* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cold War Super Powers Face Off
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Allied-occupied Austria wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Yalta Conference wikipedia , lookup
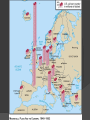
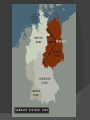
With Germany in Between Allies Become Enemies There was always tension between capitalists Americans and the communists Soviets during WWII. This was due to the non-aggression pact with Hitler and lack of Soviet involvement in the war. In 1945 at the Yalta Conference, the Soviets, British and Americans met to divide up Germany. Allies Become Enemies At the same conference Stalin agreed to enter the war against Japan. Stalin also promised that eastern European countries taken by the USSR in the war would have free elections. Also in 1945 both the U.S. and Soviet Union joined the United Nations. Allies Become Enemies The U.N. became the descendent of the League of Nations based in New York City. Each country had its own ideas how to rebuild its countries. The U.S. lost about 400,000 people while the USSR lost 1 out of 4 and many of its factories. Eastern Europe’s Iron Curtain One of the goals of the Soviet Union was to protect itself from invasion. After Yalta Stalin created communist states in seven European countries to act as a buffer. Europe became divided by what Churchill called the “Iron Curtain”. U.S. Tries Containment President Truman adopted the new foreign policy of containment to stop the spread communism. He also created the Truman Doctrine. This plan was that the U.S. would stop the rise of communism in any new countries. U.S. Tries Containment To help Europe rebuild U.S. Sec. of State George Marshall offered that the U.S. give aid to those countries. This became known as the Marshall Plan. European nations received $12.5 Billion. U.S. Tries Containment Not only did Europe become divided but so did Germany itself. The Soviets didn’t want to give up their claim to East Germany in order to keep them weak. Eventually Germany was divided into four parts, one for U.S., France, Britain and Soviet Union. U.S. Tries Containment Berlin the capital of Germany was also divided into four parts. Stalin cut off all services past the city limits. In response the U.S. air lifted supplies into West Berlin. Eventually the Berlin Wall was built to divide the city. Cold War Divides the World Each side started to make alliances as tensions grew. In 1949 NATO was formed with the U.S., Canada and 10 European nations. In response in 1955 the Warsaw Pact was formed between the Soviets and 7 Eastern European nations. Countries that weren’t aligned with either the USSR or U.S. were part of the “Third World”. Cold War Divides the World As these alliances were formed, nuclear arms began to build up. In 1949 the Soviets detonated their first Atomic Bomb. In 1953 the U.S. declared that if the Soviets or any affiliated country would attack the U.S. they would retaliate. This declaration became known as brinkmanship or the willingness to go to the brink of war. Reflection Time! How is Germany handled differently after WWII than WWI? Why do the two former allies, the U.S. and the Soviet Union go separate ways after WWII? How did these events show the political tension during the beginning of the Cold War?