World War II Starts How did Germany’s actions in 1939 trigger the start of World War II? Identify – Which British leader publicly condemned Chamberlains policy of appeasement? Explain – Why did the German-Soviet pact shock Europe? Predict – Do you think Stalin’s pact with Germany provided the best security for the Soviet Union? German Forces Turn to the West On September 3, 1939, Great Britain and France declared war on Germany. They became known as the Allies. The Allies did not attack Germany. Instead, they decided to wait for Germany to make its next move. They believed that Germany’s army would grow weak trying to invade France. Germany made plans to invade France through the Ardennes Forest. This was rugged terrain and the French army concentrated their defenses elsewhere. For example, the famed Maginot Line was to the south of the Ardennes. German Forces Turn to the West April 1940 Hitler invaded Denmark and Norway. This improved Germany’s access to the Atlantic. Both countries fell with little resistance. May 1940Germans invaded France. June 1940 Germans conquered the Netherlands and stormed into Belgium. Belgian, British, and French troops tried to stop the Germans in Belgium. By early June the Germans had trapped hundreds of thousands of Allied soldiers at the French port of Dunkirk. Meanwhile, German forces attacked France through the Ardennes. The Maginot Line had been bypassed. France surrendered to Germany and Italy. The unoccupied part of France was known as Vichy France. Many French leaders, including Charles de Gaulle, fled to Great Britain to organize resistance to German and Vichy control of France. Operation Dynamo - May 27, 1940 (03:05) The Nazis Conquer Western Europe (02:02) The War in Great Britain (02:36) Battle of Britain- Hitler called it “Sea Lion” (his plan to invade England) France had fallen so Great Britain was standing alone against the Nazi, Winston Churchill called “their finest hour”. Hitler sent bombers to bomb British cites during the summer and fall of 1939- the idea was to force the British to surrender. Factors in the British favor Ultra- intercepted and decoded Germany secret messages. RADAR- Radio, detecting, and rangingThey knew when the Germans are coming and where they would be. They could move the small RAF around and intercept the German bombers. British still had horrible losses. Even with Ultra- Conventry was bombed and many died. Germans forced to postponed the invasion. Winston Churchill Speeches June 4, 1940 – “We shall defend our island whatever the cost may be; we shall fight on beaches, landing grounds, in field, in streets and on the hills. We shall never surrender…” Two weeks later – “Hitler knows that will have to break us in the island or lose the war…Let us therefore brace ourselves to our duties, and so bear ourselves that, if the British Empire and its Commonwealth last for a thousand years, men will still say, ‘This was their finest hour’” German Forces Turn to the West Recall – What took place during the sitzkrieg? Sequence – What countries did Germany overrun between the fall of Poland and the Battle of Britain? Predict – What might have happened in Western Europe if the Allies had attacked Hitler in 1939 or early 1940? German Forces Turn to the West Identify – What European countries did the Axis invade by 1941? Evaluate – Why do you think Spain, where Germany and Italy had helped place a Fascist government in power, remained neutral during World War II rather then siding with the Axis powers? Increasing Tensions in East Asia 1934 Japan began expanding its naval forces despite promises made at the Washington Navel Conference. 1936 Japan signed an anticommunism pact with Germany. 1937 Japan began a war against China. 1940 Japan formed a military alliance with Germany and Italy. These nations were known as the Axis Powers. 1941 Japan moved to take control of French Indochina, which threatened American interests. President Roosevelt tried to reason with General Hideki Tojo, the minister of war who took control of the country in October of 1941. But the time for compromise was over. 1931; Japanese Aggression in Manchuria (01:53) Problems with Japan July 26, 1939- Because of the siezure of Manchuria by Japan in 1931m the attack of China in 1937 and the Panay Incident, the U.S. tells Japan: – – U.S. would end the JapaneseAmerican Commercial Treaty U.S. will stop sale of war materials to Japan. Japan was invading China with those arms. Tensions in East Asia Recall – What three nations formed the Axis powers? Explain – Why was the U.S. concerned about the Japanese takeover of French Indochina? Make Judgments – Should the United States have tried to reach a compromise with Japan?